Abstract
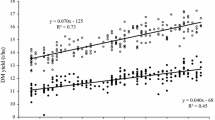
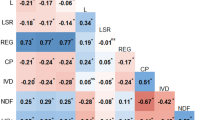
Alfalfa (Medicago Sativa L.) is increasingly adopted in the southeastern USA as a companion crop in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon L.) pastures, where poultry litter is excessively used as source of N fertilizer. This research explores the extent of genetic variation in phosphorus (P) accumulation and uptake in alfalfa germplasm grown in a soil heavily amended with poultry waste, and the expected genetic gain from selection for P accumulation and uptake. Eighteen commercial and experimental populations of alfalfa were evaluated in a soil, heavily amended with chicken litter. The soil pH was 6.8 and Mehlich-1 P content was 1039.7 kg ha−1. Significant genetic variation was observed in P accumulation, forage yield, and P uptake and removal (p < 0.01). Harvest dates effect was significant (p < 0.01), but little interaction of genotypes x harvest date. Narrow sense heritability estimates based on family-means were 0.50 for P concentration, 0.25 for biomass yield, and 0.74 for P uptake. Genetic gain from selection for forage yield based on family means was much higher than that of selection based on individual pots (40 vs. 16 %). For P uptake, gain from selection was 7 % higher using selection based on family means compared to individual pot basis (46 vs. 53 %, respectively). The data suggests that it is possible to make reasonable progress in improving P uptake in alfalfa by selection methods that take advantage of the additive genetic variation such as family selection, whether selecting indirectly for high forage yield or concurrently for P concentration and yield.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo A, Antunes I, Teixeira M (2005) Inheritance of root traits and phosphorus uptake in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under limited soil phosphorus supply. Euphytica 145(1–2):33–40. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-8772-1
Bélanger G, Richards JE (1999) Relationship between P and N concentrations in timothy. Can J Plant Sci 79(1):65–70. doi:10.4141/P97-125
Brink GE, Pederson GA, Sistani KR, Fairbrother TE (2001) Uptake of selected nutrients by temperate grasses and legumes Mississippi Agriculture and Forestry Experiment Station. Journal Article no. 9607. Agron J 93 (4). doi:10.2134/agronj2001.934887x
Caradus JR (1992) Heritability of, and relationships between phosphorus and nitrogen concentration in shoot, stolon and root of white clover (Trifolium repens L.). Plant Soil 146(1–2):209–217. doi:10.1007/BF00012014
Caradus JR, Kennedy LD, Dunn A (1998) Genetic variation for the ratio of inorganic to total phosphorus in white clover leaves. J Plant Nutr 21(10):2265–2272. doi:10.1080/01904169809365560
Casler MD, Brummer EC (2008) Theoretical expected genetic gains for among-and-within-family selection methods in perennial forage crops. Crop Sci 48(3):890–902. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.09.0499
Casler MD, Undersander DJ, Jokela WE (2008) divergent selection for phosphorus concentration in reed canarygrass. Crop Sci 48(1):119–126. doi:10.2135/cropsci2007.03.0165
Cassida KA, Stewart CB, Haby VA, Gunter SA (2006) Alfalfa as an alternative to bermudagrass for pastured stocker cattle systems in the southern USA. Agron J 98(3):705–713. doi:10.2134/agronj2005.0081
Chardon WJ, Oenema O, del Castilho P, Vriesema R, Japenga J, Blaauw D (1997) Organic phosphorus in solutions and leachates from soils treated with animal slurries. J Environ Qual 26(2):372–378. doi:10.2134/jeq1997.00472425002600020006x
Chaubey I, Edwards DR, Daniel TC, Moore Jr PA, Nichols, DJ (1994) Effectiveness of vegetative filter strips in retaining surface-applied swine manure constituents. Trans ASAE 37:845–850
Correll DL (1998) The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: a review. J Environ Qual 27(2):261–266. doi:10.2134/jeq1998.00472425002700020004x
Furlani AMC, Clark RB, Ross WM, Maranville JW (1987) Differential phosphorus uptake, distribution, and efficiency by sorghum inbred parents and their hybrids. In: Gabelman WH, Loughman BC (eds) Genetic aspects of plant mineral nutrition, vol 27. Developments in plant and soil sciences. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 287–298. doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-3581-5_26
Gardner CO (1961) An evaluation of effects of mass selection and seed irradiation with thermal neutrons on yield of corn1. Crop Sci 1(4):241–245. doi:10.2135/cropsci1961.0011183X000100040004x
Goss DW, Stewart BA (1979) Efficiency of phosphorus utilization by alfalfa from manure and superphosphate. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43(3):523–527
Haby VA, Stout SA, Hons FM, Leonard AT (2006) Nitrogen fixation and transfer in a mixed stand of alfalfa and bermudagrass. Agron J 98(4):890–898. doi:10.2134/agronj2005.0084
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. University of California, College of Agriculture, Agricultural Experiment Station, Berkeley
Holland JB, Nyquist WE, Cervantes-Martínez CT (2010) Estimating and interpreting heritability for plant breeding: an update. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews. Wiley, Oxford, pp 9–112. doi:10.1002/9780470650202.ch2
Jones JB (1998) Phosphorus toxicity in tomato plants: when and how does it occur? Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 29(11–14):1779–1784. doi:10.1080/00103629809370068
Kratochvil RJ, Coale FJ, Momen B, Harrison MR Jr, Pearce JT, Schlosnagle S (2006) Cropping systems for phytoremediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. Int J Phytoremediation 8(2):117–130. doi:10.1080/15226510600678456
Lüderitz V, Gerlach F (2002) Phosphorus removal in different constructed wetlands. Acta Biotechnol 22(1–2):91–99. doi:10.1002/1521-3846(200205)22:1/2<91:AID-ABIO91>3.0.CO;2-5
Maguire RO, Mullins GL, Brosius M (2008) Evaluating long-term nitrogen- versus phosphorus-based nutrient management of poultry litter. J Environ Qual 37(5):1810–1816. doi:10.2134/jeq2007.0528
Mallarino AP (1996) Evaluation of optimum and above-optimum phosphorus supplies for corn by analysis of plant parts. Agron J 88(3):376–380. doi:10.2134/agronj1996.00021962008800030003x
McCollum RE (1991) Buildup and decline in soil-phosphorus—30-year trends on a typic umprabuult. Agron J 83(1):77–85
Missaoui AM, Boerma HR, Bouton JH (2005) Genetic variation and heritability of phosphorus uptake in Alamo switchgrass grown in high phosphorus soils. Field Crops Res 93(2–3):186–198. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2004.09.020
Muir JP (2001) Dairy compost, variety, and stand age effects on kenaf forage yield, nitrogen and phosphorus concentration, and uptake. Agron J 93(5):1169–1173. doi:10.2134/agronj2001.9351169x
Nguyen HT, Sleper DA (1981) Genetic variability of mineral concentrations in Festuca arundinacea Schreb. Theor Appl Genet 59(1):57–63. doi:10.1007/bf00275779
Orloff, Steve B., Dan Putnam, Wilson R (2008) Maximizing fertilizer efficiency through tissue testing and improved application methods. In: 38th California Forage and Alfalfa Symposium and Western Alfalfa Seed Conference, San Diego, CA
Piepho HP, Eckl T (2014) Analysis of series of variety trials with perennial crops. Grass Forage Sci 69(3):431–440. doi:10.1111/gfs.12054
Putnam D, Russelle M, Orloff S, Kuhn J, Fitzhugh L, Godfrey L, Kiess A, Long R (2001) The importance and benefits of alfalfa in the 21st century. California alfalfa and forage association 36 Grande Vista, Novato, CA
Ranatunga TD, Reddy SS, Taylor RW (2013) Phosphorus distribution in soil aggregate size fractions in a poultry litter applied soil and potential environmental impacts. Geoderma 192:446–452. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2012.08.026
Read JJ (2012) Spring nitrogen fertilization of ryegrass-bermudagrass for phytoremediation of phosphorus-enriched soils. Agron J 104(4):908–916. doi:10.2134/agronj2011.0385
SAS (2012) SAS 9.4. Copyright (c) 2002–2012 by SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA
Sims JT, Wolf DC (1994) Poultry waste management: agricultural and environmental issues. Adv Agron 52:1–83
Sistani KR, Torbert HA, Way TR, Bolster CH, Pote DH, Warren JG (2009) Broiler litter application method and runoff timing effects on nutrient and Escherichia coli losses from tall fescue pasture. J Environ Qual 38(3):1216–1223. doi:10.2134/jeq2008.0185
Sleper DA, Garner GB, Asay KH, Boland R, Pickett EE (1977) Breeding for Mg, Ca, K, and P content in tall fescue1. Crop Sci 17(3):433–438. doi:10.2135/cropsci1977.0011183X001700030023x
Smith KF, Rebetzke GJ, Eagles HA, Anderson MW, Easton HS (1999) Genetic control of mineral concentration and yield in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.), with special emphasis on minerals related to grass tetany. Aust J Agric Res 50(1):79–86. doi:10.1071/A98070
Tewolde H, Shankle MW, Adeli A, Sistani KR, Rowe DE (2009) Macronutrient concentration in plant parts of cotton fertilized with broiler litter in a marginal upland soil. Soil Tillage Res 105(1):1–11. doi:10.1016/j.still.2009.04.007
Tunney H, Pommel B (1987) Phosphorus uptake by ryegrass from monocalcium phosphate and pig manure on two soils in pots. Irish J Agric Res 26(2/3):189–198
Williams CM, Barker JC, Sims JT (1999) Management and utilization of poultry wastes. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 162:105–157
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by funds from the University of Georgia Research Foundation cultivar development and research program. This research was supported by a grant from the Southern Region Sustainable Agriculture Research and Education Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Missaoui, A.M., Young, J. Genetic gain from selection and potential for improving alfalfa phosphorus uptake and removal from soils heavily amended with poultry litter. Euphytica 209, 495–506 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1677-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1677-3