Abstract
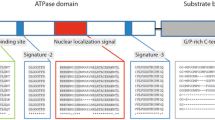
Through the RT-PCR and rapid amplification of cDNA ends, two complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) clones encoding heat-shock cognate 70 (HSC70, designated Sp-HSC70) and inducible heat-shock protein 70 (HSP70, designated Sp-HSP70) were isolated from the liver of Prenant’s schizothoracin (Schizothorax prenanti). The cDNAs were 2344- and 2292-bp in length and contained 1950- and 1932-bp open reading frames, encoded proteins of 649 and 643 amino acids, respectively. Amino acid sequence analysis indicated that both Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 contained three signature sequences of HSP70 family, two partial overlapping bipartite nuclear localization signal sequences (an ATP-binding site motif, a bipartite nuclear targeting signal), and a cytoplasmic characteristic motif EEVD. Homology analysis revealed that Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 shared 77.5 % identity and Sp-HSC70 shared more than 81.1 % identity with the known HSC70s of other vertebrates, while Sp-HSP70 shared more than 77.5 % identity with the known HSP70s of other vertebrates. Fluorescent real-time quantitative RT-PCR showed that Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 mRNAs were found in all tested tissues, including blood, brain, heart, liver, spleen, head kidney, white muscle, skin, gonad, hypophysis, red muscle, and gill. The Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 mRNA expression level in blood and head kidney displayed a significant increase in vibrio-challenged group with the bacterium Aeromonas hydrophila at 24 h post-infection compared to a control group. Temporally, there was a clear time-dependent expression pattern of Sp-HSC70 or Sp-HSP70 gene after bacterial challenge, and the expression of Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 mRNAs reached a maximum level at 12 and 6 h post-challenge, respectively. Both returned to control level after 7 × 24 h. The results suggest that Sp-HSC70 and Sp-HSP70 genes may play important roles in mediating the immune responses of A. hydrophila-related diseases in the Prenant’s schizothoracin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman PA, Forsyth RB, Mazur CF, Iwama GK (2000) Stress hormones and the cellular stress response in salmonids. Fish Physiol Biochem 23:327–336
Ahrens B, Issels RD (2002) Heat shock protein 70: role in antigen presentation and immune stimulation. Int J Hyperther 18:563–575
Basu S, Binder RJ, Suto R, Anderson KM, Srivastava PK (2000) Necrotic but not apoptotic cell death releases heat shock proteins, which deliver a partial maturation signal to dendritic cells and activate the NF-κB pathway. Int Immunol 12:1539–1546
Beg MU, Al-Subiai S, Beg KR, Butt SA, Al-Jandal N, Al-Hasan E, AI-Hussaini M (2010) Seasonal effect on heat shock proteins in fish from Kuwait Bay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84:91–95
Benjamin IJ, Williams RS (1994) 20 Expression and function of stress proteins in the ischemic heart. The biology of heat shock proteins and molecular chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory press, New York, pp 533–552
Bierkens JG (2000) Applications and pitfalls of stress-proteins in biomonitoring. Toxicology 153:61–72
Boutet I, Tanguy A, Rousseau S, Auffret M, Moraga D (2003) Molecular identification and expression of heat shock cognate 70 (hsc70) and heat shock protein 70 (hsp70) genes in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Cell Stress Chaperones 8:76–85
Bukau B, Horwich AL (1998) The HSP70 and HSP60 chaperone machines. Cell 92:351–366
Campisi J, Leem TH, Fleshner M (2003) Stress-induced extracellular Hsp72 is a functionally significant danger signal to the immune system. Cell Stress Chaperones 8:272–286
Cellura C, Toubiana M, Parrinello N, Roch P (2006) HSP70 gene expression in Mytilus galloprovincialis hemocytes is triggered by moderate heat shock and Vibrio anguillarum, but not by V. splendidus or Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Dev Comp Immunol 30:984–997
Cheng P, Liu X, Zhang G, He J (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of a HSP70 gene from Pacific abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Fish Shellfish Immunol 22:77–87
Dang W, Hu Y, Zhang M, Sun L (2010) Identification and molecular analysis of a stress-inducible HSP70 from Sciaenops ocellatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 29:600–607
Deane EE, Woo NY (2005) Cloning and characterization of the hsp70 multigene family from silver sea bream: modulated gene expression between warm and cold temperature acclimation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:776–783
Deane EE, Li J, Woo NY (2004) Modulated heat shock protein expression during pathogenic Vibrio alginolyticus stress of sea bream. Dis Aquat Org 62:205–215
Demand J, Luders J, Hohfeld J (1998) The carboxy-terminal domain of HSC70 provides binding sites for a distinct set of chaperone cofactors. Mol Cell Biol 18:2023–2038
Ding R (1994) The fishes of Sichuan, China. Sichuan Publishing House of Science and Technology, Chengdu, pp 397–406 (in Chinese)
Du Z, Huang X, Wang K (2011) Isolation and identification of etiology of skin ulcer in Schizothorax prenanti. J Sichuan Agric Univ 29(2):274–279 (in Chinese)
Eder KJ, Leutenegger CM, Köhler HR, Werner I (2009) Effects of neurotoxic insecticides on heat-shock proteins and cytokine transcription in Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:182–190
Feder ME, Hofmann GE (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu Rev Physiol 61:243–282
Franzellitti S, Fabbri E (2005) Differential HSP70 gene expression in the Mediterranean mussel exposed to various stressors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:1157–1163
Freeman BC, Myers MP, Schumacher R, Morimoto RI (1995) Identification of a regulatory motif in HSP70 that affects ATPase activity, substrate binding and interaction with HDJ-1. EMBO J 14:2281–2292
Fuertes MA, Pérez JM, Soto M, Menéndez M, Alonso C (2004) Thermodynamic stability of the C-terminal domain of the human inducible heat shock protein 70. Biochim Biophys Acta 1699:45–56
Georgopoulos C, Welch WJ (1993) Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9:601–634
Guo X (1995) Factors inducing the mechanism and effect of heat shock protein. Prog Physiol Sci 26:263–266 (in Chinese)
Hammerer-Lercher A, Mair J, Bonatti J, Watzka SB, Puschendorf B, Dirnhofer S (2001) Hypoxia induces heat shock protein expression in human coronary artery bypass grafts. Cardiovasc Res 50:115–124
Hartl FU, Martin J, Neupert W (1992) Protein folding in the cell: the role of molecular chaperones HSP70 and Hsp60. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 21:293–322
Heredia-Middleton P, Brunelli J, Drew RE, Thorgaard GH (2008) Heat shock protein (HSP70) RNA expression differs among rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) clonal lines. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem 149:552–556
James P, Pfund C, Craig EA (1997) Functional specificity among HSP70 molecular chaperones. Science 275:387–389
Jurgen F, Valerio M, Roberto R (2011) 2-DE proteomic analysis of HSP70 in mollusc Chamelea gallina. Fish Shellfish Immunol 30:739–743
Kiang JG, Tsokos GC (1998) Heat shock protein 70 kDa: molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology. Pharmacol Ther 80:183–201
Lin Y (2009) Study on the differential expression of HSP 70 gene in Cyprinus carpio. J. Anhui Agri. Sci 37(11):4915–4916, 5077 (in Chinese)
Lindquist S (1986) The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem 55:1151–1191
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-DDCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Ming J, Xie J, Xu P, Liu W, Ge X, Liu B, Cheng H, Zhou Y, Pan Q (2010) Molecular cloning and expression of two HSP70 genes in the Wuchang bream (Megalobrama amblycephala Yih). Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:407–418
Morimoto RI (1998) Regulation of the heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators. Genes Dev 12:3788–3796
Mukhopadhyay I, Nazir A, Saxena DK, Chowdhuri DK (2003) Heat shock response: HSP70 in environmental monitoring. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 17:249–254
Rhee JS, Raisuddin S, Lee KW, Seo JS, Ki JS, Kim IC, Lee JS (2009) Heat shock protein (Hsp) gene responses of the intertidal copepod Tigriopus japonicus to environmental toxicants. Comp Biochem Phys C 149:104–112
Rossi S, Snyder MJ (2001) Competition for space among sessile marine invertebrates: changes in HSP70 expression in two pacific cnidarians. Biol Bull 201:385–393
Song L, Wu L, Ni D, Chang Y, Xu W, Xing K (2006) The cDNA cloning and mRNA expression of heat shock protein 70 gene in the haemocytes of bay scallop (Argopecten irradians, Lamarck 1819) responding to bacterial challenge and naphthalin stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 21:335–345
Sørensen JG, Kristensen TN, Loeschcke V (2003) The evolutionary and ecological role of heat shock proteins. Ecol Lett 6:1025–1037
Srivastava P (2002) Roles of heat heat-shock proteins in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2:185–194
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tao J, Lai Y, Ren Y, Gong H, Kang G, Zhang X, Shi C, Wu S (2010) Development of a production procedure for bulk of inactivated mandarinfish pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila vaccine. Chin J Biologicals 23(11):1222–1225 (in Chinese)
Tomanek L, Sanford E (2003) Heat-shock protein 70 (HSP70) as a biochemical stress indicator: an experimental field test in two congenic intertidal gastropods (genus: Tegula). Biol Bull 205:276–284
Wang W, Wang J, Li A, Cai T (2004) Changes of cortisol and lysozyme levels in Carassius auratus blood after crowding stress and the fish sensitivity to pathogen. J Fish Sci China 11(5):408–412 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Xu J, Sheng L, Zheng Y (2007) Field and laboratory investigations of the thermal influence on tissue-specific HSP70 levels in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp Biochem Phys A 148:821–827
Wang Z, Wu Z, Jian J, Lu Y (2009) Cloning and expression of heat shock protein 70 gene in the haemocytes of pearl oyster (Pinctada fucata, Gould 1850) responding to bacterial challenge. Fish Shellfish Immunol 26:639–645
Webb D, Gagnon MM (2009) The value of stress protein 70 as an environmental biomarker of fish health under field conditions. Environ Toxicol 24:287–295
Wu S, Liu F, Hu S, Wang C (2001) Different combinations of the heat-shock cognate protein 70 (HSC70) C-terminal functional groups are utilized to interact with distinct tetratricopeptide repeat-containing proteins. Biochem J 359:419–426
Wu R, Sun Y, Lei L, Xie S (2008) Molecular identification and expression of heat shock cognate 70 (HSC 70) in the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mol Biol 42:234–242
Yenari MA, Giffard RG, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK (1999) The neuroprotective potential of heat shock protein 70 (HSP70). Mol Med Today 5:525–531
Zafarullah M, Wisniewski J, Shworak NW, Schieman S, Misra S, Gedamu L (1992) Molecular cloning and characterization of a constitutively expressed heat-shock-cognate hsc71 gene from rainbow trout. Eur J Biochem 204:893–900
Zhang J, Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Cui M (2009) HSC70 gene and its tissue expression analysis in yellow catfish. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 33(3):426–434 (in Chinese)
Zhang A, Zhou X, Wang X, Zhou H (2011) Characterization of two heat shock proteins (HSP70/HSC70) from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): evidence for their differential gene expression, protein synthesis and secretion in LPS-challenged peripheral blood lymphocytes. Comp Biochem Phys B 159:109–114
Zhou J, Wang W, He W, Wang L, Xin Y, Liu Y, Wang A (2010) Expression of HSP60 and HSP70 in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei in response to bacterial challenge. J Invertebr Pathol 103:170–178
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-11-0347). We would like to thank Dr. Yi Geng for providing Aeromonas hydrophi1a and suggestion for the challenge experiment, and Dr. Peter S. Rand for his revision of English writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jiuxuan Li and Haibin Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, X. et al. Molecular cloning and expression of two heat-shock protein genes (HSC70/HSP70) from Prenant’s schizothoracin (Schizothorax prenanti). Fish Physiol Biochem 41, 573–585 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0030-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-015-0030-4