Abstract
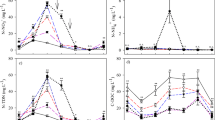
Swine feed is often supplemented with Cu and Zn, but > 90% of the ingested metal is excreted, ultimately accumulating in soil treated with liquid swine manure (LSM) to meet nitrogen (N) requirements. A maize field experiment was conducted between 2002 and 2015 in the Ebro Valley (north-east Spain) to determine the effects of long-term LSM application at two rates [30 and 50 m3 ha−1, equivalent to ~ 220 (218) and ~ 390 (389) kg N ha−1] compared to 0 and 300 kg N ha−1 mineral fertilizer. The highest Cu concentration in plants (5.03 mg kg−1) was observed following the 300 kg N ha−1 treatment. The treatments did not affect plant Zn levels (~ 21 mg kg−1). All whole-plant and grain metal concentrations were lower than threshold values for animal and human ingestion (30 mg Cu kg−1 and 500–1300 mg Zn kg−1). After 12 years, the soil organic carbon (SOC) of 13 g kg−1 in the first year (2002) increased by 19% and 26% at the low and high LSM rates, respectively. Mineral fertilization (300 kg N ha−1) achieved a 22% increase in SOC and also the 0 kg N ha−1 control treatment caused the SOC to rise by 11%. LSM applications do not seem to have adverse effects on maize yields after 12 years of applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berenguer P, Cela S, Santiveri F, Boixadera J, Lloveras J (2008a) Copper and zinc soil accumulation and plant concentration in irrigated maize fertilized with liquid swine manure. Agron J 100(4):1056–1061
Berenguer P, Santiveri F, Boixadera J, Lloveras J (2008b) Fertilization of irrigated maize with pig slurry combined with mineral nitrogen. Eur J Agron 28(4):635–645
Biau A, Santiveri F, Mijangos I, Lloveras J (2012) The impact of organic and mineral fertilizers on soil quality parameters and the productivity of irrigated maize crops in semiarid regions. Eur J Soil Biol 53:56–61
Bril J, Salomons W (1990) Chemical composition of animal manure: a modelling approach. Netherlands J Agric Sci 38:333–351
Brock EH, Ketterings QM, McBride M (2006) Copper and zinc accumulation in poultry and dairy manure-amended fields. Soil Sci 171(5):388–399
Comas J, Domínguez C, Salas-Vázquez DI, Parera J, Díez S, Bayona JN (2014) Input and leaching potential of copper, zinc, and selenium in agricultural soil from swine slurry. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66(2):277–286
Coppenet M, Golven J, Simon JC, Le Corre L, Le Roy M (1993) Évolution chimique des sols en explotations d’élevage intensif: exemple du Finistère. Agronomie 13:77–83
Daudén A, Quílez D (2004) Pig slurry versus mineral fertilization on corn yield and nitrate leaching in a Mediterranean irrigated environment. Eur J Agron 21:7–19
Díez JA, Hernaiz P, Muñoz MJ, Torre ADL, Vallejo A (2004) Impact of pig slurry on soil properties, water salinization, nitrate leaching and crop yield in a four-year experiment in Central Spain. Soil Use Manag 20(4):444–450
Dourmad JY, Jondreville C (2007) Impact of nutrition on nitrogen, phosphorus, Cu and Zn in pig manure, and on emissions of ammonia and odours. Livest Sci 112(3):192–198
Edmeades DC (2003) The long-term effects of manures and fertilizers on soil productivity and quality: a review. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 66:165–180
Eghball B, Power JF (1999) Phosphorus-and nitrogen-based manure and compost applications corn production and soil phosphorus. Soil Sci Soc Am J 63(4):895–901
European Union (1986) Council directive 86/278/EEC of 12 June 1986 on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/?uri=celex%3A31986L0278
European Union (1991) Council directive 91/676/EEC concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by Nitrates from agricultural sources. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/ALL/?uri=CELEX:31991L0676
European Union (2003) Regulation (EC) No 1831/2003 of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2003 on additives for use in animal nutrition. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/ES/TXT/?uri=CE LEX%3A32003R1831
Fertiliser Group Meeting (2014) Comission expert group. Agriculture and Rural Development, European Comission of the European Union, Luxembourg
Generalitat de Catalunya (2009) Decret 136/2009, d’1 de setembre, d’aprovació del programa d’actuació aplicable a les zones vulnerables en relació amb la contaminació de nitrats que procedeixen de fonts agràries i de gestió de les dejeccions ramaderes (Decree 136/2009 of 1 September, approving the action program applicable to zones vulnerable to nitrate pollution coming from agricultural sources and management of livestock manure)
Gigliotti G, Businelli D, Giusquiani PL (1996) Trace metals uptake and distribution in corn plants grown on a 6-year urban waste compost amended soil. Agric Ecosyst Environ 58(2):199–206
Gobierno de España (1990) Real Decreto 1310/1990, de 29 de octubre, por el que se regula la utilización de los lodos de depuración en el sector agrario (Royal Decree 1310/1990, of 29 October, of the regulation on the use of sewage sludge in agriculture)
Gobierno de España (2013) Real Decreto 506/2013, de 28 de junio, sobre productos fertilizantes (Royal Decree 506/2013, of June 28, on fertilizers)
Györi Z, Lányi A, Ruzsányi L, Kovács B, Loch J (1993) Effects of fertilization, irrigation and crop rotation on the transition and toxic element uptake of corn. Sci Total Environ 134:367–380
Harris Z, Gitlin J (1996) Genetic and molecular basis for copper toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr 63:836S–841S
Izaurralde R, McGill W, Robertson J, Juma N, Thurston J (2001) Carbon balance of the Breton Classical Plots over half a century. Soil Sci Soc Am 65:431–441
Japenga J, Harmsen K (1990) Determination of mass balances and ionic balances in animal manure. Neth J Agric Sci 38:353–367
Jarausch-Wehrheim B, Mocquot B, Mench M (1996) Uptake and partitioning of sludge-borne copper in field-grown maize (Zea mays L.). Eur J Agron 5(3):259–271
JMP (2012) Version 12. SAS Institute Inc, Cary
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Klimek B, Niklinska M (2007) Zinc and copper toxicity to soil bacteria and fungi from zinc polluted and unpolluted soils: a comparative study with different types of biolog plates. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:112–117
Kunito T, Saeki K, Oyaizu H, Matsumoto S (1999) Influences of copper forms on the toxicity to microorganisms in soils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 44(2):174–181
Lavado R, Porcelli C, Alvarez R (2001) Nutrient and heavy metal concentration and distribution in corn, soybean and wheat as affected by different tillage systems in the Argentine Pampas. Soil Tillage Res 62(1):55–60
Li Y, McCrory DF, Powell JM, Saam H, Joackson-Smith D (2005) A survey of selected heavy metal concentrations in Wisconsin dairy feeds. J Dairy Sci 88:2911–2922
López-Arias M, Grau-Corbí JM (2004) Metales pesados, material orgánica y otros parámetros de la capa superfi cial de los suelos agríco-las y de pastos de la España peninsular. II: Resultados por Provincias. INIA, Madrid, Spain (Heavy metals, organic matter and other parameters of the layer superfi cial agricultural soils and pasture in mainland Spain. II: Results by provinces)
Magrama (2015) Ministerio de agricultura, alimentación y medio ambiente. http://www.magrama.gob.es/es/estadistica/temas/estadisticas-agrarias/ganaderia/encuestas-ganaderas/#para4
Mantovi P, Bonazzi G, Maestri E, Marmiroli N (2003) Accumulation of copper and zinc from liquid manure in agricultural soils and crop plants. Plant Soil 250(2):249–257
Martinez J, Peu P (2000) Nutrient fluxes from a soil treatment process for pig slurry. Soil Use Manag 16:100–107
Mattias J, Ceretta C, Nesi C, Girotto E, Trentin E, Lourenzi C, Vieira R (2010) Copper, zinc and manganese in soils of two watersheds in Santa Catarina with intensive use of pig slurry. Rev Bras Ciên Solo 34(4):1445–1454
McGrath S, Chaudri A, Giller K (1995) Long-term effects of metals in sewage sludge on soils, microorganisms and plants. J Ind Microbiol 14:94–104
Mills HA, Jones B (1996) Preparation and analysis. In: Plant analysis handbook II. Micro Macro Publishing, Jefferson City, pp 116–124
Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food (1986) The analysis of agricultural materials. In: Reference book 427. HMSO, London
Moral R, Perez-Murcia MD, Perez-Espinosa JMoreno-Caselles, Paredes C, Rufete B (2008) Salinity, organic content, micronutrients and heavy metals in pig slurries from South-eastern Spain. Waste Manag 28(2):367–371
National Research Council (2001) Nutrient requirements of dairy cattle. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
National Research Council (2005) Mineral tolerance of animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Ndayegamiye A, Cote D (1989) Effect of long-term pig slurry and solid cattle manure application on soil chemical and biological properties. Can J Soil Sci 69(1):39–47
Nicholson F, Chambers B, Williams J, Unwin RJ (1999) Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales. Bioresour Technol 70:23–31
Nolan T, Troy S, Gilkinson S, Frost P, Xie S, Zhan X (2012) Economic analysis of pig manure treatment options in Ireland. Bioresour Technol 105:15–23
O’Connor GA (1988) Use and misuse of the DTPA soil test. J Environ Qual 17(4):715–718
Olivares M, Uauy R (1996) Limits of metabolic tolerance to copper and biological basis for present recommendations and regulations. Am J Clin Nutr 63:846S–852S
Panagos P, Van Liedekerke M, Jones A, Montanarella L (2012) European soil data centre: response to European policy support and public data requirements. Land Use Policy 29(2):329–338
Petruzzelli G, Lubrano L, Guidi G (1989) Uptake by corn and chemical extractability of heavy metals from a four year compost treated soil. Plant Soil 116:23–27
Rajkumara S (2008) Lodging in cereals—a review. Agricultural Reviews 29(1):55–60
Ritchie SW, Hanway JJ (1989) How a corn plant develops. In: No. REP-11237. CIMMYT
Sánchez M, González J (2005) The fertilizer value of pig slurry. I. Values depending on the type of operation. Bioresour Technol 96(10):1117–1123
Sisquella M, Lloveras J, Álvaro J, Santiveri F, Cantero C (2004) Técnicas de cultivo para la producción de maíz, trigo y alfalfa en los regadíos del valle del Ebro. Proyecto Trama-Life, Lleida, Spain, p. 47. (Management of maize, wheat and alfalfa in the irrigated areas of the Ebro Valley)
Smith K, Chalmers A, Chambers B, Christie P (1998) Organic manure phosphorus accumulation, mobility and management. Soil Use Manage 14(s4):154–159
Soil Survey Staff (2014) Keys to soil taxonomy. USDA, Natural Resources Conservation Series, Washington, DC
Temmerman L, Vanongeval L, Boon W, Hoenig M, Geypens M (2003) Heavy metal content of arable soils in northern Belgium. Water Air Soil Pollut 148(1):61–76
Tóth G, Hermann T, Szatmári G, Pásztor L (2016) Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci Total Environ 565:1054–1062
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38
Wilhelm W, Johnson J, Karlen D, Lightle D (2007) Corn stover to sustain soil organic carbon further constrains biomass supply. Agron J 99(6):1665–1667
Xu Y, Yu W, Ma Q, Zhou H (2013) Accumulation of copper and zinc in soil and plant within ten-year application of different pig manure rates. Plant Soil Environ 59(11):492–499
Yagüe M, Quílez D (2010) Response of maize yield, nitrate leaching, and soil nitrogen to pig slurry combined with mineral nitrogen. J Environ Qual 39(2):686–696
Yagüe M, Quílez D (2013) Residual effects of fertilization with pig slurry: double cropping and soil. Agron J 105(1):70–78
Acknowledgements
We would thank the agronomists of the University of Lleida Field Crops Department, and Carlos Ortíz, Elena Puigpinós and Jaume Boixadera of the Department of Agriculture of Catalonia (DARP), Ricardo Blanco for help with statistical analysis, and Paula Prieto and all the people who directly or indirectly participated in this study. This work was funded by the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología (CICYT) of Spain through Projects AGL2001-2214-C06-05, AGL2005-0820-05-03/AGR, AGL2009-12897/C02-01 and AGL2012-35122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez, E., Maresma, A., Biau, A. et al. Long-term effects of liquid swine manure on soil organic carbon and Cu/Zn levels in soil and maize. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 118, 193–205 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10093-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-020-10093-7