Abstract
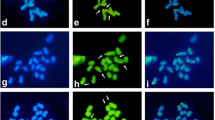
This study was aimed to differentiate parental genomes, examining intergenomic composition, and mapping mitotic metaphase chromosomes by localizing parental and 18S rDNA probes in seven interspecific hybrid progenies that originated from Lilium longiflorum. Since single method of in situ hybridization has been widely used in interspecific lily breeding, while in this study, flow cytometry was used in conjunction with genomic and fluorescent in situ hybridization to determine the genomic contribution of each parent to the interspecific progenies. A significant variation was observed in the DNA content, chromosome length, and 18S loci in F1 as compared to the female and male parents. L. longiflorum showed nearly two times higher DNA content than the male parents and L. longiflorum × Asiatic progenies, but eight times higher than L. longiflorum × L. hansonii. Genomic in situ hybridization results revealed that both female and male parents contributed an equal number of chromosomes to their interspecific F1 offspring. Fluorescent in situ hybridization mapping revealed that 18S rDNA had 8, 6 and 7 loci in L. longiflorum parents, i.e., White heaven, Bright tower, and White tower, respectively, whereas each Asiatic cultivar and L. hansonii used as male showed 8 and 12 loci respectively. Interspecific progenies showed 8 and 7 loci in LA, and 10–11 in LM hybrids. These cytogenetic results implied equal genetic and chromosomal contribution from both parents to their intergenomic progenies. Therefore, this combined cytogenetic method has the potential to be genome specific and time-saving approach in lily breeding that could determine the status of hybrids and their genomic origin while achieving physical mapping and detecting genes in different genomes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn YJ, Hwang YJ, Younis A, Sung M-S, Ramzan F, Kwon MJ, Kang YI, Kim CK, Lim KB (2017) Investigation of karyotypic composition and evolution in Lilium species belonging to the section martagon. Plant Biotechnol Rep 11:407–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-017-0462-7
Barba-Gonzalez R, Ramanna M, Visser RG, Van Tuyl J (2005) Intergenomic recombination in F1 lily hybrids (Lilium) and its significance for genetic variation in the BC1 progenies as revealed by GISH and FISH. Genome 48:884–894. https://doi.org/10.1139/g05-057
Cao Q, Lian Y, Wang L, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Jia G, He H (2019) Physical mapping of 45S rDNA loci in Lilium OT hybrids and interspecific hybrids with Lilium regale. Sci Hortic 252:48–54
Chester M, Leitch AR, Soltis PS, Soltis D (2010) Review of the application of modern cytogenetic methods (FISH/GISH) to the study of reticulation (polyploidy/hybridisation). Gene 1:166–192. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes1020166
Fujiwara A, Fujiwara M, Nishida-Umehara C, Abe S, Masaoka T (2007) Characterization of Japanese flounder karyotype by chromosome bandings and fluorescence in situ hybridization with DNA markers. Genetica 131:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-006-9136-z
Gao T, Sun H, Fang L, Qian H, Xin H, Shi J, Wu Z, Xi M (2014) Cytogenetic analysis of Asiatic lily cultivars and their hybrids using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Acta Hortic. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2014.1027.19
Hembree WG, Ranney TG, Lynch NP, Jackson B (2020) Identification, genome sizes, and ploidy of deutzia. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 145:88–94. https://doi.org/10.21273/jashs04779-19
Hwang Y-J, Kim HH, Kim J-B, Lim K-B (2011) Karyotype analysis of Lilium tigrinum by FISH. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 52:292–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-011-0225-2
Islam MM, Yesmin R, Jung M-J, Kim H-Y, Kim C-K, Lim K-B (2020) Investigation of the morphological and cytogenetic variations of an intraspecific Asiatic lily hybrid using 5S and 18S rDNA probes. Hortic Environ Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-019-00216-7
Jo YK, Mazharu IM, Kim C-K, Kim H-Y, Lim K-B (2019) Morphological characteristics and FISH analysis of hibiscus f1 hybrids and parental lines. Hortic Sci Technol 37:630–639. https://doi.org/10.7235/HORT.20190063
Karlov G, Khrustaleva L, Lim K, Van Tuyl J (1999) Homoeologous recombination in 2 n-gametes producing interspecific hybrids of Lilium (Liliaceae) studied by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). Genome 42:681–686. https://doi.org/10.1139/g98-167
Kumari S, Kanth BK, Jeon Y, Jang J-Y, Kim H-S, Lee G-J (2018) Internal transcribed spacer-based CAPS marker development for Lilium hansonii identification from wild Lilium native to Korea. Sci Hortic 236:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2018.03.013
Kwon M-J, Ramzan F, Ahn Y-J, Hwang Y-J, Kang Y-I, Kim C-K, Younis A, Lim K-B (2017) Chromosomal analysis of Lilium longiflorum x Asiatic hybrids using GISH (genomic in situ hybridization). Hortic Environ Biotechnol 58:591–600
Lim K-B (2014) Ecological, morphological and cytogenetic analysis of Korean Martagon Lilium species. Acta Hortic. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2014.1027.3
Lim K-B, Wennekes J, Jong JHd, Jacobsen E, Van Tuyl J (2001) Karyotype analysis of Lilium longiflorum and Lilium rubellum by chromosome banding and fluorescence in situ hybridisation. Genome 44:911–918. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-44-5-911
Lim K-B, Ramanna M, Jacobsen E, Van Tuyl J (2003) Evaluation of BC 2 progenies derived from 3x–2x and 3x–4x crosses of Lilium hybrids: a GISH analysis. Theor Appl Genet 106:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1070-6
Lim K-B, De Jong H, Yang T-J, Park J-Y, Kwon S-J, Kim JS, Lim M-H, Kim JA, Jin M et al (2005) Characterization of rDNAs and tandem repeats in the heterochromatin of Brassica rapa. Mol Cells 19:436
Lim K-B, Barba-Gonzalez R, Zhou S, Ramanna M, Van Tuyl J (2008) Interspecific hybridization in lily (Lilium): taxonomic and commercial aspects of using species hybrids in breeding. Floric Ornam Plant Biotechnol 5:146–151
Liu Y-H, Huang C-J, Chen C-Y (2008) Evidence of induced systemic resistance against Botrytis elliptica in lily. Phytopathology 98:830–836. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-98-7-0830
Lucidos JG, Ryu KB, Younis A, Kim C-K, Hwang Y-J, Son B-G, Lim K-B (2013) Different day and night temperature responses in Lilium hansonii in relation to growth and flower development. Hortic Environ Biotechnol 54:405–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13580-013-1241-1
Mazharul I, Reshma Y, Jung J, Mohammad D, Lim K (2019) Cytogenetic assessment of Lilium longiflorum× L. hansonii revealed by genomic in situ hybridization (GISH). Acta Hortic. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2019.1237.10
Merhaut D, Newman J (2005) Effects of substrate type on plant growth and nitrate leaching in cut flower production of oriental lily. Hort Sci 40:2135–2137. https://doi.org/10.21273/hortsci.40.7.2135
Naing AH, Yun H, Lucidos J, Hwang Y-J, Kim CK, Ahn BJ, Lim K-B (2014) Plant regeneration through various explants of Lilium longiflorum hybrid “Bright Tower” and determination of ploidy level of regenerated plants. Plant Biosyst 148:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/11263504.2012.754384
Nakazawa D, Kishimoto T, Sato T, Saito T, Amano J, Kuwayama S, Okuno H, Godo T, Watanabe Y et al (2011) Genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) analysis of intergeneric hybrids in Colchicaceae. Euphytica 181:197–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0393-2
Ramanna M (1992) The use of 2n gametes in breeding polysomic polyploid species; some achievements and perspectives. In: Proc. workshop gametes with somatic chromosome number in the evolution of and breeding of polyploid polysomic species: achievements and perspectives. Perugia, Italy, 91–100
Ramzan F, Younis A, Lim K, Bae S, Kwon M, Ahn S, Ge G, Co V (2016) Analysis of oriental× trumpet (OT) lilium hybrids by genomic in situ hybridization based on ploidy level. Acta Hortic 2016:253–258. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2017.1171.33
Ramzan F, Younis A, Lim K-B (2017) Application of genomic in situ hybridization in horticultural science. Int J Genom 2017:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7561909
Robledo G, Lavia G, Seijo G (2009) Species relations among wild Arachis species with the A genome as revealed by FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection. Theor Appl Genet 118:1295–1307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0981-x
Schwarzacher T, Anamthawat-Jonsson K, Harrison G, Islam A, Jia J, King I, Leitch A, Miller T, Reader S et al (1992) Genomic in situ hybridization to identify alien chromosomes and chromosome segments in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84:778–786. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00227384
Silva G, Souza M (2013) Genomic in situ hybridization in plants. Genet Mol Res 12:2953–2965. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.august.12.11
Sun Y, Xu C, Wang M, Zhi D, Xia G (2014) Genomic changes at the early stage of somatic hybridization. Genet Mol Res 13:1938–1948. https://doi.org/10.4238/2014.march.17.21
Takahashi C, Leitch I, Ryan A, Bennett M, Brandham P (1997) The use of genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) to show transmission of recombinant chromosomes by a partially fertile bigeneric hybrid, Gasteria lutzii× Aloe aristata (Aloaceae), to its progeny. Chromosoma 105:342–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02529749
Tang X, Yu C, Zhang K, Zeng Y, Zhao L, Zhang H, Liu X (2020) Detection the ploidy levels in asiatic lily cross-breeding through karyotype analysis and fish. Pak J Bot 52:975–985
Van Laere K, Khrustaleva L, Van Huylenbroeck J, Van Bockstaele E (2010) Application of GISH to characterize woody ornamental hybrids with small genomes and chromosomes. Plant Breed 129:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2009.01692.x
Van Tuyl J, De Jeu M, Univ C, Press N (1997) Methods for overcoming interspecific crossing barriers. Pollen Biotechnol Crop Prod Improv. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511525469.015
Van Tuyl JM, Lim KB, Ramanna MS (2002) Interspecific hybridization and introgression. In: Vainstein A (ed) Breeding for ornamentals: classical and molecular approaches. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 85–103. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-0956-9_5
van Tuyl JM, Arens P (2010) Lilium: breeding history of the modern cultivar assortment. In II International Symposium on the Genus Lilium. Acta Hort 900:223–230. https://doi.org/10.17660/actahortic.2011.900.27
Younis A, Ramzan F, Hwang Y-J, Lim K-B (2015) FISH and GISH: molecular cytogenetic tools and their applications in ornamental plants. Plant Cell Rep 34:1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-015-1828-3
Zhou S, Ramanna M, Visser RG, van Tuyl J (2008a) Genome composition of triploid lily cultivars derived from sexual polyploidization of Longiflorum× Asiatic hybrids (Lilium). Euphytica 160:207–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9538-8
Zhou S, Ramanna MS, Visser RG, van Tuyl J (2008b) Analysis of the meiosis in the F1 hybrids of Longiflorum× Asiatic (LA) of lilies (Lilium) using genomic in situ hybridization. Genomics 35:687–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1673-8527(08)60091-0
Zhou S, Zhong L, Zhang L, Xu Z, Liu X, Li K, Zhou G (2015) Study on the homology of the genomes of tetraploid Asiatic lilies (Lilium) using FISH. Genome 58:453–461. https://doi.org/10.1139/gen-2015-0057
Acknowledgements
We thank to Prof Hong-Yul Kim and especially Professor Lim Ki-Byung for their intensive efforts and for adding valuable information, technical and language editing to make the manuscript meaningful.
Funding
This work was supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry (iPET) through Agri-Bio industry Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (grant number iPET318021-4). This work was also supported by a grant from Regional Subgenebank Support Program of Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea (Project No. PJ0143802019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MI, LH, DMD designed the manuscript and RY, FR and HYK worked on the acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation. KBL gave his valuable time for critical revisions of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest, and all the authors have read, revised, and finally approved this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.M., Lee, H., Deepo, D.M. et al. Chromosome characterization and physical mapping of 18S rDNA in Lilium longiflorum originated interspecific hybrids using combined genomic and fluorescent in situ hybridization. Euphytica 218, 133 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03066-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-022-03066-0