Abstract
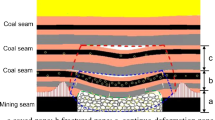
The characteristic of the distribution and evolution of the fractured zone has important guiding significance for gas drainage design. In this paper, the 2ZW11 face of the Dahuangshan coal mine was chosen as an engineering example, and the evolution of the fractured zone was analysed using physical and numerical simulations. The results showed that in the vertical direction, the heights of the fractured zone and the caved zone tended to be stable after the face advanced to 200 m. The heights of the two zones drawn from the physical and numerical simulations were supported by the field test. The traditional empirical formula may not be appropriate for predicting the heights of the two zones of working faces with large mining heights. In the horizontal direction, the bed-separated ratio of the overburden strata above the face position was slightly higher than that of the overburden strata above the open-off cut position. Finally, a high-level drainage was designed and undertaken in the 2ZW11 face.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen RH, Bai HB, Feng MM (2006) Determination of the height of water flowing fractured zone in overburden strata above fully-mechanized top-coal caving face. J Min Saf Eng 23(2):220–223
Cheng WM, Sun LL, Wang G et al (2016) Similar material simulation test of steep-inclined extra-thick coal seam. J Min Saf Eng 33(3):387–392
Gao YF, Qu ZJ, Xing F et al (2009) Observation of height of excavating face H2106 in Longkoubeizao mine under sea. Coal Geol Explor 37(6):35–38
Gao FQ, Stead D, Coggan J (2014) Evaluation of coal longwall caving characteristics using an innovative UDEC Trigon approach. Comput Geotech 55(55):448–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.09.020
He GC, Xiao FG, Zhang ZJ et al (2011) Prediction of the height of the transmissive fractured belt of a mining stope under aquifer in kang jiawan mine. J Min Saf Eng 28(1):122–126
He MC, Zhu GL, Guo ZB (2015) Longwall mining “cutting cantilever beam theory” and 110 mining method in China—The third mining science innovation. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 7(5):483–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.07.002
Itasca Consulting Group, Inc (2013) Universal Distinct Element Code (UDEC) manual. Minneapolis
Liu XS, Tan YL, Ning JG et al (2015) The height of water-conducting fractured zones in longwall mining of shallow coal seams. Geotech Geol Eng 33(3):693–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9851-2
Meng ZP, Shi XC, Li GQ (2016) Deformation, failure and permeability of coal-bearing strata during longwall mining. Eng Geol 208:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.029
Ministries of the People’s Republic of China (1984) Mine hydrogeological procedures. China Coal Industry Publishing House, Beijing
Qian DY, Zhang N, Shimada H et al (2016) Stability of goaf-side entry driving in 800-m-deep island longwall coal face in underground coal mine. Arab J Geosci 9(1):1–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2119-6
Song ZQ (1979) Basic rules for stope overlying strata. J S Inst Min Technol 1:12–25
Song YJ, Cheng GQ, Guo WJ (2011) Study of distribution of overlying strata fissures and its porosity characteristics. Rock Mech 32(2):533–536
Sui WH, Shen W, Di QS (1990) Engineering geological analysis and finite element simulation of strata stress deformation and failure in the goaf. J China Coal Soc 15(3):72–82
Tu M (2008) Analysis of mining rock mechanics in relieved drainage of coal bed methane and its application. Dissertation, China University of Mining and Technology
Unver B, Yasitli NE (2006) Modelling of strata movement with a special reference to caving mechanism in thick seam coal mining. Int J Coal Geol 66(4):227–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2005.05.008
Wang SM (2006) A brief review of the methods determining the height of permeable fracture zone. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 5:126–128
Wang G, Huang WP, Sun LL et al (2016a) High drilling methane drainage in fracturing zones formed by water injection into boreholes. Arch Min Sci 61(1):137–156. https://doi.org/10.1515/amsc-2016-0011
Wang G, Wu M, Wang R et al (2016b) Height of the mining-induced fractured zone above a coal face. Eng Geol 216:140–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.024
Xu JL, Qian MG (2006) Study on influences of key stratum on mining-induced fractures distribution in overlying strata. J Mines Metals Fuels 54(12):240–244
Yu WJ, Wang WJ, Wu GS et al (2017) Three zones and support technique for large section incline shaft crossing goaf. Geotech Geol Eng 35(1):1921–1931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0217-9
Zhang DS, Fan GM, Ma LQ et al (2011) Aquifer protection during longwall mining of shallow coal seams: a case study in the Shendong coalfield of China. Int J Coal Geol 86(2):190–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.01.006
Zhang WQ, Li B, Zhang GB et al (2017) Investigation of water-flow fracture zone height in fully mechanized cave mining beneath thick alluvium. Geotech Geol Eng 35(4):1745–1753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0205-0
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2014ZDPY23), which is a project funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Q., Wu, B. Evolution of the Fractured Zone Above a Coal Face with a Large Mining Height: A Case Study of the Dahuangshan Coalmine, China. Geotech Geol Eng 36, 3559–3571 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0557-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0557-0