Abstract
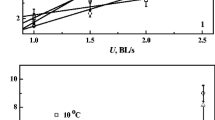
The objective of this study is to provide information on changes in swimming capability and respiration of the sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus, Linnaeus 1758) caused by different levels of fasting. Before testing, the four groups of sturgeon (body length: 12.1–15.4 cm, body mass: 10.0–20.2 g) fasted for 6 h, 2 days, 1 and 2 weeks, respectively. Swimming tests were then performed to measure critical swimming speed and oxygen consumption at 20 ± 0.5 °C. Results show: (1) Fasting times shorter than 2 days has little effect on swimming capability, but it decreases significantly when the fasting time is longer than a week. (2) After 2 weeks of fasting, swimming efficiency is significantly reduced. (3) Anaerobic capacity increases when digestion nears completion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agius C, Roberts RJ (1981) Effects of starvation on the melano-macrophage centres of fish. J Fish Biol 19:161–169
Alsop DH, Wood CM (1997) The interactive effects of feeding and exercise on oxygen consumption, swimming performance and protein usage in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Exp Biol 200:2337–2346
Bahr R (1992) Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption magnitude, mechanisms, and practical implications. Acta Physiol Scand 605:1–70
Bainbridge R (1958) The speed of swimming of fish as related to size and to the frequency and amplitude of the tail beat. J Exp Biol 35:109–133
Bainbridge R (1960) Speed and stamina in three fish. J Exp Biol 37:129–153
Bemis WE, Kynard B (1997) Sturgeon rivers: an introduction to acipenseriform biogeography and life history. Environ Biol Fish 48:167–183
Bernatchez L, Dodson JJ (1987) Relationship between bioenergetics and behavior in anadromous fish migrations. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:399–407
Bilton HT, Robins GL (1973) The effects of starvation and subsequent feeding on survival and growth of fulton channel sockeye salmon fry (Oncorhynchus nerka). J Fish Board Can 30:1–5
Black EC, Bosomworth NJ, Docherty GK (1966) Combined effect of starvation and severe exercise on glycogen metabolism of Rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. J Fish Res Board Can 23:1461–1463
Brett JR (1964) The respiratory metabolism and swimming performance of young sockeye salmon. J Fish Res Board Can 21:1183–1226
Cai L, Taupier R, Johnson D, Tu Z, Liu G, Huang Y (2013) Swimming capability and swimming behavior of juvenile Acipenser schrenckii. J Exp Zool Part A 319:149–155
Cai L, Chen L, Johnson D, Gao Y, Mandal P, Fang M, Tu Z, Huang Y (2014a) Integrating water flow, locomotor performance and respiration of Chinese sturgeon during multiple fatigue-recovery cycles. PLoS ONE 9:e94345
Cai L, Liu G, Taupier R, Fang M, Johnson D, Tu Z, Huang Y (2014b) Effect of temperature on swimming performance of juvenile Schizothorax prenanti. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:491–498
Castro-Santos T, Sanz-Ronda FJ, Ruiz-Legazpi J (2013) Breaking the speed limit - comparative sprinting performance of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) and brown trout (Salmo trutta). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 70:280–293
Clark TD, Samdblom E, Jutfelt F (2013) Aerobic scope measurements of fishes in an era of climate change: respirometry, relevance and recommendations. J Exp Biol 216:2771–2782
Dingle H, Drake VA (2007) What is migration? Bioscience 57:113–121
Fry FEJ (1947) Effects of environment on animal activity. University of Toronto Press, Toronto
Fu SJ, Cao ZD, Peng JL (2007) Effect of feeding and fasting on excess post-exercise oxygen consumption in juvenile southern catfish (Silurus meridionalis Chen). Comp Biochem Phys A 146:435–439
Fu SJ, Zeng LQ, Li XM, Pang X, Cao ZD, Peng JL, Wang YX (2009) Effect of meal size on excess post-exercise oxygen consumption in fishes with different locomotive and digestive performance. J Comp Physiol B 179:509–517
Fu SJ, Cao ZD, Yan GJ, Fu C, Pang X (2013) Integrating environmental variation, predation pressure, phenotypic plasticity and locomotor performance. Oecologia 173:343–354
Gaesser GA, Brooks GA (1984) Metabolic bases of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption: a review. Med Sci Sport Exerc 16:29–43
Gamped AK, Rodnick KJ, Faust HA, Venn EC, Bennett MT, Crawshaw LI, Keeley ER, Powell MS, Li HW (2002) Metabolism, swimming performance, tissue biochemistry of high desert redband trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss ssp.): evidence for phenotypic differences in physiological function. Physiol Biochem Zool 75:413–431
Gesner J, Freyhof J, Kottelat M (2010) Acipenser ruthenus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T227A13039007. http://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-1.RLTS.T227A13039007.en
Gisbert E, Doroshov SI (2003) Histology of the developing digestive system and the effect of food deprivation in larval green sturgeon (Acipenser medirostris). Aquat Living Resour 16:77–89
Hatry C, Thiem JD, Hatin D, Dumont P, Stamplecoskie KM, Molina JM, Smokorowski KE, Cooke SJ (2014) Comparative physiology and relative swimming performance of three redhorhorse (Moxostoma spp.) species: associations with fishway passage success. Physiol Biochem Zool 87:148–159
Hinch SG, Bratty J (2000) Effects of swim speed and activity pattern on success of adult sockeye salmon migration through an area of difficult passage. Trans Am Fish Soc 129:598–606
Jones DR (1982) Anaerobic exercise in teleost fish. Can J Zool 60:1131–1134
Katopodis C (2005) Developing a toolkit for fish passage, ecological flow management and fish habitat works. J Hydraul Res 43:451–467
Kynard B, Parker E, Parker T (2005) Behavior of early life intervals of Klamath River green sturgeon, Acipenser medirostris, with a note on body color. Environ Biol Fish 72:85–97
Lee CG, Farrell AP, Lotto A, Hinch SG, Healey MC (2003) Excess post-exercise oxygen consumption in adult sockeye (Oncorhynchus nerka) and coho (O. kisutch) salmon following critical speed swimming. J Exp Biol 206:3253–3260
Marriner BA, Baki ABM, Zhu DZ, Thiem JD, Cooke SJ, Katopodis C (2014) Field and numerical assessment of turning pool hydraulics in a vertical slot fishway. Ecol Eng 63:88–101
McKenzie DJ, Martinez RM, Morales A, Acosta J, Morates R, Taylor EW, Steffensen JF, Estrada MP (2003) Effects of growth hormone transgenesis on metabolic rate, exercise performance and hypoxia tolerance in tilapia hybrids. J Fish Biol 63:398–409
Pang X, Can ZD, Peng JL, Fu SJ (2010) The effects of feeding on the swimming performance and metabolic response of juvenile southern catfish, Silurus meridionalis, acclimated at different temperatures. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 155:253–258
Pavlov DS (1989) Structures assisting the migrations of non-salmonid fish: USSR. FAO Fish Tech Pap 308:1–97
Peake S (2005) Swimming and respiration. Sturgeons and Paddlefish of North America 27:147–166
Peake S, Beamish FWH, McKinley RS, Scruton DA, Katopodis C (1997) Relating swimming performance of lake sturgeon, Acipenser fulvescenus, to fishway design. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 54:1361–1366
Shi X, Zhuang P, Zhang L, Chen L, Xu B, Feng G, Huang X (2010) Optimal starvation time before blood sampling to get baseline data on several blood biochemical parameters in Amur sturgeon, Acipenser schrenckii. Aquacult Nutr 16:544–548
Trump CL, Leggett W (1980) Optimum swimming speeds in fish: the problem of currents. Can J Fish Aquat 37:1086–1092
Tu Z, Li L, Yuan X, Huang Y, Johnson D (2012) Aerobic swimming performance of juvenile Largemouth bronze gudgeon (Coreius guichenoti) in the Yangtze River. J Exp Zool Part A 317:294–302
Videler JJ, Nolet BA (1990) Cost of swimming measured at optimum speed scale effects, differences between swimming styles, taxonomic groups and submerged and surface swimming. Comp Biochem Physiol A 97:91–99
Videler JJ, Wardle CS (1991) Fish swimming stride by stride: speed limits and endurance. Rev Fish Biol Fish 1:23–40
Webber JD (2007) Upstream swimming performance of adult white sturgeon: effects of partial baffles and ramp. Trans Am Fish Soc 136:402–408
Weihs D (1973) Optimal fish cruising speed. Nature 245:48–50
Acknowledgments
We thank Miss Xiang Rongrong and Miss He Da who also contributed to the work providing assistance with writing. This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 51609155), Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment in the National Twelfth Five-Year Plan of China (Grant Number: 2012ZX07104-002-04), National Key Research Program of China (2016YFC0502206), the introduction of the internationally advanced water science and technology program (Program 948) of Ministry of Water Resources in China (No. 201210), and Hubei Province Key Laboratory Foundation of Three Gorges Project for Conservation of Fishes (Grant Number: 0704102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, L., Johnson, D., Fang, M. et al. Effects of feeding, digestion and fasting on the respiration and swimming capability of juvenile sterlet sturgeon (Acipenser ruthenus, Linnaeus 1758). Fish Physiol Biochem 43, 279–286 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0285-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0285-4