Abstract
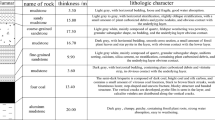
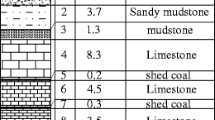
The study of roof breaking law is very important for the behavior of the underground pressure in fully mechanized top-coal caving face under the condition of weak roof. In this paper, the research is to study the soft and thick roof breaking law in the fully mechanized top-coal caving face 2–100 in coal seam 2#. The theoretical analysis, numerical simulation and field measurement methods are used to analyze the breaking law of the weak thick layer roof in the fully mechanized top-coal caving face. First, the mining conditions of the working face are introduced systematically, the mechanical properties of the weak roof are analyzed, the mechanical model of the immediate roof caving structure and the mechanical model of the main roof fracture structure are established, and the instability characteristics of the immediate roof and the main roof are analyzed. Through UDEC numerical simulation, the failure structure of the soft and thick roof in fully mechanized caving face, the plastic zone and stress distribution of the roof under different propulsive lengths, and the roof subsidence of the basic roof are obtained. It is found that the immediate roof caving will form an “arch” structure, and the main roof fracture will form a “three hinge arches” structure. Under this mine condition, the initial roof caving step is 17.8 m, and the main roof initial fracture step is 41.3 m, the periodic fracture step distance is 16.7 m. Under the condition of instability of immediate roof “arch” structure, when the displacement distance of the vault reaches 5.1 m, the “arch” structure will be unstable. Conditions of sliding instability of main roof “three hinge arches” structure: the ratio of coal seam thickness to the span of main roof is less than 0.2, and when the back angle is less than 8°, it is not easy to slip and lose stability. Through the observation of the field measurement results of fully mechanized top-coal caving face 2–100, the breaking rule of the soft and thick roof in fully mechanized top-coal caving face is verified.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai YQ, Geng XY (2009) Consolidation analysis of a semi-infinite transversely isotropic saturated soil under general time-varying loadings. Comput Geotech 36(3):484–492
Chen H, Ye Y-C et al (2020) Study on the failure form of direct roof in roadway soft layer based on rock beam-block theory. Rock and Soil Mechanics 4:1–8
Cheng ZB, Zhang YN, Li LH, Lv HY (2018) Theoretical solution and analysis of the elastic modulus and foundation coefficient of coal-rock combination material. Int J Mater Sci Res 1(1):23–31
Cheng Z, Yang S, Li L, Zhang L (2019a) Support working resistance determined on top-coal caving face based on coal-rock combined body. Geomech Eng 19(3):255–268
Cheng Z, Pan W, Li X, Sun W (2019b) Numerical simulation on strata behaviours of TCCWF influenced by coal-rock combined body. Geomech Eng 19(3):269–282
Cheng ZB, Li LH, Zhang YN (2020) Laboratory investigation of the mechanical properties of coal-rock combined body. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1947–1958
Kong D, Cheng Z, Zheng S (2019) Study on failure mechanism and stability control measures in large-cutting-height coal mining face with deep-buried seam. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(8):6143–6157
Li G-C (2008) Study on the stability and safety control of surrounding rock in soft interlayer roof roadway. China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing
Li J-W (2019) Study on breaking law and control of hard top plate in fully mechanized caving face with extra thick coal seam. Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an
Li H-T, Liu C-Y, Wang L-Q (2008) The formation and instability evolution of the “loose arch” structure of the upper direct roof. J Coal Ind 04:378–381
Liu X-J, Cheng Z-B (2019) Changes in subsidence-field surface movement in shallow-seam coal mining. J South Afr Inst Min Metall 119:201–206
Liu C-Y, Yang Jing X, Yu B, Wu F-F (2015) Determination of support resistance of fully mechanized caving face in extra thick coal seam under the condition of multi-layer hard roof of overburden. J Min Saf Eng 32(01):7–13
Liu F, Guo Z, Lv H, Cheng Z (2018) Test and analysis of blast wave in mortar test block. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 108:80–85
Liu X, Cheng Z, Jin D (2020) Performance analysis of soft roadway surrounding rock in Yushujing coal mine. Geotech Geol Eng 38(1):497–505
Miao X-X, Qian M-G (1995) Mechanical model of surrounding rock and masonry beam in stope. Ground Press Strata Control z1: 3–12 + 197
Shi H (2005) Stability analysis and application of thick and hard roof in fully mechanized top coal caving stope. Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao
Shi L, Xu C, Cai Y, Geng X (2014) Dynamic impedances and free-field vibration analysis of pile groups in saturated ground. J Sound Vib 333(16):3709–3731
Wang J-C (2005) Discussion on fully mechanized caving mining technology and its deep development in China. Coal Sci Technol 01:14–17
Wang J-H (2013) Key technology of large mining height fully mechanized caving mining in extra thick coal seam. J China Coal Soc 38(12):2089–2098
Wang Z, Cheng Z (2016) Hard roof fracturing form and dynamic disaster control in short island mining face. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 35(S2):4018–4028
Wang J, Ning J-G, Qian K, Sun Y, Ling Y-C (2014) The mechanical mechanism of the fracture formation of the combined three hinge arch of the compound roof roadway. Saf Coal Mines 45(12):64–67
Wang J, Gao Z, Fu H, Ding G, Cai Y, Geng X, Shi C (2019) Effect of surcharge loading rate and mobilized load ratio on the performance of vacuum–surcharge preloading with PVDs. Geotext Geomembr 47(2):121–127
Wu J (1999) 15 years review of fully mechanized caving mining technology in China. China Coal Z1: 9–16 + 61
Yan H, He F-L, Wang S-G (2014) Roof control measures and safety evaluation of soft and thick coal seam in super large section roadway. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(05):1014–1023
Yang S, Wang Z, Kong D, Cheng Z, Song G (2016) Overlying strata failure process and support resistance determination in large mining height face. J Min Saf Eng 33(2):199–207
Yang D-M, Guo W-B, Zhao G-B, Tan Y, Yang W-Q (2019) Development height of water diversion fracture zone in fully mechanized caving mining under soft overburden of thick loose layer. J China Coal Soc 44(11):3308–3316
Zhang Y, Cheng Z, Lv H (2019) Study on failure and subsidence law of frozen soil layer in coal mine influenced by physical conditions. Geomech Eng 18(1):97–109
Zhao Y-X, Wang X-Z, Zhou J-L, Li Q-S, Zhang C (2019) The influence law of the basic top thickness span ratio of the comprehensive mining face on its initial fracture instability. J China Coal Soc 44(01):94–104
Zheng S-S, Kong D-Z (2019) Fracture characteristics of hard top plate and migration law of overburden. Saf Coal Mines 50(05):257–262
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Fund (Nos. 51904082, 51964007), and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (2204080) and the Youth Science and Technology Talent Development Project of the Guizhou Education Department (Guizhou Education Co-operation KY character [2018] 114) and the Science and technology planning project of guizhou province (guizhou science and technology foundation [2020] 1y214).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, D., Li, Q., Wang, N. et al. Analysis on the Breaking Law of Soft and Thick Roof of Fully Mechanized Top-Coal Caving Face. Geotech Geol Eng 38, 5941–5953 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01404-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01404-4