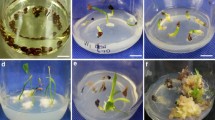
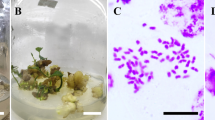
Abstract
Polyploidization confers many advantages over diploidy in crop production. Asiatic hybrid lilies contain several polyploid cultivars; however, the characteristics improved by polyploidization have not been sufficiently evaluated. Lilium leichtlinii is among the important parental species used for Asiatic hybrid lily establishment and is also used as an edible lily in Japan. In this study, tetraploid L. leichtlinii plants were induced in vitro in a colchicine-containing medium, and their ploidy levels were confirmed using flow cytometry. Subsequently, the characteristics of the tetraploid plants were evaluated in the field to determine those that were improved by polyploidization. Tetraploid L. leichtlinii plants exhibited significantly earlier flowering, wider leaves, and larger tepals than their diploid counterparts. The effects of tetraploidy on flowering time vary among lily species and hybrid groups because tetraploid L. longiflorum plants present with delayed flowering. Because early flowering and large flowers are desirable characteristics for cut flower production, polyploidization is an effective method for improving Asiatic hybrid lilies. Tetraploid plants showed a higher tolerance to Botrytis disease than diploid plants, which is advantageous for both cut flowers and edible lily production. Bulb fresh weight increased 25% in tetraploid plants compared with diploid plants with p value of 0.052 (t-test), indicating that tetraploidization tend to increase the yield of lily bulbs. The bulb yield of polyploid lilies has not been evaluated before.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comber HF (1949) A new classification of the genus Lilium. Lily yearbook, vol 13. Royal Horticultural Society, London, pp 86–105
Corneillie S, De Storme N, Van Acker R, Fangel JU, De Bruyne M, De Rycke R, Geelen D, Willats WGT, Vanholme B, Boerjan W (2019) Polyploidy affects plant growth and alters cell wall composition. Plant Physiol 179:74–87. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.18.00967
Denaeghel H, Van Laere K, Leus L, Lootens P, Van Huylenbroeck J, Van Labeke MC (2018) The variable effect of polyploidization on the phenotype in Escallonia. Front Plant Sci 9:354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00354
Emsweller SL (1949) Colchicine-induced polyploidy in Lilium longiflorum. Am J Bot 36:135–144. https://doi.org/10.2307/2438130
Emsweller SL, Lumsden DV (1943) Polyploidy in the Easter lily. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 42:593–596
Fu L, Zhu Y, Li M, Wang C, Sun H (2019) Autopolyploid induction via somatic embryogenesis in Lilium distichum Nakai and Lilium cernuum Komar. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 139:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-019-01671-x
Hennig A, Kleinschmit JRG, Schoneberg S, Löffler S, Janßen A, Polle A (2015) Water consumption and biomass production of protoplast fusion lines of poplar hybrids under drought stress. Front Plant Sci 6:330. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00330
Heo JY, Jeong SH, Choi HR, Park SM (2016) Polyploid production Lilium leichtlinii var. Maximowiczii using colchicine. J Anim Plant Sci 26:1111–1116
Hoshino Y, Nakata M, Godo T (2019) Estimation of chromosome number among the progeny of a self-pollinated population of triploid Senno (Lychnis senno Siebold et Zucc.) by flow cytometry. Sci Hortic 256:108542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108542
Islam MM, Deepo DM, Nasif SO, Siddique AB, Hassan O, Siddique AB, Paul NC (2022) Cytogenetics and consequences of polyploidization on different biotic-abiotic stress tolerance and the potential mechanisms involved. Plants 11:2684. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11202684
Kumari S, Kanth BK, Jy A, Kim JH, Lee G (2021) Genome-wide transcriptomic identification and functional insight of lily WRKY genes responding to Botrytis fungal disease. Plants 10:776. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040776
Li S, Lin Y, Pei H, Zhang J, Zhang J, Luo J (2020) Variations in colchicine-induced autotetraploid plants of Lilium davidii var. unicolor. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 141:479–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01805-6
Manzoor A, Ahmad T, Bashir MA, Hafiz IA, Silvestri C (2019) Studies on colchicine induced chromosome doubling for enhancement of quality traits in ornamental plants. Plants 8:194. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8070194
Marasek-Ciolakowska A, Nishikawa T, Shea DJ, Okazaki K (2018) Breeding of lilies and tulips—Interspecific hybridization and genetic background—. Breed Sci 68:35–52. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs.17097
Niu L, Tao Y, Chen M, Fu Q, Dong Y, He H, Xu Z (2016) Identification and characterization of tetraploid and octoploid Jatropha curcas induced by colchicine. Caryologia 69:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2015.1110308
Noda S (1986) Cytogenetic behavior, chromosomal differentiations, and geographic distribution in Lilium lancifolium (Liliaceae). Plant Spec Biol 1:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-1984.1986.tb00016.x
Notsuka K, Tsuru T, Shiraishi M (2000) Induced polyploid grapes via in vitro chromosome doubling. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 69:543–551. https://doi.org/10.2503/jjshs.69.543
Okazaki K, Hane Y (2005) Comparison of diploid and chimeric forms (4×/2×) of Asiatic hybrid lilies (Lilium spp.) under natural and early forcing culture. N Z J Crop Hortic Sci 33:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1080/01140671.2005.9514358
Planchais S, Glab N, Inzé D, Bergounioux C (2000) Chemical inhibitors: a tool for plant cell cycle studies. FEBS Lett 476:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01675-6
Rathod AD, Patil SR, Taksande PN, Karad GW, Kalamkar VB, Jayade VS (2018) Effect of colchicine on morphological and biometrical traits in African marigold. J Soils Crops 28:72–80
Ruiz M, Oustric J, Santin J, Morillon R (2020) Synthetic polyploidy in grafted crops. Front Plant Sci 11:540894. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.540894
Sattler MC, Carvalho CR, Clarindo WR (2016) The polyploidy and its key role in plant breeding. Planta 243:281–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-015-2450-x
Suzuki T, Yamagishi M (2016) Aneuploids without bulbils segregated in F1 hybrids derived from triploid Lilium lancifolium and diploid L. leichtlinii Crosses. Hort J 85:224–231. https://doi.org/10.2503/hortj.MI-089
Tolety J, Sane A (2011) Antirrhinum. In: Kole C (ed) Wild crop relatives: genomic and breeding resources plantation and ornamental crops. Springer, New York, pp 1–14
Van Laere K, França SC, Vansteenkiste H, Van Huylenbroeck J, Steppe K, Van Labeke MC (2011) Influence of ploidy level on morphology, growth and drought susceptibility in Spathiphyllum wallisii. Acta Physiol Plant 33:1149–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-010-0643-2
Wang L, Gao X, Jia G (2021) Stomata and ROS changes during Botrytis elliptica infection in diploid and tetraploid Lilium rosthornii Diels. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:366–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.08.008
Wu JH, Ferguson AR, Murray BG, Jia Y, Datson PM, Zhang J (2012) Induced polyploidy dramatically increases the size and alters the shape of fruit in Actinidia chinensis. Ann Bot 109:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcr256
Yahmed JB, Costantino G, Amiel P, Talon M, Ollitrault P, Morillon R, Luro F (2016) Diversity in the trifoliate orange taxon reveals two main genetic groups marked by specific morphological traits and water deficit tolerance properties. J Agric Sci 154:495–514. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859615000234
Zahumenická P, Fernández E, Šedivá J, Žiarovská J, Ros-Santaella JL, Martínez-Fernández D, Russo D, Milella L (2018) Morphological, physiological and genomic comparisons between diploids and induced tetraploids in Anemone sylvestris L. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 132:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1331-3
Zhou S, Zhou G, Li K (2011) Euploid endosperm of triploid x diploid/tetraploid crosses results in aneuploidy embryo survival in Lilium. Hortic Sci 46:558–562. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.46.4.558
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (Grant No. 19H02945) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MY designed the study, conducted experiments, and wrote the manuscript. MY, YJ, and YH analyzed the data. All the authors have read and approved the submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was waived because the study did not involve human participants or animal experiments.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yamagishi, M., Jitsuyama, Y. & Hoshino, Y. Agronomic performance in tetraploid Lilium leichtlinii: larger flowers and earlier flowering. Euphytica 219, 126 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-023-03250-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-023-03250-w