Abstract
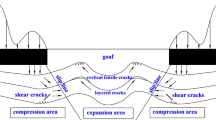
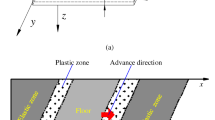
To obtain the water resistance performance of floor strata under different rock layers and fracture combination, the two cracks’ propagation path under different situations was given by using minimum plastic zone theory according to the change of the fracture factor and the plastic strain of different strata combination cracks under the influence of fault, water pressure and mining. The shortest distance of the rock bridge between the two cracks after bursting in different strata combination was obtained. And the water resistance performance of every strata combination was analyzed. The conclusion was that the water resistance performance of the floor strata under the 3214 combination of soft–soft–hard–hard was the worst. While the 1243 combination of soft rock, hard rock, soft rock, hard rock was the best. The fracture factor combination and the plastic strain of the crack would reach maximum under mining condition. And the crack was mostly easy to destroy. The distance of the rock bridge between the two cracks after bursting was the shortest under the 3214 combination of soft–soft–hard–hard strata. The distance of the rock bridge between the two cracks after bursting was the longest under the 1243 combination of soft rock, hard rock, soft rock, hard rock strata. And the distance of the rock bridge between the two cracks after bursting would be shorten when considering the water pressure inside the crack and fault, which resulted in the decrease of rock water resistance performance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng MM, Mao XB, Zhu QH (2010) Effect of lithologic association of the water-resisting strata in coal seam floor on water insulating. J Min Saf Eng 27(3):404–409 (in Chinese)
Huang QS, Cheng JL (2017) Research on stress distribution and failure characteristics of coal mining floor in soft-hard alternant strata. Rock Soil Mech 38(supp.1):36–42 (in Chinese)
Li WJ, Yang JB (2010) “Down3 zones” theory and “P-h” critical curve method for floor water-bursting forecast. Coal Min Technol 15(5):45–47 (in Chinese)
Li BJ, Liu HX, Liu XW (2011) Application of water inrush coefficients in deep mining. J Hebei Univ Eng (Nat Sci Edit) 28(3):68–70 (in Chinese)
Li ZH, Zhai CZ, Li LF (2016) Experimental study on water inrush mechanism due to floor faults activation in mining above confined aquifer. J Cent South Univ (Sci Technol) 46(5):1806–1811 (in Chinese)
Liu RX, Cao DT, Hu DX (2016) A study of the impermeability of the lower coal seam floor rocks at the Yanzhou coalfield based on in situ test. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 43(1):105–110 (in Chinese)
Qiao W, Li WP, Zhao CX (2009) Water inrush coefficient-unit inflow method for water inrush evaluation of coal mine floor. Chin J Rock Mechan Eng 28(12):2466–2474 (in Chinese)
Shi LQ (2009) Summary of research on mechanism of water-inrush from seam floor. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci) 28(3):17–23 (in Chinese)
Shi LQ, Han J (2005) Theory and practice of dividing coal mining area floor into four-zone. J China Univ Min Technol 42(1):16–23 (in Chinese)
Sun J, Wang LG, Hou HQ (2013) Research on water-isolating capacity of the compound water-resisting key strata in coal seam floor. J China Univ Min Technol 42(4):560–566 (in Chinese)
Wang ZC, Zhao DS, Wu HJ (2012) Study on toughening on crack prevention of jointed rock mass with different pre-stress anchor cables. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Sci) 17(5):552–558
Wang LG, Han M, Wang ZS et al (2013) Stress distribution and damage law of mining floor. J Min Saf Eng 30(3):317–322 (in Chinese)
Yu XG, Shi LQ, Wei JC (2006) Application of “four zones” theory in face floor on evaluation of floor water inrush. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci) 25(4):14–17 (in Chinese)
Zhai XR, Zhang HM, Dou ZS et al (2016) Study on fluid-solid coupling mechanism for water resistance effect of coal floor based on different combination of rock strata. J Saf Sci Technol 12(7):16–21 (in Chinese)
Zhang WQ, Li B, Gao B (2017) Research status and development trend of mine roof water inrush prediction. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci) 6:15–23 (in Chinese)
Zhu SY, Cao DT, Zhou HY et al (2014) Restrictive function of lithology and its composite structure on deformation and failure depth of mining coal seam floor. J Min Saf Eng 31(1):90–96 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by 2017 Key Technologies of Prevention and Control of Serious and Major Accidents in Safety Production (liaoning-0005-2017AQ) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51774199).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Wang, Z. & Wang, C. The Mechanism Study of Cracks Propagation of Different Floor Strata Combinations Under Mining. Geotech Geol Eng 36, 3743–3749 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0568-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0568-x