Abstract
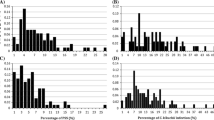
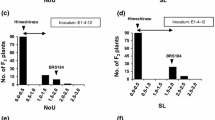
Because the six major known resistance genes to Asian soybean rust (ASR) are pathotype-specific, they rarely offer durable resistance to all ASR pathogens. Thus, other types of resistance such as field resistance or tolerance that confer broad-spectrum resistance to ASR pathogens are required for soybean breeding. The Chinese soybean variety Lu Pi Dou has a green cotyledon color (CC) and a no leaf yellowing (LY) phenotype was previously identified during ASR infection of this strain. This phenotype may reduce yield losses of soybean cultivars infected with ASR infections if it is independent of pathotype-specific major resistance genes and undesirable phenotypes. Thus, to identify associations of LY and CC and other color traits and loci that are linked to the six known ASR resistance genes, recombinant inbred lines (RILs) and backcross (BC) BC2F5 lines were derived from Lu Pi Dou and BRS184 plant strains. Comparisons of LY, CC, and genotypes of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers revealed that the absence of LY is tightly associated with green CC in accordance with the expression of the genes d1 and d2. However, although variations of LY in RILs with yellow CC predominantly reflected the infection index (IFI), no associations were observed between LY and pubescence color, pod color, seed coat color, or flanking SSR markers for six known ASR resistance loci. An association of LY with CC and IFI was also shown in data from BC populations. Therefore, prevention of LY during ASR infection of Lu Pi Dou was primarily dependent on the double-recessive genotype d1d1d2d2 for CC and secondarily on low IFI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akamatsu H, Yamanaka N, Yamaoka Y, Soares RM, Morel W, Ivancovich AJG, Bogado AN, Kato M, Yorinori JT, Suenaga K (2013) Pathogenic diversity of soybean rust in Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay. J Gen Plant Pathol 79:28–40. doi:10.1007/s10327-012-0421-7
Arias CAA, Toledo JFF, Almeida LA, Pipolo AE, Carneiro GES, Abdelnoor RV, Rachid BF, Ribeiro AS (2008) Asian rust in Brazil: Varietal resistance. In: Kudo H, Suenaga K, Soares RM, Toledo A (eds) JIRCAS Working Report No. 58: Facing the challenge of soybean rust in South America. JIRCAS, Tsukuba, pp 29–30
Brogin RL (2005) Mapeamento de genes de resistência à ferrugem e de QTLs envolvidos na resistência à septoriose em soja. Dissertation, Universidade de São Paulo
Garcia A, Calvo ES, Kiihl RAS, Harada A, Hiromoto DM, Vieira LGE (2008) Molecular mapping of soybean rust (Phakopsora pachyrhizi) resistance genes: discovery of a novel locus and alleles. Theor Appl Genet 117:545–553. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0798-z
Goellner K, Loehrer M, Langenbach C, Conrath U, Koch E, Schaffrath U (2010) Phakopsora pachyrhizi, the causal agent of Asian soybean rust. Mol Plant Pathol 11:169–177. doi:10.1111/J.1364-3703.2009.00589.X
Grant D, Nelson RT, Cannon SB, Shoemaker RC (2010) SoyBase, the USDA-ARS soybean genetics and genomics database. Nucleic Acids Res 38:843–846. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp798
Guiamét JJ, Giannibelli MC (1996) Nuclear and cytoplasmic `stay-green’ mutations of soybean alter the loss of leaf soluble proteins during senescence. Physiol Plant 96:655–661. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1996.tb00239.x
Guiamét JJ, Teeri JA, Noodén LD (1990) Effects of nuclear and cytoplasmic genes altering chlorophyll loss on gas exchange during monocarpic senescence in soybean. Plant Cell Physiol 31:1123–1130
Guiamét JJ, Schwartz E, Pichersky E, Noodén LD (1991) Characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear mutations affecting chlorophyll and chlorophyll-binding proteins during senescence in soybean. Plant Physiol 96:227–231. doi:10.1104/pp.96.1.227
Hartman GL, Miles MR, Frederick RD (2005) Breeding for resistance to soybean rust. Plant Dis 89:664–666. doi:10.1094/PD-89-0664
Hartwig EE, Bromfield KR (1983) Relationships among three genes conferring specific resistance to rust in soybeans. Crop Sci 23:237–239. doi:10.2135/cropsci1983.0011183X002300020012x
Hossain MM, Akamatsu H, Morishita M, Mori T, Yamaoka Y, Suenaga K, Soares RM, Bogado AN, Ivancovich AJG, Yamanaka N (2015) Molecular mapping of Asian soybean rust resistance in soybean landraces PI 594767A, PI 587905 and PI 416764. Plant Pathol 64:147–156. doi:10.1111/ppa.12226
Hyten DL, Hartman GL, Nelson RL, Frederick RD, Concibido VC, Narvel JM, Gregan PB (2007) Map location of the Rpp1 locus that confers resistance to soybean rust in soybean. Crop Sci 47:835–838. doi:10.2135/cropsci2006.07.0484
Hyten DL, Smith JR, Frederick RD, Tucker ML, Song Q, Cregan PB (2009) Bulked segregant analysis using the GoldenGate assay to locate the Rpp3 locus that confers resistance to soybean rust in soybean. Crop Sci 49:265–271. doi:10.2135/cropsci2008.08.0511
Laperuta LDC, Arias CAA, Ribeiro AS, Rachid BF, Pierozzi PHB, Toledo JFFD, Pípolo AE, Carneiro GEDS (2008) New genes conferring resistance to Asian soybean rust: allelic testing for the Rpp2 and Rpp4 loci. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 43:1741–1747. doi:10.1590/S0100-204X2008001200014
Lemos NG, Braccini AL, Abdelnoor RV, Oliveira MCN, Suenaga K, Yamanaka N (2011) Characterization of genes Rpp2, Rpp4, and Rpp5 for resistance to soybean rust. Euphytica 182:53–64. doi:10.1007/s10681-011-0465-3
Li S, Smith JR, Ray JD, Frederick RD (2012) Identification of a new soybean rust resistance gene in PI 567102B. Theor Appl Genet 125:133–142. doi:10.1007/s00122-012-1821-y
Luquez VM, Guiamét JJ (2001) Effects of the ‘Stay Green’ genotype GGd1d1d2d2 on leaf gas exchange, dry matter accumulation and seed yield in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Ann Bot 87:313–318. doi:10.1006/anbo.2000.1324
Luquez VM, Guiamét JJ (2002) The stay green mutations d1 and d2 increase water stress susceptibility in soybeans. J Exp Bot 53:1421–1428. doi:10.1093/jexbot/53.373.1421
Nakano M, Yamada T, Masuda Y, Sato Y, Kobayashi H, Ueda H, Morita R, Nishimura M, Kitamura K, Kusaba M (2014) A green-cotyledon/stay-green mutant exemplifies the ancient whole-genome duplications in soybean. Plant Cell Physiol 55:1763–1771. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcu107
Oliveira ACB, Godoy CV, Martins MC (2005) Avaliação da tolerância de cultivares de soja à ferrugem asiática no Oeste da Bahia. Fitopatol Bras 30:658–662
Ott A, Yang Y, Bhattacharyya M, Horner HT, Palmer RG, Sandhu D (2013) Molecular mapping of D1, D2 and ms5 revealed linkage between the cotyledon color locus D2 and the male-sterile locus ms5 in soybean. Plants 2:441–454. doi:10.3390/plants2030441
Ribeiro AS, Moreira JUV, Pierozzi PHB, Rachid BF, De Toledo JFF, Arias CAA, Soares RM, Godoy CV (2007) Genetic control of Asian rust in soybean. Euphytica 15:15–25. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9404-8
Silva DCG, Yamanaka N, Brogin RL, Arias CAA, Nepomuceno AL, Di Mauro AO, Pereira SS, Nogueira LM, Passianotto ALL, Abdelnoor RV (2008) Molecular mapping of two loci that confer resistance to Asian rust in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 117:57–63. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0752-0
Woodworth CM (1921) Inheritance of cotyledon, seed-coat, hilum and pubescence colors in soy-beans. Genetics 6:487–553
Yamanaka N, Yamaoka Y, Kato M, Lemos NG, Passianotto ALL, Santos JVM, Benitez ER, Abdelnoor RV, Soares RM, Suenaga K (2010) Development of classification criteria for resistance to soybean rust and differences in virulence among Japanese and Brazilian rust populations. Trop Plant Pathol 35:153–162. doi:10.1590/S1982-56762010000300003
Yamanaka N, Lemos NG, Akamatsu H, Yamaoka Y, Silva DCG, Passianotto ALL, Abdelnoor RV, Soares RM, Suenaga K (2011) Soybean breeding materials useful for resistance to soybean rust in Brazil. JARQ 45:385–395
Yamanaka N, Akamatsu H, Yamaoka (2013a) Laboratory manual for studies on soybean rust resistance. JIRCAS website. http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp/english/manual/soybean_rust/soybean_rust.html. Accessed 1 December 2013
Yamanaka N, Lemos NG, Uno M, Akamatsu H, Yamaoka Y, Abdelnoor RV, Braccini AL, Suenaga K (2013b) Resistance to Asian soybean rust in soybean lines with the pyramided three Rpp genes. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 13:75–82. doi:10.1590/S1984-70332013000100009
Yorinori JT (2008) Soybean germplasms with resistance and tolerance to Asian rust and screening methods. In: Kudo H, Suenaga K, Soares RM, Toledo A (eds) JIRCAS Working Report No. 58: Facing the challenge of soybean rust in South America. JIRCAS, Tsukuba, pp 70–87
Young LD, Ross JP (1978) Resistance evaluation and inheritance of a nonchlorotic response to brown spot of soybean. Crop Sci 18:1075–1077. doi:10.2135/cropsci1978.0011183X001800060043x
Acknowledgments
We thank Mio Morishita, Tomomi Mori, Akiko Takahashi, Sachiko Nishimura, Yukie Muraki, and Iwao Ohyama (JIRCAS) for their technical assistance, advice, and encouragement. We are grateful to the Jilin Academy of Agricultural Sciences (JAAS) in China and the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation (Embrapa) for providing seeds of the parental varieties. This study was financially supported and conducted by the JIRCAS research project “Development of Breeding Technologies toward Improved Production and Stable Supply of Upland Crops.” The authors N. G. L. and M. M. H. were financially supported by the JIRCAS Visiting Research Fellowship Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamanaka, N., Lemos, N.G., Jara, R.C. et al. Prevention of leaf yellowing in Asian soybean rust infected plants is associated with green cotyledon color and the infection index. Euphytica 205, 475–482 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1414-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1414-3