Abstract
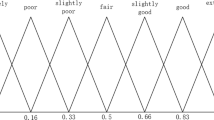
Probabilistic linguistic term set solves the problem of probabilistic distribution of linguistic terms. Due to the objective and subjective factors such as the decision makers’experience and preference, the credibility of the linguistic terms is different. However, current studies on PLTSs ignore this difference. In this paper, we first propose a novel concept called Z probabilistic linguistic term set (ZPLTS). As an extension of existing tools, it takes advantage of the fact that Z-number can represent both information and corresponding credibility. At the same time, we discuss the normalization, operational rules, ranking method and distance measure for ZPLTSs. Then, we propose a new weight calculation method, an aggregation-based method and an extended TOPSIS method, and apply them to multi-attribute group decision making in Z probabilistic linguistic environment. Finally, a numerical example and some comparisons with other methods illustrate the necessity and effectiveness of the proposed method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, C. Z., Zhang, R., Qian, L. X., & Wu, Y. N. (2017). Comparisons of probabilistic linguistic term sets for multi-criteria decision making. Knowledge-Based Systems,119((C)), 284–291.
Beg, I., & Rashid, T. (2013). Topsis for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 28(12), 1162–1171.
Gou, X. J., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Novel basic operational laws for linguistic terms, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and probabilistic linguistic term sets. Information Sciences, 372, 407–427.
Herrera, F., Herrera-viedma, E., & Verdegay, J. L. (1996). A model of consensus in group decision making under linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 78(1), 73–87.
Herrera, F., Herrera-viedma, E., & Verdegay, J. L. (1997). A rational consensus model in group decision making using linguistic assessments. Fuzzy Sets & Systems, 88(1), 31–49.
Jin, C., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2019). Uncertain probabilistic linguistic term sets in group decision making. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 21(4), 1241–1258.
Kang, B. Y., Yong, H., Deng, Y., & Zhou, D. Y. (2016). A new methodology of multicriteria decision-making in supplier selection based on z-numbers. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 1, 1–17.
Liao, H. C., Mi, X. M., & Xu, Z. S. (2020). A survey of decision-making methods with probabilistic linguistic information: bibliometrics, preliminaries, methodologies, applications and future directions. Fuzzy Optimization and Decision Making, 19, 81–134.
Pang, Q., Wang, H., & Xu, Z. S. (2016). Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Information Sciences, 369, 128–143.
Rodriguez, R. M., Martinez, L., & Herrera, F. (2012). Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 20(1), 109–119.
Torra, V. (2010). Hesitant fuzzy sets. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 25(6), 529–539.
Wang, H. (2015). Extended hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their aggregation in group decision making. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 8(1), 14–33.
Wang, J. Q., Cao, Y. X., & Zhang, H. Y. (2017). Multi-criteria decision-making method based on distance measure and choquet integral for linguistic z-numbers. Cognitive Computation, 9(6), 827–842.
Wei, C. P., Zhao, N., & Tang, X. J. (2014). Operators and comparisons of hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 22(3), 575–585.
Wu, X. L., & Liao, H. C. (2018). An approach to quality function deployment based on probabilistic linguistic term sets and Oreste method for multi-expert multi-criteria decision making. Information Fusion, 43, 13–26.
Xian, S. D., Chai, J. H., & Yin, Y. B. (2019). A visual comparison method and similarity measure for probabilistic linguistic term sets and their applications in multi-criteria decision making. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 21(4), 1154–1169.
Xian, S. D., Chai, J. H., & Guo, H. L. (2019). Z linguistic-induced ordered weighted averaging operator for multiple attribute group decision-making. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 34(2), 271–296.
Xian, S. D., & Sun, W. J. (2014). Fuzzy linguistic induced Euclidean OWA distance operator and its application in group linguistic decision making. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 29(5), 478–491.
Xiao, Z. Q. (2014). Application of z-numbers in multi-criteria decision making. International Conference on Informative & Cybernetics for Computational Social Systems, 91–95.
Xu, Z. S. (2004). Uncertain linguistic aggregation operators based approach to multiple attribute group decision making under uncertain linguistic environment. Information Sciences, 168(1), 171–184.
Xu, Z. S. (2005). Deviation measures of linguistic preference relations in group decision making. Omega-international Journal of Management Science, 33(3), 249–254.
Yaakob, A. M., & Gegov, A. (2016). Interactive topsis based group decision making methodology using z-numbers. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 9(2), 311–324.
Zadeh, L. A. (1965). Fuzzy sets. Information & Control, 8(3), 338–353.
Zadeh, L. A. (1975). The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning. Information Sciences, 8(3), 199–249.
Zadeh, L. A. (2011). A note on z-numbers. Information Sciences, 181(14), 2923–2932.
Zhang, Y. X., Xu, Z. S., Wang, H., & Liao, H. C. (2016). Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Applied Soft Computing, 49(C), 817–833.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chongqing Research and Innovation Project of Graduate Students (No. CYS19254), Graduate Teaching Reform Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (No. YJG183074) and the Chongqing Social Science Planning Project (No. 2018YB SH085).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, J., Xian, S. & Lu, S. Z probabilistic linguistic term sets and its application in multi-attribute group decision making. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 20, 529–566 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-021-09351-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10700-021-09351-2