Abstract
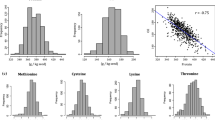
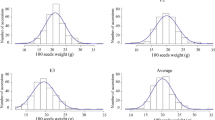
Soybean seeds contain high levels of oil and protein, providing 57 and 69% of a person's dietary requirements, respectively. Although many quantitative trait loci for the 100-seed weight (100SW), protein content (PRC), and oil content (OIC) have been reported, their genetic controls in soybeans remain unclear. The QTL–allele constitution of three traits in the Sichuan and Chongqing eco-regions population (SCLBP) was studied using a representative sample composed of 228 accessions. These were tested in four environments and analyzed using 135 simple sequence repeats (SSR) and 107,081 valid single nucleotide polymorphism linkage (SNP) markers. The range of 100SW, PRC, and OIC in SCLBP accessions were 4.82–33.35, 36.47–49.75%, and 14.68–21.77%, respectively. The heritability (h2) and genetic coefficient of variation (GCV) of the three traits were high. As a result, 26, 33, and 31 QTLs were found using SSR for 100SW, PRC, and OIC, respectively. The allele of Sat_260 for 100SW was detected in the four environments. In addition, 28, 198, and 250 loci for 100SW, PRC, and OIC, respectively, were found using SNP and mixed linear model (MLM). Further SNP haplotype analysis revealed that 13, 35, and 60 blocks were found for 100SW, RPC, and OIC, respectively. The block of Gm11_9895764-9,917,646 for 100SW was simultaneously detected in the four environments. Among these QTLs, 1, 5, and 7 for 100SW, PRC and OIC were found using two methods of SSR and SNP at the same time. A majority of these QTLs overlapped with the previously reported loci. However, 9, 11, and 9 loci for 100SW, PRC, and OIC using SSR; and 3, 5, and 8 for 100SW, PRC, and OIC hadn’t been reported using SNP. Moreover, the genes of Glyma.11g130800, Glyma.13g217000, and Glyma.08g122600 were considered the most likely genes controlling 100SW, PRC, and OIC, respectively. These findings provide evidence for mixed major plus polygenes inheritance for the three traits and an extended understanding of their genetic architecture for the molecular dissection and breeding of soybeans.


Note: The distribution of chromosomes, blocks, MAF, and SNP was from outside to inside


Note: a LD decay b Linkage disequilibrium in genome

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akond M, Liu S, Boney M, Kantartzi S, Meksem K, Bellaloui N, Lightfoot D, Kassem M (2014) Identification of quantitative trait loci (QTL) underlying protein, oil, and five major fatty acids’ contents in soybean. Am J Plant Sci 5:158–167
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Chang FG, Guo CY, Sun FL, Zhang JS, Wang ZL, Kong JJ, He QY, Sharmin RA, Zhao TJ (2018) Genome-wide association studies for dynamic plant height and number of nodes on the main stem in summer sowing soybeans. Front in Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01184
Chen Y, Sun AJ, Wang M, Zhu Z, Ouwerkerk PBF (2014) Functions of the CCCH type zinc finger protein OsGZF1 in regulation of the seed storage protein GluB-1 from rice. Plant Mol Biol 84:621–634
Diers BW, Keim P, Shoemaker RC, Fehr WR (1992) RFLP analysis of soybean seed protein and oil content. Theor Appl Genet 83(5):608–612
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Falke KC, Maurer HP, Melchinger AE, Piepho H, Flachenecker C, Frisch M (2007) Linkage disequilibrium in two European F2 flint maize populations under modified recurrent full-sib selection. Theor Appl Genet 115(2):289–297
Farnir F, Coppieters W, Arranz JJ, Berzi P, Cambisano N, Grisart B, Karim L, Marcq F, Moreau L, Mni M, Nezer C, Simon P, Vanmanshoven P, Wagenaar D, Georges M (2000) Extensive genome-wide linkage disequilibrium in cattle. Genome Res 10:220–227
Fasoula VA, Harris DK, Boerma HR (2004) Validation and designation of quantitative trait loci for seed protein, seed oil, and seed weight from two soybean populations. Crop Sci 44:1218–1225
Fulgione A, Hancock AM (2018) Archaic lineages broaden our view on the history of Arabidopsis Thaliana. New Phytol 219(4):1194–1198
Gaut BS, Long AD (2003) The lowdown on linkage disequilibrium. Plant Cell 15(7):1502–1506
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Han YP, Li DM, Zhu D, Li HY, Li YP, Teng WL, Li WB (2012) QTL analysis of soybean seed weight across multi-genetic backgrounds and environments. Theor Appl Genet 125(4):671–683
He QY, Yang HY, Xiang SH, Tian D, Wang WB, Zhao TJ, Gai JY (2015) Fine mapping of the genetic locus L1 conferring black bods using a chromosome segment substitution line population of soybean. Plant Breeding 134:437–445
Hu R, Xiao J, Gu T, Yu XF, Zhang Y, Chang JL, Yang G, X., He G.Y. (2018) Genome-wide identification and analysis of WD proteins in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Genomics 19:803
Huang X, Wei X, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C, Zhu C, Lu T, Zhang Z, Li M, Fan D, Guo Y, Wang A, Wang L, Deng L, Li W, Lu Y, Weng Q, Liu K, Huang T, Zhou T, Jing Y, Li W, Lin Z, Buckler ES, Qian Q, Zhang QF, Li J, Han B (2010) Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet 42:961–967
Illumina (2012) Evalution of infinium genotyping assay controls training guide. San Diego,CA 92122 USA.
Jiang DK, Sun JL, Cao GW, Liu Y, Lin DX, Gao YZ, Ren WH, Long XD, Zhang HX, Ma XP, Wang Z, Jiang W, Chen TY, Gao Y, Sun LD, Long JR, Huang HX, Wang D, Yu HJ, Zhang PY, Tang LS, Peng B, Cai H, Liu TT, Zhou P, Liu F, Lin XL, Tao S, Wan B, Yin HXGS, Qin LX, Yin JH, Liu L, Wu C, Pei Y, Zhou YF, Zhai Y, Lu PX, Tan AH, Zuo XB, Fan J, Chang J, Gu XL, Wang NJ, Li Y, Liu YK, Zhai K, Zhang HW, Hu ZB, Liu J, Yi Q, Xiang YB, Shi R, Ding Q, Zheng W, Shu XO, Mo ZN, Shugart YY, Zhang XJ, Zhou GQ, Shen HB, Zheng SL, Xu JF, Yu L (2013) Genetic variants in STAT4 and HLA-DQ genes confer risk of hepatitis B virus–related hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature Genetic 45:72–75
Jun T, Van K, Kim M, Lee S, Walker D (2008) Association analysis using SSR markers to find QTL for seed protein content in soybean. Euphytica 162(2):179–191
Keim P, Diers BW, Olson TC, Shoemaker RC (1990) RFLP mapping in soybean: association between marker loci and variation in quantitative traits. Genetics 126(3):735–742
Kim S, Plagnol V, Hu TT, Toomajian C, Clark RM, Ossowski S, Ecker JR, Weigel D, Nordborg M (2007) Recombination and linkage disequilibrium in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 39(9):1151–1155
Lassner MW, Levering CK, Davies HM, Knutzon DS (1995) Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase from meadowfoam mediates insertion of erucic acid at the sn-2 position of triacylglycerol in transgenic rapeseed oil. Plant Physiol 109(4):1389–1394
Li C, Dong Y, Zhao T, Li L, Li C, Yu E, Mei L, Daud MK, He Q, Chen J, Zhu S (2016) Genome-wide SNP linkage mapping and QTL analysis for fiber quality and yield traits in the upland cotton recombinant inbred lines population. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01356
Li XH, Shao ZQ, Tian R, Zhang H, Du H, Kong YB, Li WL, Zhang CY (2019) Mining QTLs and candidate genes for seed protein and oil contents across multiple environments and backgrounds in soybean. Mol Breeding 39(11):139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-1055-7
Liu R, Gong J, Xiao X, Zhang Z, Li J, Liu A, Lu Q, Shang H, Shi Y, Ge Q, Iqbal MS, Deng X, Li S, Pan J, Duan L, Zhang Q, Jiang X, Zou X, Hafeez A, Chen Q, Geng H, Gong W, Yuan Y (2018) GWAS analysis and QTL identification of fiber quality traits and yield components in upland cotton using enriched high-density SNP markers. Front in Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01067
Lu X, Xiong Q, Cheng T, Li QT, Liu XL, Bi YD, Li W, Zhang WK, Ma B, Lai YC (2017) A PP2C-1 allele underlying a quantitative trait locus enhances soybean 100-seed weight. Mol Plant 10(5):670–684
Mansur LM, Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Cregan PB, Lark KG (1996) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits using recombinant inbred lines of soybean. Crop Sci 36(5):1327–1336
Maughan PJ, Maroof MAS, Buss GR (1996) Molecular-marker analysis of seed-weight: genomic locations, gene action, and evidence for orthologous evolution among three legume species. Theor Appl Genet 93(4):574–579
McMullen MD, Kresovich S, Villeda HS, Bradbury P, Li H, Sun Q, Flint-Garcia S, Thornsberry J, Acharya C, Bottoms C, Brown P, Browne C, Eller M, Guill K, Harjes C, Kroon D, Lepak N, Mitchell SE, Peterson B, Pressoir G, Romero S, Oropeza RM, Salvo S, Yates H, Hanson M, Jones E, Smith S, Glaubitz JC, Goodman M, Ware D, Holland JB, Buckler ES (2009) Genetic properties of the maize nested association mapping population [J]. Science 325(5941):737–740
Miller JM, Poissant J, Malenfant RM, Hogg JT, Coltman DW (2015) Temporal dynamics of linkage disequilibrium in two populations of bighorn sheep. Ecol Evol 5(16):3401–3412
Orf JH, Chase K, Jarvik T, Mansur LM, Cregan PB, Adler FR, Lark KG (1999) Genetics of soybean agronomic traits: I comparison of three related recombinant inbred populations. Crop Sci 39(6):1652–1656
Pritchard JK, Przeworkski M (2001) Linkage disequilibrium in humans: models and data. Am J Hum Genet 69:1–14
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155(2):945–959
Rossi M, Orf J, Liu L, Dong Z, Rajcan I (2013) Genetic basis of soybean adaptation to North American vs. Asian mega-environments in two independent populations from Canadian x Chinese crosses. Theor Appl Genet 126(7):1809–1823
Saghai-Maroof M, Soliman AKM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81(24):8014–8018
Schaid DJ, Chen WN, Larson NB (2018) From genome-wide associations to candidate causal variants by statistical fine-mapping [J]. Nat Rev Genet 19:491–504
Shaun P. (2010) PLINK (1.07) documentation. Center for Human Genetic Research
Shin JH, Blay S, McNeney B, Graham J (2006) LD heatmap: an R function for graphical display of pairwise linkage disequilibria between single nucleotide polymorphisms. J Stat Softw 16:1–9
Specht JE, Chase K, Macrander M, Graef GL, Chung J, Markwell JP, Germann M, Orf JH, Lark KG (2001) Soybean response to water: a QTL analysis of drought tolerance. Crop Sci 41(2):493–509
Song QJ, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Concibido VC, Delannay X, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2004) A new integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean. Theor Appl Genet 109:122–128
Sun Y, Pan J, Shi X, Du X, Wu Q, Qi Z, Jiang H, Xin D, Liu C, Hu G, Chen Q (2012) Multi-environment mapping and meta-analysis of 100-seed weight in soybean. Mol Biol Rep 39(10):9435–9443
Tang Y, Liu XL, Wang JB, Li M, Wang QS, Tian F, Su ZB, Pan YC, Liu D, Lipka AE, Buckler ES, Zhang ZW (2016) GAPIT Version 2: An enhanced integrated tool for genomic association and prediction. The Plant Genome 9(2):1–9
Wang XZ, Jiang GL, Gree M, Scott RA, Song QJ, Hyten DL, Cregan PB (2014) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for seed yield, oil and protein contents in two recombinant inbred line populations of soybean. Mol Genet Genomics 289:935–949
Yang HY, Wang WB, He QY, Xiang SH, Tian D, Zhao TJ, Gai JY (2019) Identifying a wild allele conferring small seed size, high protein content and low oil content using chromosome segment substitution lines in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 132(6):2793–2807
Yang W, Guo Z, Huang C, Duan L, Chen G, Jiang N, Fang W, Feng H, Xie W, Lian X, Wang G, Luo Q, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Xiong L (2014) Combining high-throughput phenotyping and genome-wide association studies to reveal natural genetic variation in rice. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6087
Yang W, Guo Z, Huang C, Wang K, Jiang N, Feng H, Chen G, Liu Q, Xiong L (2015) Genome-wide association study of rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaf traits with a high-throughput leaf scorer. J Exp Bot 66(18):5605–5615
Yang ZL, Zhou XA (2020) Breeding advance of high protein soybean in China. Hefei: Conference of promotion of soybean industry chain in Anhui.
Zhang JP, Song QJ, Cregan PB, Nelson RL, Wang XZ, Wu JX, Jiang GL (2015) Genome-wide association study for flowering time, maturity dates and plant height in early maturing soybean (Glycine max) germplasm. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1441-4
Zhang WK, Wang YJ, Luo GZ, Zhang JS, He CY, Wu XL, Gai JY, Chen SY (2004) QTL mapping of ten agronomic traits on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) genetic map and their association with EST markers. Theor Appl Genet 108(6):1131–1139
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Province (2019YJ0679, SCCXTD-2020-20), the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0201006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31871711, 31601325), the Anhui Provincial College Program for Natural Science (KJ2019A0812), The Key R & D projects of Anhui (202104a06020029), the Key R & D projects of Sichuan (2021YFYZ0018) and the Key Projects of Anhui Science and Technology (2021zrzd13).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Q., Xiang, S., Yang, H. et al. A genome-wide association study of seed size, protein content, and oil content using a natural population of Sichuan and Chongqing soybean. Euphytica 217, 198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02931-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-021-02931-8