Abstract
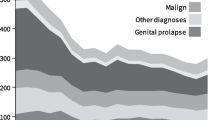
Clinical pathways are defined as evidence-based, multidisciplinary care algorithms that outline essential steps in the management of patients. Pathway implementation in healthcare and industries outside of healthcare demonstrated success in reduction of inefficiencies and elimination of waste of financial and other resources by standardizing processes. The UPMC Health System introduced an evidence-based pathway treatment algorithm for hysterectomy in 2012 with an overarching goal of reducing variations in surgical care and abdominal hysterectomy rates, thereby promoting cost containment and decreased patient morbidity. In 2016, we reported on the impact of hysterectomy pathways on the reduction of open hysterectomy rates and improved patient outcomes between 2012 and 2014. In this follow-up commentary, we looked at years 2015 to 2019 to evaluate the continued success of hysterectomy pathway initiative. Initial studies, as well as follow-up results, both led to the understanding that hysterectomy clinical pathways serve as an effective instrument in decreasing the rates of open hysterectomies, thus reducing complications and undesired practice variability while providing consistent care. We concluded that physician and patient factors that impact the utilization of hysterectomy pathways must be continuously monitored to ensure optimal quality of care for hysterectomy patients. Introduction of clinical pathways across health systems represent an opportunity to introduce a systematic and sustainable change with the goal of achieving improved health outcomes locally and globally.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brownlee S, Chalkidou K, Doust J, Elshaug AG, Glasziou P, Heath I, Nagpal S, Saini V, Srivastava D, Chalmers K, Korenstein D (2017) Evidence for overuse of medical services around the world. Lancet 390(10090):156–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32585-5
Buchert AR, Butler GA (2016) Clinical pathways: driving high-reliability and high-value care. Pediatr Clin 63(2):317–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcl.2015.12.005
Burkett D, Horwitz J, Kennedy V, Murphy D, Graziano S, Kenton K (2011) Assessing current trends in resident hysterectomy training. Female Pelvic Med Reconstr Surg 17(5):210–214. https://doi.org/10.1097/SPV.0b013e3182309a22
Dawes M, Summerskill W, Glasziou P, Cartabellotta A, Martin J, Hopayian K, Porzsolt F, Burls A, Osborne J (2005) Sicily statement on evidence-based practice. BMC Med Educ 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-5-1
Einarsson JI, Sangi-Haghpeykar H (2009) Perceived proficiency in minimally invasive surgery among senior OB/GYN residents. JSLS 13(4):473–478
Einarsson JI, Young A, Tsien L, Sangi-Haghpeykar H (2002) Perceived proficiency in endoscopic techniques among senior obstetrics and gynecology residents. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc 9(2):158–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1074-3804(05)60124-7
Flores EJ, Mull NK, Lavenberg JG, Mitchell MD, Leas BF, Williams A, Brennan PJ, Umscheid CA (2019) Using a 10-step framework to support the implementation of an evidence-based clinical pathways programme. BMJ Qual Saf 28(6):476–485. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjqs-2018-008454
Jackman D, Hamilton J, Foster E, Bunnell C, Culot L, Tremonti C, Jacobson J (2020) Lessons from the front: designing and implementing clinical pathways by and for clinicians. Am J Managed Care 26(2 Spec No.):SP57. https://doi.org/10.37765/ajmc.2020.42549
Jacoby VL, Autry A, Jacobson G, Domush R, Nakagawa S, Jacoby A (2009) Nationwide use of laparoscopic hysterectomy compared with abdominal and vaginal approaches. Obstet Gynecol 114(5):1041–1048. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b9d222
Linkov F, Sanei-Moghaddam A, Edwards RP, Lounder PJ, Ismail N, Goughnour SL, Kang C, Mansuria SM, Comerci JT (2017) Implementation of hysterectomy pathway: impact on complications. Womens Health Issues 27(4):493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.whi.2017.02.004
Linkov F, Adambekov S, Qi M, Harris J, Mansuria SM, Edwards RP (2019) Patient outcomes in a large hospital system during the implementation of a same day discharge for hysterectomies [16OP]. Obstet Gynecol 133:S1-2. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000559074.07831.65
Moen M, Noone M, Cholkeri-Singh A, Vassallo B, Locker B, Miller C (2014) Progressive reduction in abdominal hysterectomy rates: impact of laparoscopy, robotics and surgeon factors. J Robot Surg 8(1):13–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-013-0412-5
Morgan DM, Kamdar NS, Swenson CW, Kobernik EK, Sammarco AG, Nallamothu B (2018) Nationwide trends in the utilization of and payments for hysterectomy in the United States among commercially insured women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 218(4):425.e421-425.e418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2017.12.218
Moynihan R, Bero L, Hill S, Johansson M, Lexchin J, Macdonald H, Mintzes B, Pearson C, Rodwin MA, Stavdal A, Stegenga J, Thombs BD, Thornton H, Vandvik PO, Wieseler B, Godlee F (2019) Pathways to independence: towards producing and using trustworthy evidence. BMJ 367:l6576. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l6576
NWHN (2015) Hysterectomy. https://www.nwhn.org/hysterectomy/.
Pulliam SJ, Berkowitz LR (2009) Smaller pieces of the hysterectomy pie: current challenges in resident surgical education. Obstet Gynecol 113(2 Pt 1):395–398. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181955011
Rogers RM Jr, Julian TM (2005) Training the gynecologic surgeon. Obstet Gynecol 105(1):197–200. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000150578.60931.a6
Sanei-Moghaddam A, Ma T, Goughnour SL, Edwards RP, Lounder PJ, Ismail N, Comerci JT, Mansuria SM, Linkov F (2016) Changes in hysterectomy trends after the implementation of a clinical pathway. Obstet Gynecol 127(1):139–147. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000001185
Sanei-Moghaddam A, Goughnour S, Edwards R, Comerci J, Kelley J, Donnellan N, Linkov F, Mansuria S (2017) Hysterectomy Pathway as the Global Engine of Practice Change: Implications for Value in Care. Central Asian J Glob Health. https://doi.org/10.5195/cajgh.2017.299
Sanei-Moghaddam A, Kang C, Edwards RP, Lounder PJ, Ismail N, Goughnour SL, Mansuria SM, Comerci JT, Linkov F (2018) Racial and socioeconomic disparities in hysterectomy route for benign conditions. J Racial Ethn Health Disparities 5(4):758–765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-017-0420-7
Schimpf MO, Feldman DM, O’Sullivan DM, LaSala CA (2007) Resident education and training in urogynecology and pelvic reconstructive surgery: a survey. Int Urogynecol J 18(6):613–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-006-0203-x
Van Herck P, Vanhaecht K, Sermeus W (2004) Effects of clinical pathways: do they work? J Integr Care Pathw 8(3):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1177/147322970400800302
Varghese A, Doglioli M, Fader AN (2019) Updates and controversies of robotic-assisted surgery in gynecologic surgery. Clin Obstet Gynecol 62(4):733–748. https://doi.org/10.1097/grf.0000000000000489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Godiwala, A., Mansuria, S., Edwards, R.P. et al. Systemic long-term impact of clinical pathways: UPMC experience with hysterectomy patients. Environ Syst Decis 41, 184–188 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-021-09801-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-021-09801-7