Abstract
In-orbit experience has shown that soft protons are funneled more efficiently through focusing Wolter-type optics of X-ray observatories than simulations predicted. These protons can degrade the performance of solid-state X-ray detectors and contribute to the instrumental background. Since laboratory measurements of the scattering process are rare, an experiment for grazing angles has been set up at the accelerator facility of the University of Tübingen. Systematic measurements at incidence angles ranging from 0.3° to 1.2° with proton energies around 250 keV, 500 keV, and 1 MeV have been carried out. Parts of spare mirror shells of the eROSITA (extended ROentgen Survey with an Imaging Telescope Array) instrument have been used as scattering targets. This publication comprises a detailed description of the setup, the calibration and normalization methods, and the scattering efficiency and energy loss results. A comparison of the results with a theoretical scattering description and with simulations is included as well.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Part of the SRIM package; http://www.srim.org
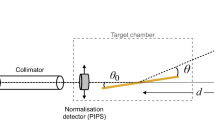
The scattering angle has been transformed to match the convention used in this study.
Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica
Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics
Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics
References
Weisskopf, M.C. et al.: An overview of the performance and scientific results from the chandra X-Ray Observatory. PASP 114(791), 1–24 (2002)
Lo, D.H., Srour, J.R.: Modeling of proton-induced CCD degradation in the Chandra X-ray observatory. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 50(6), 2018–2023 (2003)
Jansen, F. et al.: XMM-newton observatory I. The spacecraft and operations. A&A 365, L1–L6 (2002)
Kendziorra, E. et al.: The effect of low energy protons on the performance of the EPIC pn-CCD detector on XMM-newton. Proc. SPIE 4140, 32–41 (2000)
Firsov, O.B.: Reflection of fast ions from a dense medium at glancing angles. Sov. Phys.-Doklady 11(8), 732–733 (1967)
Agostinelli, S. et al.: Geant4 – a simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 506, 250–303 (2003)
Lei, F. et al.: Update on the use of Geant4 for the Simulation of low-energy protons scattering off X-ray mirrors at grazing incidence angles. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 51(6), 3408–3412 (2004)
Rasmussen, A. et al.: Proton scattering off of XMM optics: XMM mirror and RGS grating samples, XMM Document RGS-COL-CAL-99009, Columbia Astrophysics Laboratory (1999)
Nartallo, R. et al.: Radiation environment induced degradation on chandra and implications for XMM, ESA Report (2000)
Diebold, S. et al.: A setup for soft proton irradiation of X-ray detectors for future astronomical space missions. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. A 721, 65–72 (2013)
Feroci, M. et al.: The large observatory for x-ray timing. Proc. SPIE 9144, 9144–100 (2014)
Ziegler, J.F. et al.: SRIM – The stopping and range of ions in matter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 268, 1818–1823 (2010)
Perinati, E. et al.: Analysis of proton propagation through the eROSITA telescope. Proc. SPIE 9144, 9144–190 (2014)
Predehl, P. et al.: eROSITA on SRG. Proc. SPIE 9144, 9144–64 (2014)
Nandra, K. et al.: Athena: exploring the hot and energetic universe. Proc. SPIE 9144, 9144–84 (2014)
Brown, R.B. et al.: Precision ion beam energy measurement of a Van de Graaff accelerator using a generating voltmeter. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 151, 377–380 (1978)
Kump, P. et al.: An absolute calibration of electrostatic accelerators in the energy region from 0.7 MeV to 2.1 MeV. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 112, 489–494 (1973)
Diebold, S. et al.: A facility for soft proton irradiation and instrument testing for future space missions. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 61(4), 1937–1942 (2014)
Winter, H. et al.: Energy loss of fast protons in grazing scattering from an Al(111)-surface. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 125, 124–127 (1997)
Pfandzelter, R. et al.: Probing the stopping power near the surface by specular reflection of protons from graphite. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect. B 72, 163–175 (1997)
Acknowledgments
This work is partially supported by the Bundesministerium für Wirtschaft und Technologie through the Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt (Grant FKZ 50 OO 1110).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diebold, S., Tenzer, C., Perinati, E. et al. Soft proton scattering efficiency measurements on x-ray mirror shells. Exp Astron 39, 343–365 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-015-9451-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10686-015-9451-4