Abstract
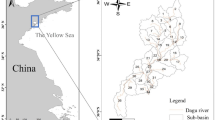
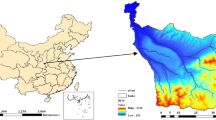
Critical source area (CSAs) identification and subzone delineation could aid in streamlining watershed management. However, how to build a comprehensive evaluation index system based on the identification of CSAs is the key to solving the problem of management zoning, and this issue has not been fully reported yet. We applied the soil and water assessment tool to investigate non-point source (NPS) pollution for two periods from 1967 to 1990 and from 2000 to 2020 in the Jing River Basin, identify the CSAs in each period using four methods, and delineate the watershed management subzones using K-means cluster analysis. Results showed that, from 1970 to 1990, the annual average sediment yield in the basin was 46.91 Mg/ha/year, while from 2000 to 2020, it decreased by 53.24% to 22.01 Mg/ha/year. Between 2000 and 2020, the average load of total phosphorous (TP) pollution was 0.168 kg/ha/year, which was around 92.1% less than that from 1967 to 1990. Although the areas with the most severe total nitrogen (TN) load (15–18 kg/ha/year) had been treated, the pollution intensity was still relatively serious, and there was a trend of large-scale diffusion. The comprehensive evaluation index could effectively identify CSAs under the triple superposition of sediment yield, TN, and TP, which could be defined as one of the important indicators affecting the management subzones of the Jing River Basin. The watershed was divided into four different management zones, namely: northern loess hills and ravines ecological restoration zone, the priority management subzone in the middle west, the middle-eastern forested ecological conservation area, and the southeastern pollution control zone. This study could provide reference and specific directions for decision makers in efficient and sustainable watershed NPS pollution management at the scale of sub-watershed and management subzone.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, [Lei Wu], upon reasonable request.
References
Arnold, J. G., Srinivasan, R., Muttiah, R. S., & Williams, J. R. (1998). Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: Model development. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 34, 73–89. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Bai, X., Wang, B., & Qi, Y. (2021). The effect of returning farmland to grassland and coniferous forest on watershed runoff—A case study of the Naoli river basin in Heilongjiang province, China. Sustainability, 13(11), 6264. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13116264
Chang, D., Lai, Z., Li, S., Li, D., & Zhou, J. (2021). Critical source areas’ identification for non-point source pollution related to nitrogen and phosphorus in an agricultural watershed based on SWAT model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(34), 47162–47181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13973-9
Chen, C., Xie, G., Zhen, L., Geng, Y., & Leng, Y.-F. (2008). Analysis of Jinghe watershed vegetation dynamics and evaluation of its relation to precipitation. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 03, 925–938.
Chen, D., Jin, G., Zhang, Q., Arowolo, A. O., & Li, Y. (2016). Water ecological function zoning in Heihe River Basin, Northwest China. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts a/b/c, 96, 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2016.08.005
Chen, P., Yuan, Y., Li, W., LeDuc, S. D., Lark, T. J., Zhang, X., & Clark, C. (2021). Assessing the impacts of recent crop expansion on water quality in the Missouri river basin using the soil and water assessment tool. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 13(6), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020MS002284
Chen, Y., Xu, C. Y., Chen, X., Xu, Y., Yin, Y., Gao, L., & Liu, M. (2019). Uncertainty in simulation of land-use change impacts on catchment runoff with multi-timescales based on the comparison of the HSPF and SWAT models. Journal of Hydrology, 573, 486–500.
Choi, J., Park, B., Kim, J., Lee, S., Ryu, J., Kim, K., & Kim, Y. (2021). Determination of NPS pollutant unit loads from different landuses. Sustainability, 13(13), 7193.
Dan, Y., Dong, X., Xie, P., Wei, C., Liu, J., Hu, X., Wang, K., Xu, S., Wan, H., & Su, Z. (2020). Prioritization of critical source areas for soil and water conservation by using a one-at-a-time removal approach in the upper Huaihe River basin. Land Degradation and Development, 32(3), 1513–1524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3814
Di, C., Zhengqing, L., Shuo, L., Dan, L., & Jun, Z. (2021). Critical source areas’ identification for non-point source pollution related to nitrogen and phosphorus in an agricultural watershed based on SWAT model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13973-9
Ellison, D., Morris, C. E., Locatelli, B., Sheil, D., Cohen, J., Murdiyarso, D., Gutierrez, V., Van Noordwijk, M., Creed, I. F., Pokorny, J., & Gaveau, D. (2017). Trees, forests and water: Cool insights for a hot world. Global Environmental Change, 43, 51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2017.01.002
Fan, Y., Jin, X., Gan, L., Jessup, L. H., Pijanowski, B. C., Yang, X., Xiang, X., & Zhou, Y. (2018). Spatial identification and dynamic analysis of land use functions reveals distinct zones of multiple functions in eastern China. Science of the Total Environment, 642, 33–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.383
Fu, Y., Shi, X., He, J., Yuan, Y., & Qu, L. (2020). Identification and optimization strategy of county ecological security pattern: A case study in the Loess Plateau, China. Ecological Indicators, 112, 106030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.106030
Gao, Y., Feng, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, J. L., Li, S. C., & Zhu, Y. K. (2014). Clustering urban multifunctional landscapes using the self-organizing feature map neural network model. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, 140(2), 05014001. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)UP.1943-5444.0000170
Geng, R., Yin, P., & Sharpley, A. N. (2019). A coupled model system to optimize the best management practices for nonpoint source pollution control. Journal of Cleaner Production, 220, 581–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.127
Hanief, A., & Laursen, A. E. (2019). Meeting updated phosphorus reduction goals by applying best management practices in the Grand River watershed, southern Ontario. Ecological Engineering, 130, 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.02.007
Himanshu, S. K., Pandey, A., Yadav, B., & Gupta, A. (2019). Evaluation of best management practices for sediment and nutrient loss control using SWAT model. Soil and Tillage Research, 192, 42–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2019.04.016
Huang, J. J., Lin, X., Wang, J., & Wang, H. (2015). The precipitation driven correlation based mapping method (PCM) for identifying the critical source areas of non-point source pollution. Journal of Hydrology, 524, 100–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.02.011
Huang, W., Jia, Y., Huang, G., Niu, C., & Zhang, H. (2022). Temporal and spatial distribution and management measures of non-point source pollution in lake Hongfeng watershed. Water Resources Protection, 2022, 1–8.
Izydorczyk, K., Piniewski, M., Krauze, K., Courseau, L., Czyż, P., Giełczewski, M., Kardel, I., Marcinkowski, P., Szuwart, M., Zalewski, M., & Frątczak, W. (2019). The ecohydrological approach, SWAT modelling, and multi-stakeholder engagement—A system solution to diffuse pollution in the Pilica basin, Poland. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109329
Ji, H., Peng, D., Fan, C., Zhao, K., Gu, Y., & Liang, Y. (2022). Assessing effects of non-point source pollution emission control schemes on Beijing’s sub-center with a water environment model. Urban Climate, 43, 101148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2022.101148
Jin, Y. Y., Li, J., Zhou, Z. X., & Tang, C. Y. (2022). Spatial pattern optimization of ecosystem services based on Bayesian networks: A case of the Jing River Basin. Arid Land Geography, 45(4), 1268–1280.
Li, H., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., Zhang, W., Zhang, S., Yu, P., & Song, Z. (2022). A framework to assess spatio-temporal variations of potential non-point source pollution risk for future land-use planning. Ecological Indicators, 137, 108751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108751
Li, H., Zhang, S., Yu, P., Song, Z., Xie, C., & Zhang, J. (2023). Non-point source pollution assessment and key source area identification based on improved output coefficient model: A case study of the upper watershed of the North Canal. Environmental Science, 146, 1–15.
Li, H. L., Zhang, S. H., Yu, P. D., Song, Z. Y., Xie, C. X., & Zhang, J. J. (2023). Estimation and critical source area identification of non-point source pollution based on improved export coefficient models: A case study of the upper Beiyun River Basin. Environmental Science, 44(11), 6194–6204.
Li, S., Li, J., Xia, J., & Hao, G. (2021). Optimal control of nonpoint source pollution in the Bahe River Basin, Northwest China, based on the SWAT model. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(39), 55330–55343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14869-4
Liu, R., Xu, F., Zhang, P., Yu, W., & Men, C. (2016). Identifying non-point source critical source areas based on multi-factors at a basin scale with SWAT. Journal of Hydrology, 533, 379–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.12.024
Liu, X., Beusen, A. H., Van Beek, L. P., Mogollón, J. M., Ran, X., & Bouwman, A. (2018). Exploring spatiotemporal changes of the Yangtze River (Changjiang) nitrogen and phosphorus sources, retention and export to the East China Sea and Yellow Sea. Water Research, 142, 246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.06.006
Liu, Y., Yang, C., Yu, X., Wang, M., & Qi, W. (2021). Monitoring the landscape pattern and characteristics of non-point source pollution in a mountainous river basin. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(21), 11032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111032
Liu, Z., Huang, Q., Zhou, Y., & Sun, X. (2022). Spatial identification of restored priority areas based on ecosystem service bundles and urbanization effects in a megalopolis area. Journal of Environmental Management, 308, 114627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114627
López-Ballesteros, A., Senent-Aparicio, J., Srinivasan, R., & Pérez-Sánchez, J. (2019). Assessing the impact of best management practices in a highly anthropogenic and ungauged watershed using the SWAT model: A case study in the El Beal watershed (Southeast Spain). Agronomy, 9(10), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9100576
Lyu, D., Yang, Y., Zhao, W., Xu, X., He, L., Guo, J., Lei, S., Liu, B., & Zhang, X. (2022). Effects of different vegetation restoration types on soil hydro-physical properties in the hilly region of the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Research, 61, 94–105.
Martin, J. F., Kalcic, M. M., Aloysius, N., Apostel, A. M., Brooker, M. R., Evenson, G., Kast, J. B., Kujawa, H., Murumkar, A., Becker, R., & Boles, C. (2021). Evaluating management options to reduce Lake Erie algal blooms using an ensemble of watershed models. Journal of Environmental Management, 280, 111710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111710
Merriman, K. R., Daggupati, P., Srinivasan, R., Toussant, C., Russell, A. M., & Hayhurst, B. (2018). Assessing the impact of site-specific BMPs using a spatially explicit, field-scale SWAT model with edge-of-field and tile hydrology and water-quality data in the Eagle Creek watershed, Ohio. Water, 10(10), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101299
Michalek, A., Zarnaghsh, A., & Husic, A. (2021). Modeling linkages between erosion and connectivity in an urbanizing landscape. Science of the Total Environment, 764, 144255.
Nanda, S. J., & Panda, G. (2014). A survey on nature inspired metaheuristic algorithms for partitional clustering. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 16, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2013.11.003
Niraula, R., Kalin, L., Srivastava, P., & Anderson, C. J. (2013). Identifying critical source areas of nonpoint source pollution with SWAT and GWLF. Ecological Modelling, 268, 123–133.
Özcan, Z., Kentel, E., & Alp, E. (2017). Evaluation of the best management practices in a semi-arid region with high agricultural activity. Agricultural Water Management, 194, 160–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2017.09.007
Pang, S., Wang, X., Melching, C. S., Guo, H., & Li, W. (2022). Identification of multilevel priority management areas for diffuse pollutants based on streamflow continuity in a water-deficient watershed. Journal of Cleaner Production, 351, 131322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131322
Risal, A., & Parajuli, P. B. (2022). Evaluation of the impact of best management practices on streamflow, sediment and nutrient yield at field and watershed scales. Water Resources Management, 36(3), 1093–1105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-022-03075-7
Shukla, S., Jain, S. K., & Kansal, M. L. (2021). Hydrological modelling of a snow/glacier-fed western Himalayan basin to simulate the current and future streamflows under changing climate scenarios. Science of the Total Environment, 795, 148871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148871
Sun, Y., Hao, R., Qiao, J., & Xue, H. (2020). Function zoning and spatial management of small watersheds based on ecosystem disservice bundles. Journal of Cleaner Production, 255, 120285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120285
Tao, Y., Xu, J., Ren, H. J., Guan, X. Y., You, L. J., & Wang, S. L. (2021). Spatiotemporal variation and factors analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution in the Yellow River Basin. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 37(04), 257–264. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.04.031
Trumbore, S., Brando, P., & Hartmann, H. (2015). Forest health and global change. Science, 349(6250), 814–818. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac6759
Uniyal, B., Jha, M. K., Verma, A. K., & Anebagilu, P. K. (2020). Identification of critical areas and evaluation of best management practices using SWAT for sustainable watershed management. Science of the Total Environment, 744, 140737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140737
Volk, M., Bosch, D., Nangia, V., & Narasimhan, B. (2016). SWAT: Agricultural water and nonpoint source pollution management at a watershed scale. Agricultural Water Management, 175, 1–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2016.06.013
Wang, B., Yang, Q., & Liu, Z. (2009). Effect of conversion of farm land to forest or grassland on soil erosion intensity changes in Yanhe River Basin, Loess Plateau of China. Frontiers for China, 4(1), 68–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11461-009-0015-5
Wang, J., Peng, J., Zhao, M., Liu, Y., & Chen, Y. (2017). Significant trade-off for the impact of Grain-for-Green Programme on ecosystem services in North-western Yunnan, China. Science of the Total Environment, 574, 57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.026
Wang, Z., Jiao, J., Rayburg, S., Wang, Q., & Su, Y. (2016). Soil erosion resistance of “Grain for Green” vegetation types under extreme rainfall conditions on the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA, 141, 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.02.025
Wei, W., Chen, L., Fu, B., Lü, Y., & Gong, J. (2009). Responses of water erosion to rainfall extremes and vegetation types in a loess semiarid hilly area, NW China. Hydrological Processes, 23(12), 1780–1791. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7294
Wu, C. L., Herrington, S. J., Charry, B., Chu, M. L., & Knouft, J. H. (2021). Assessing the potential of riparian reforestation to facilitate watershed climate adaptation. Journal of Environmental Management, 277, 111431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111431
Wu, L., Li, X., & Ma, X. (2019). Particulate nutrient loss from drylands to grasslands/forestlands in a large-scale highly erodible watershed. Ecological Indicators, 107, 105673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105673
Wu, L., Liu, X., Yang, Z., Yu, Y., & Ma, X. Y. (2022). Effects of single- and multi-site calibration strategies on hydrological model performance and parameter sensitivity of large-scale semi-arid and semi-humid watersheds. Hydrological Processes, 36(6), e14616.
Wu, L., Ma, X., Wang, Y., & Zhou, J. G. (2023). Increasing areas of aquaculture ponds and reservoirs reshape runoff coefficients: Evidence from a subtropical catchment, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 41253–41271.
Wu, L., Qi, T., & Zhang, J. (2017). Spatiotemporal variations of adsorbed nonpoint source nitrogen pollution in a highly erodible Loess Plateau watershed. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 26(3), 1343–1352. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/67974
Wu, L., Yao, W. W., & Ma, X. Y. (2018). Using the comprehensive governance degree to calibrate a piecewise sediment delivery ratio algorithm for dynamic sediment predictions: A case study in an ecological restoration watershed of northwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 564, 888–899.
Xu, C., Jiang, Y., Su, Z., Liu, Y., & Lyu, J. (2022). Assessing the impacts of grain-for-green programme on ecosystem services in Jinghe River basin, China. Ecological Indicators, 137, 108757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.108757
Xu, K., Wang, J., Wang, J., Wang, X., Chi, Y., & Zhang, X. (2020). Environmental function zoning for spatially differentiated environmental policies in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 255, 109485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109485
Xue, Y. Y., Jin, X., Li, H., Zhang, S., Xu, B., & Fan, W. (2015). Investigation on the occurrence and control of apple canker in Gansu Province. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 50(06), 81–87. https://doi.org/10.13432/j.cnki.jgsau.2015.06.015
Yang, L., Pang, S., Wang, X., Du, Y., Huang, J., & Melching, C. S. (2021a). Optimal allocation of best management practices based on receiving water Capa-city constraints. Agricultural Water Management, 258, 107179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107179
Yang, X., Liu, S., Jia, C., Liu, Y., & Yu, C. (2021b). Vulnerability assessment and management planning for the ecological environment in urban wetlands. Journal of Environmental Management, 298, 113540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113540
Yang, X., Warren, R., He, Y., Ye, J., Li, Q., & Wang, G. (2018). Impacts of climate change on TN load and its control in a River Basin with complex pollution sources. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 1155–1163.
Yu, D., Dong, X., Xie, P., Wei, C., Liu, J., Hu, X., Wang, K., Xu, S., Wan, H., & Su, Z. (2021). Prioritization of critical source areas for soil and water conservation by using a one-at-a-time removal approach in the upper Huaihe River basin. Land Degradation & Development, 32(3), 1513–1524. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3814
Zhang, C. Q., Zhang, B., Li, W., Yang, Y. G., & Wang, B. (2011). Control mechanism and effect of forest ecosystem on non-point source pollution and its influencing factors. Resources Science, 2, 236–241.
Zhang, X., Li, P., Li, Z. B., Yu, G. Q., & Li, C. (2018). Effects of precipitation and different distributions of grass strips on runoff and sediment in the loess convex hillslope. CATENA, 162, 130–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.12.002
Zhou, J., Fu, B., Gao, G., Lü, Y., Liu, Y., Lü, N., & Wang, S. (2016). Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid e-nvironment in the Loess Plateau, China. CATENA, 137, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.08.015
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China (52070158, 42277073, 51679206).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Wu, L. et al. Identification of critical source areas and delineation of management subzones of non-point source pollution in Jing River Basin. Environ Dev Sustain (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04206-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04206-9