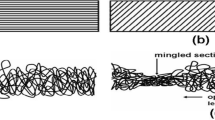
The effect of the degree of water vapor sorption on mechanical properties of needle-punched nonwoven fabric based on a blend of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) fibers with 0.33 and 1.7 tex linear densities in 45:55 % ratio is investigated. The fabric strength is estimated by nominal breaking stress. A parameter expressing the ratio between nominal stress and relative tensile elongation in the first stage of the process is proposed for estimation of tensile strength. The structure of the fabric based on fibers with various linear densities is studied and the mechanism of its elongation and breaking is proposed. Increase of tensile strength and strength of moistened fabric in longitudinal and transverse directions is observed at sorption degrees ranging from 0 to 4.5-5.0 kg/kg.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Jianyong and Z. Jianchun, Text. Res. J., 83, 2191-2203 (2013).
S. Sakthivel, J.J. Ezhil Anban, and T. Ramachandran, J. Eng. Fibers a. Fabrics, 9, No. 1, 149-153 (2014).
A.V. Dedov and V.G. Nazarov, Fibre Chemistry, 47, No. 2, 121-125 (2015).
H.H. Epps and K.K. Leonas, Inter. Nonwovens J., 9, No. 2, 1-8 (2000).
A. Abdou and I. Budaiwi, Construct. a. Building Mater., 43, No. 3, 533-544 (2013).
A.V. Dedov, A.V. Evdokimov, and V.G. Nazarov, Fibre Chemistry, 50, No. 2, 1-5 (2018).
M. Tascan and E.A. Vaughn, Textile Res. J., 78, No. 4, 289-296 (2008).
E. Cincik and E. Koc, Text. Res. J., 82, No. 5, 430-442 (2012).
A.V. Dedov, V.A. Kuznetsov, and V.G. Nazarov, Fibre Chemistry, 51, No. 6, 440-443 (2020).
V.G. Nazarov and A.V. Dedov, Fibre Chemistry, 53, No. 2, 143-148 (2021).
A. Rawal, S. Anand, and T. Shah, J. Industr. Textiles, 37, No. 4, 341-356 (2008).
A.V. Dedov, B.A. Roev, et al., Fibre Chemistry, 49, No. 5, 334-337 (2018).
A.V. Dedov and V.G. Nazarov, Fibre Chemistry, 43, No. 3, 259-262 (2011).
A.V. Dedov and V.G. Nazarov, Khim. Volokna, No. 5, 42-44 (2017).
The research was carried out with financial support of the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (State Assignment No. FZRR-2023-0003.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskie Volokna, No. 5, pp. 46-49, September-October 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Leshchenko, T.A., Chernousova, N.V., Dedov, A.V. et al. Mechanical Properties of Moistened Needle-Punched Nonwoven Fabric Based on Blend of Fibers with Various Linear Densities. Fibre Chem 54, 321–324 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-023-10400-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10692-023-10400-2