Abstract
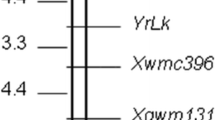
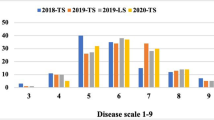
Southern corn rust, a devastating fungal disease of maize, can cause significant loss of grain yield during intermittent outbreak. Growing resistant varieties is the most cost-effective way to manage southern rust in field corn. However, the prevalence of incomplete resistance owing to rapid evolution of pathogen warrants the necessities of discovering new resistant resources. To this end, the disease occurrence of 15 maize inbred lines in response to southern rust was examined in fields located in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions respectively. Overall, the character of resistance or susceptibility was rather steady among locations for most of inbred lines although infrequent variations existed. A tropical inbred line, SCML205, displayed fully resistant response in all the locations tested. By contrast, Jing24, W1636, Zheng58, W541 and G10-2426 exhibited completely susceptible response. A 3:1 segregation ratio of resistance to susceptibility was identified in the progeny of F2 population generated from the cross of SCML205 × Jing24, demonstrating SCML205 harbors a single dominant resistant gene. Allelism test was performed to confirm the resistance conferred by a novel locus, which was designated as RppS. Genetic mapping were conducted to locate RppS to the distal arm of chromosome 10S, a region close to other resistant genes known so far. Together, our survey of the resistance to southern rust in numerous inbred lines leads to the identification of a novel resistant gene, which would be tremendously valuable for plant breeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- IDP:
-
InDel polymorphic marker
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide
- LOD:
-
Logarithmic odds
- cM:
-
Centimorgan
References
Agarwal P, Khetarpal RK, Payak MM (2001) Polysora rust of maize caused by Puccinia polysora. Indian J Agric Sci 71:275–276
Brewbaker JL, Kim SK, So YS, Logroño M, Moon HG, Ming R, Lu X, Josue AD (2011) General Resistance in Maize to Southern Rust (Underw.). Crop Sci 51:1393–1409
Cammack RH (1958) Studies on Puccinia polysora underw: i. The world distribution of forms of P. polysora. Trans Br Mycol Soc 41:89–94
Chen C, Wang Z, Yang D, Ye C, Zhao Y, Jin D, Weng M, Wang B (2004) Molecular tagging and genetic mapping of the disease resistance gene RppQ to southern corn rust. Theor Appl Genet 108:945–950
Collins N, Drake J, Ayliffe M, Sun Q, Ellis J, Hulbert S, Pryor T (1999) Molecular characterization of the maize Rp1-D rust resistance haplotype and its mutants. Plant Cell 11:1365–1376
Duan D, He H (1984) Description of a rust Puccinia polysora on corn in Hainan Island. Acta Mycol Sin 3:125–126
Godoy Cláudia V, Lílian Amorim, Filho Armando B, Silva Herbert P, Silva Willian J, Berger Richard D (2003) Temporal progress of southern rust in maize under different environmental conditions. Fitopatol Bras 28:273–278
Gore MA, Chia J, Elshire RJ, Sun Q, Ersoz ES, Hurwitz BL, Peiffer JA, McMullen MD, Grills GS, Ross-Ibarra J (2009) A first-generation haplotype map of maize. Science 326:1115–1117
Hulbert SH, Bennetzen JL (1991) Recombination at the Rp1 locus of maize. Mol Gen Genet 226:377–382
Jiang K (2013) Identification of resistance to southern corn rust (Puccinia polysora Underw) in maize germplasm. J Plant Genet Resour 14:711–714
Jines MP, Balint-Kurti P, Robertson-Hoyt LA, Molnar T, Holland JB, Goodman MM (2007) Mapping resistance to Southern rust in a tropical by temperate maize recombinant inbred top cross population. Theor Appl Genet 114:659–667
Kosambi DD (1943) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Liu Y, Shi J, Wang Q (1999) Southern corn rust occurred in Hebei Province in 1998. Plant Prot 25:53
Liu Z, Wang S, Dai J, Huang L, Cao H (2003) Studies of genetic analysis and SSR linked marker location of gene resistance to southern rust in inbred line P25 of maize. Acta Genet Sin 30:706–710
Meyers BC, Kaushik S, Nandety RS (2005) Evolving disease resistance genes. Curr Opin Plant Biol 8:129–134
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Raid RN, Pennypacker SP, Stevenson RE (1988) Characterization of Puccinia polysora epidemics in Pennsylvania and Maryland. Phytopathology 78:579–585
Rhind D, Waterston JM, Deighton FC (1952) Occurrence of Puccinia polysora Underw. in West Africa. Nature 169:631
Robert AL (1962) Host ranges and races of the Corn rusts. Phytopathology 52:1010–1012
Rodriguez-Ardon R, Scott GE, King SB (1980) Maize yield losses caused by southern corn rust. Crop Sci 20:812–814
Ryland AK, Storey HH (1955) Physiological races of Puccinia polysora Underw. Nature 176:655–656
Schnable PS, Ware D, Fulton RS, Stein JC, Wei F, Pasternak S, Liang C, Zhang J, Fulton L, Graves TA (2009) The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326:1112–1115
Storey HH, Howland AK (1957) Resistance in maize to the tropical American rust fungus, Puccinia polysora Underw. I. Genes Rpp1 and Rpp2. Heredity 11:289–301
Storey HH, Howland AK (1961) The tropical rust disease of maize caused by Puccinia polysora Underw. East Afr Agr For Res Organ Ann Rep 1962:55–57
Storey HH, Howland AK (1967) Resistance in maize to a third East African race of Puccinia polysora Underw. Ann Appl Biol 60:297–303
Storey HH, Ryland AK (1954) Resistance to the maize rust, Puccinia polysora. Nature 173:778–779
Ullstrup AJ (1965) Inheritance and linkage of a gene determining resistance in maize to an American race of Puccinia polysora. Phytopathology 55:425–428
Wang S (1999) Southern corn rust was epidemic in the Province of Shandong, Henan and Jiangsu. Plant Prot Technol Dissemin 3:40–41
Xin M, Yang R, Li G, Chen H, Laurie J, Ma C, Wang D, Yao Y, Larkins BA, Sun Q, Yadegari R, Wang X, Ni Z (2013) Dynamic expression of imprinted genes associates with maternally controlled nutrient allocation during maize endosperm development. Plant Cell 25:3212–3227
Yue J, Meyers BC, Chen J, Tian D, Yang S (2012) Tracing the origin and evolutionary history of plant nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) genes. New Phytol 193:1049–1063
Zhang Y, Xu L, Zhang D, Dai J, Wang S (2010) Mapping of southern corn rust-resistant genes in the W2D inbred line of maize (Zea mays L.). Mol Breed 25:433–439
Zhao P, Zhang G, Wu X, Li N, Shi D, Zhang D, Ji C, Xu M, Wang S (2013) Fine Mapping of RppP25, a Southern Rust Resistance Gene in Maize. J Integr Plant Biol 55:462–472
Zhou C, Chen C, Cao P, Wu S, Sun J, Jin D, Wang B (2007) Characterization and fine mapping of RppQ, a resistance gene to southern corn rust in maize. Mol Genet Genomics 278(6):723–728
Acknowledgments
We thank all lab members for help and assistance during the research. This work was supported by the National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863) (2012AA10A305 and 2011AA10A103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Na Li is the co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Li, N., Zhao, P. et al. Geographic and genetic identification of RppS, a novel locus conferring broad resistance to southern corn rust disease in China. Euphytica 205, 17–23 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1376-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1376-5