Abstract
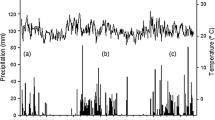
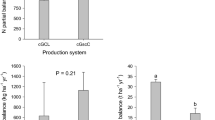
Management intensification has raised concerns about the sustainability of homegardens in the Nuba Mountains, Sudan. This study aimed at assessing the sustainability of these agroecosystems following the approach of carbon (C) and nutrient balances. Three traditional (low input) and three intensified (high input) homegardens were selected for monitoring of relevant input and output fluxes of C, nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K). The fluxes comprised those related to management activities (soil amendments, irrigation, and biomass removal) as well as estimates of biological N2 fixation, C fixation by photosynthesis, wet and dry deposition, gaseous emission, and leaching. Annual balances for C and nutrients amounted to −21 kg C ha−1, −70 kg N ha−1, 9 kg P ha−1 and −117 kg K ha−1 in high input homegardens and to −1,722 kg C ha−1, −167 kg N ha−1, −9 kg P ha−1 and −74 kg K ha−1 in low input homegardens. Photosynthesis C was the main C input flux with averaged of 7,047 and 5,610 kg C ha−1 a−1 in high and low input systems, respectively. Biological N2 fixation (17 kg N ha−1 a−1) was relevant only in low input systems. In both systems, the annual input of 77 kg K ha−1 through dust was highly significant and annual gaseous C losses of about 5,900 kg C ha−1 were the main C loss. In both garden types, the removal of biomass accounted for more than half of total nutrient exports of which one-third resulted from weeding and removal of plant residues and two-third from harvest. The observed negative nutrient balances may lead to a long-term decline of crop yields. Among other measures the reuse of C and nutrients in biomass removals during the cleaning of homegardens may allow to partially close C and nutrient cycles.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla S, Predotova M, Gebauer J, Buerkert A (2012) Horizontal nutrient flows and balances in irrigated urban gardens of Khartoum. Sudan. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 92(2):119–132
Abdelgabar O (1997) Mechanised farming and Nuba peasants: an example for non-sustainable development in the Sudan. Lit Verlag, Hamburg
Abdoellah O, Hadikusumah H, Takeuchi K, Okubo S, Parikesit P (2006) Commercialization of homegardens in an Indonesian village: vegetation composition and functional changes. Agrofor Syst 68(1):1–13
Abdu N, Abdulkadir A, Agbenin J, Buerkert A (2011) Vertical distribution of heavy metals in wastewater-irrigated vegetable garden soils of three West African cities. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 89(3):387–397
Abebe T, Wiersum KF, Bongers F, Sterck F (2006) Diversity and dynamics in homegardens of southern Ethopia. In: Kumar B, Nair P (eds) Tropical homegardens: A time-tested example of sustainable agroforestry. Springer, Netherlands, pp 123–142
Achiano KA, Giliomee JH, Pringle KL (1999) The use of ash from Aloe marlothii Berger for the control of maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), in stored maize. Afr Entomol 7(1):169–172
Bationo A, Lompo F, Koala S (1998) Research on nutrient flows and balances in west Africa: state-of-the-art. Agric Ecosyst Environ 71(1–3):19–35
Bindraban PS, Stoorvogel JJ, Jansen DM, Vlaming J, Groot JJR (2000) Land quality indicators for sustainable land management: proposed method for yield gap and soil nutrient balance. Agric Ecosyst Environ 81(2):103–112
Bischoff W-A (2007) Development and applications of the self-integrating accumulators: A method to quantify the leaching losses of environmentally relevant substances. PhD thesis, Technical University Berlin, Faculty VI of Planning, Building and Environment, Berlin, Germany
Brouwer J, Powell JM (1995) Soil aspects of nutrient cycling in a manure application experiment in Niger. In: Powell JM, Fernández-Rivera S, Williams TO, Renard C (eds) Livestock and sustainable nutrient cycling in mixed farming systems of Sub-Saharan Africa. Proceedings of an international conference, 22–26 November 1993. International Livestock Centre for Africa (ILCA), Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1995
Christensen J (1990a) The Brüel&Kjær photoacoustic transducer system and its physical properties. Brüel&Kjær Technical Review 1:1–39
Christensen J (1990b) Optical filters and their use with the type 1302 & type 1306 photoacoustic gas monitors. Brüel&Kjær Technical Review 2:1–50
Cobo JG, Dercon G, Cadisch G (2010) Nutrient balances in African land use systems across different spatial scales: a review of approaches, challenges and progress. Agric Ecosyst Environ 136(1–2):1–15
Dilkes NB, Jones DL, Farrar J (2004) Temporal Dynamics of Carbon Partitioning and Rhizodeposition in Wheat. Plant Physiol 134(2):706–715
Diogo RVC, Buerkert A, Schlecht E (2010) Horizontal nutrient fluxes and food safety in urban and peri-urban vegetable and millet cultivation of Niamey. Niger. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 87(1):81–102
Drechsel P, Giordano M, Gyiele L (2004) Valuing nutrients in soil and water: Concepts and techniques with examples from IWMI studies in the developing world. Colombo, Sri Lanka: International Water Management Institute (IWMI Research Report 82)
Drees LR, Manu A, Wilding LP (1993) Characteristics of aeolian dusts in Niger. West Africa. Geoderma 59(1–4):213–233
Fujita K, Ofosu-Budu KG, Ogata S (1992) Biological nitrogen fixation in mixed legume-cereal cropping systems. Plant Soil 141:155–175
Gad N, Abd El-Noez MR, Khaled SM (2012) Groundnut physiological and chemical response to molybdenum. World Journal of Chemistry 7(2):53–58
Goenster S, Wiehle M, Kehlenbeck K, Jamnadass R, Gebauer J, Buerkert A (2011) Indigenous fruit trees in homegardens of the Nuba Mountains, Central Sudan: tree diversity and potential for improving the nutrition and income of rural communities. Acta Hort 911:355–364
Goudie AS, Middleton NJ (2001) Saharan dust storms: nature and consequences. Earth-Sci Rev 56(1–4):179–204
Guo LB, Gifford RM (2002) Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a meta analysis. Glob Change Biol 8(4):345–360
Hafner H, Bley J, Bationo A, Martin P, Marschner H (1993) Long-term nitrogen balance for pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.) in an acid sandy soil of Niger. Z Pflanz Bodenkunde 156(2):169–176
Hassan JEAE (2005) Chronic conflict and livelihood in Heiban: Nuba Mountains of the Sudan. Noragric, Department of International Environment and Development Studies Ås, Norway
Henao J, Baanante CA (1999) Estimating rates of nutrient depletion in soils of agricultural lands of Africa. Technical Bulletin, T-48. IFDC—International Center for Soil Fertility and Agricultural Development, Muscle Shoals, Alabama, USA
Henao J, Baanante CA (2006) Agricultural production and soil nutrient mining in Africa: Implications for resource conservation and policy development. Technical Bulletin, T-72. IFDC—International Center for Soil Fertility and Agricultural Development, Muscle Shoals, Alabama, USA
Henry C, Sharma M, Lapenu C, Zeller M (2003) Microfinance poverty assessment tool. Technical Tools Series No. 5. Consultative Group to Assist the Poor (CGAP)/The World Bank, Washington, DC, USA
Herridge D, Peoples M, Boddey R (2008) Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems. Plant Soil 311(1–2):1–18
Hoffmann G (1991) Band I Die Untersuchung von Böden. In: Verband Deutscher Landwirtschaftlicher Untersuchungs- und Forschungsanstalten (VDLUFA) (ed) Handbuch der landwirtschaftlichen Versuchs- und Untersuchungsmethodik, Methodenbuch. 4 edn. VDLUFA-Verlag, Darmstadt, Germany
Holcombe SH (1987) Strengthening rural women producers in Darfur Region: constraints and opportunities. GeoJournal 14(1):19–28
Hudson NW (1993) Field measurement of soil erosion and runoff. FAO Soils Bulletin, vol 68. FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization fo the United Nations), Rome, Italy
IPI (International Potash Institute) (1983) Nutrient balances and the need for fertilizers in semi-arid and arid regions: Proceedings of the 17th colloquium of the International Potash Institute held in Rabat and Marrakech, Morocco. International Potash Institute, Horgen, Switzerland
Katanga Apuuli J, Villet MH (1996) The use of wood ash for the protection of stored cowpea seed (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) against Bruchidae (Coleoptera). Afr Entomol 4(1):97–98
Kehlenbeck K, Maass BL (2004) Crop diversity and classification of homegardens in Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. Agrofor Syst 63:53–62
Khai NM, Ha PQ, Öborn I (2007) Nutrient flows in small-scale peri-urban vegetable farming systems in Southeast Asia - A case study in Hanoi. Agric Ecosyst Environ 122(2):192–202
Khan KM, Yoshida T (1995) Nitrogen fixation in peanut at various concentrations of 15N-Urea and slow release 15N-fertilizer. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 41(1):55–63
Krogh L (1997) Field and village nutrient balances in millet cultivation in northern Burkina Faso: a village case study. J Arid Environ 35:147–159
Kumar BM, Nair PKR (2004) The enigma of tropical homegardens. Agrofor Syst 61–62(1):135–152
Kuzyakov Y, Domanski G (2000) Carbon input by plants into the soil Review. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 163(4):421–431
Langlois JL, Johnson DE, Mehuys GR (2003) Adsorption and recovery of dissolved organic phosphorus and nitrogen by mixed-bed ion-exchange resin. Soil Sci Soc Am J 67:889–894
Liu Y, Wu L, Baddeley J, Watson C (2011) Models of biological nitrogen fixation of legumes, A review. Agron Sustain Dev 31(1):155–172
Makhado RA, Scholes RJ (2011) Determinants of soil respiration in a semi-arid savanna ecosystem, Kruger National Park. South Africa. Koedoe 53(1):1–8
Obeidalla AA, Riley JJ (1983) Development of the horticultural potential of Kordofan region of Sudan. I.S.H.S. Eighth Africa Symposium on Horticultural Crops. March 20–24. Wad Medani, Sudan
Pantuliano S (2005) Changes and potential resilience of food systems in the Nuba Mountains conflict. Working Papers no. 05-07. Agricultural and Development Economics Division (ESA) and Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations (FAO), Rome, Italy
Peel MC, Finlayson BL, McMahon TA (2007) Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 11(5):1633–1644
Predotova M, Gebauer J, Diogo RVC, Schlecht E, Buerkert A (2010a) Emissions of ammonia, nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide from urban gardens in Niamey. Niger. Field Crop Res 115(1):1–8
Predotova M, Schlecht E, Buerkert A (2010b) Nitrogen and carbon losses from dung storage in urban gardens of Niamey. Niger. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 87(1):103–114
Predotova M, Bischoff W-A, Buerkert A (2011) Mineral-nitrogen and phosphorus leaching from vegetable gardens in Niamey. Niger. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(1):47–55
Roy RN, Misra RV, Lesschen JP, Smaling E (2003) Assessment of soil nutrient balance: approaches and methodologies. Fertilizer and Plant Nutrition Bulletins, vol 14. FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization fo the United Nations), Rome, Italy
Safi Z, Predotova M, Schlecht E, Buerkert A (2011) Horizontal matter fluxes and leaching losses in urban and peri-urban agriculture of Kabul. Afghanistan. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(6):942–951
Sangare S, Compaore E, Buerkert A, Vanclooster M, Sedogo M, Bielders C (2012) Field-scale analysis of water and nutrient use efficiency for vegetable production in a West African urban agricultural system. Nutr Cycl Agroecosys 92(2):207–224
Scoones I, Toulmin C (1998) Soil nutrient balances: what use for policy? Agric Ecosyst Environ 71(1–3):255–267
Siegfried K, Dietz H, Schlecht E, Buerkert A (2011) Nutrient and carbon balances in organic vegetable production on an irrigated, sandy soil in northern Oman. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 174(4):678–689
Siegfried K, Vazhacharickal PJ, Predotova M, Buerkert A (2012) Sorption and desorption characteristics of ion exchange resins to estimate leaching losses in the field. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 43(7):1065–1072
Siemens J, Kaupenjohann M (2002) Contribution of dissolved organic nitrogen to N leaching from four German agricultural soils. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 165(6):675–681
Šimek M, Brůček P, Hynšt J (2010) Diurnal fluxes of CO2 and N2O from cattle-impacted soil and implications for emission estimates. Plant Soil Environ 56:451–457
Smaling EMA, Stoorvogel JJ, Windmeijer PN (1993) Calculating soil nutrient balances in Africa at different scales – II District Scale. Fert Res 35(3):237–250
Smith KA, Ball T, Conen F, Dobbie KE, Massheder J, Rey A (2003) Exchange of greenhouse gases between soil and atmosphere: interactions of soil physical factors and biological processes. Eur J Soil Sci 54(4):779–791
Stahr K, Herrmann L (1996) Origin, deposition, and composition of dust, and consequences for soil and site properties with special reference to the semi-arid regions of West Africa. In: Buerkert B, Allisin RE, Von Oppen M (eds) Wind erosion in Niger: implications and control measures in a millet-based farming system. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, p 255
Sterk G, Herrmann L, Bationo A (1996) Wind-blown nutrient transport and soil productivity changes in southwest Niger. Land Degrad Dev 7(4):325–335
Stoorvogel JJ, Smaling EMA (1990) Assessment of soil nutrient depletion in sub-Saharan Africa: 1983–2000. Report 28. The Winand Staring Centre, Wageningen, The Netherlands
Stoorvogel JJ, Smaling EMA, Janssen BH (1993) Calculating soil nutrient balances in Africa at different scales – I Supra-national scale. Fert Res 35(3):227–235
Torquebiau E (1992) Are tropical agroforestry homegardens sustainable? Agric Ecosyst Environ 41:189–207
Unkovich MJ, Pate JS (2000) An appraisal of recent field measurements of symbiotic N2 fixation by annual legumes. Field Crop Res 65(2–3):211–228
Van den Bosch H, Gitari JN, Ogaro VN, Maobe S, Vlaming J (1998) Monitoring nutrient flows and economic performance in African farming systems (NUTMON).: III. Monitoring nutrient flows and balances in three districts in Kenya. Agric Ecosyst Environ 71(1–3):63–80
van Kessel C, Clough T, van Groenigen JW (2009) Dissolved organic nitrogen: an overlooked pathway of nitrogen loss from agricultural systems? J Environ Qual 38:393–401
Wortmann CS, Kaizzi CK (1998) Nutrient balances and expected effects of alternative practices in farming systems of Uganda. Agric Ecosyst Environ 71(1–3):115–129
Zougmorea R, Kamboua FN, Ouattaraa K, Guillobez S (2000) Sorghum-cowpea intercropping: an effective technique against runoff and soil erosion in the Sahel (Saria, Burkina Faso). Arid Soil Res Rehab 14(4):329–342
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) for funding of this project (BU 1308/9-1 & GE 2094/1-1) and to Alexandra zum Felde for her careful revision of an earlier version of this paper. The analytical help of Eva Wiegard and Claudia Thieme is gratefully acknowledged. Furthermore, the authors’ special thanks go to the villagers of Sama for their hospitality, patience and infrastructural support and to the University of Karthoum for its logistical help and many fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goenster, S., Wiehle, M., Gebauer, J. et al. Carbon and nutrient fluxes and balances in Nuba Mountains homegardens, Sudan. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 100, 35–51 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9624-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-014-9624-y