Abstract
The decline in soil quality and unsustainable productivity of tropical ecosystems has made the investigation of land use induce changes essential for effective management options. The objective of the work was to describe the variations in the soil quality indicators as affected by land-use changes and management within Kyayya, Guinea Savanna Agro-ecological Zone of Nigeria. Soil quality was assessed using the physical and chemical analyses of soil under cultivated and deforested at 0–20 cm and forested land at 0–30 cm depths. The results revealed that the soil is sandy loam with significant differences (p = 0.01) among the particle sizes. Soil organic carbon and organic matter decreased following the conversion from forested land to cultivated land at 42% and 43%, respectively. Soil pH under cultivated area was slightly acidic and also recorded the lowest available phosphorus value (28.0 ppm). Results of the simple correlation coefficients displayed the interaction between the soil variables showed the influence of land-use changes and management patterns. The conversion from Forested to Cultivated land-use management types had a detrimental impact on the studied soil quality indicators. Therefore, there is an urgent need for national policies to prevent the remaining forested areas from being converted into cultivated areas and agroforestry practices as a viable option to ensure food security.

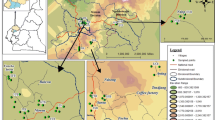
Source: Magaji and Shat (2019)
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author [Obidike-Ugwu, E.O].
References
Abaje, I. B., Ati, O. F., & Ishaya, S. (2009). Nature of potable water supply and demand in Jema’a local government area of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Research Journal of Environmental Earth Science., 1(1), 16–21.
Abaje, I. B., Ishaya, S., & Usman, S. U. (2010). An analysis of rainfall trends in kafanchan, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Research Journal of Environmental and Earth Sciences, 2(2), 89–96.
Abaje, I. B., Sawa, B. A., Iguisi, E. O., & Ibrahim, A. A. (2016). Assessment of rural communities’ adaptive capacity to climate change in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Journal of Environment and Earth Science, 5(20), 14–23.
Abrishamkesh, S., Gorji, M., & Asadi, H. (2011). Long-term effects of land use on soil aggregate stability. International Agrophysics, 25, 103–108.
Adegbite, K. A., Okafor, M. E., Adekiya, A. O., Alori, E. T., & Adebiyi, O. T. V. (2019). Characterization and classification of soils of a toposequence in a derived Savannah Agroecological Zone of Nigeria. The Open Agriculture Journal, 13, 44–50. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874331501913010044
Akinrinde, E. A. & Obigbesan G.O. (2000). Evaluation of fertility status of selected soils for crop production in five ecological areas of Nigeria. In Proceedings of 26th Annual Conference on Soil Science Socitey. Nig Ibadan, Oyo State. pp 279 –288.
Amanuel, W., Yimer, F., & Karltun, E. (2018). Soil organic carbon variation in relation to land use changes: The case of Birr watershed, upper Blue Nile River Basin, Ethiopia. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 42, 16–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41610-018-0076-1
Amezketa, E. (1999). Soil aggregate stability: A review. Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 14(2–3), 83–151.
Assefa, F., Elias, E., Soromessa, T., & Ayele, G. T. (2020). Effect of changes in land-use management practices on soil physicochemical properties in Kabe Watershed, Ethiopia. Air, Soil and Water Research, 13, 1–16.
Atiyong, B.R. & Michael, H.Y (2022). Nature and variation of soil properties under different land management practices in Southern part of Kaduna, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Science World Journal, Vol. 17 no 1 p 31 – 37. www.scienceworldjournal.org
Awdenegest, M., Melku, D., & Fantaw, Y. (2013). Land use effects on soil quality indicators: A case study of Abo-Wonsho Southern Ethiopia. Hindawi Publishing Corporation.
Ayolagha, G. A. (2001). Survey and classification of Yenagoa meander belt soils in the Niger Delta. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference of Soil Science Society of Nigeria 5–9th Nov. 2001 Calabar, Nigeria.
Benton, J. J. (2012). Plant nutrition and fertility manual (2nd ed., p. 27). CRC Press.
Bremmer, J. M., & Mulvaney, C. S. (1996). Nitrogen-total. Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Soil Science Society of America Book Series, 5, 1085–1121.
Chude, V. O., Malgwi, W. B., Amapu, I. Y. & Ano, A. O. (2011). Manual on Soil Fertility Assessment. Federal Fertilizer Department. FAO and National Programme on Food Security, Abuja, Nigeria. 62p.
Delelegn, Y. T., Purahong, W., Blazevic, A., Yitaferu, B., Wubet, T., Göransson, H., & Godbold, D. L. (2017). Changes in land use alter soil quality and aggregate stability in the highlands of Northern Ethiopia. Scientific Report, 7, 13602. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14128-y
Doran, J. W. (2002). Soil health and global sustainability: Translating science into practice. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 88, 119–127.
Doran, J. W., & Zeiss, M. R. (2000). Soil health and sustainability: Managing the biotic component of soil quality. Applied Soil Ecology, 15, 3–11.
Duncan, M.R. (2002). Soil Acidity and P Deficiency: Management Strategies for the Northern Tablelands of NSW, NSW Agriculture, Leaflet No. 9 of Acid Soil Management Series. http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au
El Mazi, M., Hmamouchi, M., Saber, E., Bouchantouf, S., & Houari, A. (2022). Deforestation effects on soil properties and erosion: A case study in the central Rif, Morocco. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science. https://doi.org/10.18393/ejss.1098600
Enwezor, W, O, Ohiri, A. C., Opowaribo, E. E. & Udo, E. J. (1990). A review of soil fertilizer uses in crops in the Southeastern zone of Nigeria (in five volumes). Produced by the Fed. Min. Agric and Nat. Re. Lagos.
Eroarome, M. A. (2005). Country Pasture/Forage Resource Profile Nigeria. Retrieved from http://www.fao.org/ag/agp/agpc/doc/counprof/nigeria/nigeria.htm.
FAO. (2005). Global Forest resources assessment 2005: Progress towards sustainable forest management. FAO.
Gebrekidan, H., & Negassa, W. (2006). Impact of land use and management practices on chemical properties of some soils of Bako area, western Ethiopia. Ethiopian Journal of Natural Resources, 8(2), 177–197.
Gholoubi, A., Emami, H., & Caldwell, T. (2019). Deforestation effects on soil aggregate stability quantified by the high energy moisture characteristic method. Geoderma, 355, 113919.
Girmay, G., Singh, B. R., Mitiku, H., Borresen, T., & Lal, R. (2008). Carbon stocks in Ethiopian soils in relation to land use and soil management. Land Degradation and Development, 19(4), 351–367.
Greenland, D. J., Wild, A. & Adams, D. (1992). Organic matter dynamics in soils of the tropics—From myth to complex reality. In “Myths and Science of Soils of the Tropics” (R. Lal and P. A. Sanchez, Eds.), pp. 17–33. SSSA-ASA, Madison, WI.
Gülser, C., Ekberli, İ, & Gülser, F. (2021). Effects of deforestation on soil properties and organic carbon stock of a hillslope position land in Black Sea Region of Turkey. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science, 10(4), 278–284.
Hajabbasi, M. A., Besalatpoor, A., & Melali, A. R. (2007). Effect of rangeland change to agricultural land on some soil physical and chemical properties in South of Isfahan. Science and Technology of Agriculture and Natural Resources, 42, 525–534.
Hargreaves, P. (2015). Soil texture and pH effects on potassium and phosphorus availability. The potash Development Association: London, UK.
Imadojemu, P. E., Osujieke, D. N., & Obasi, S. N. (2017). Evaluation of Fadama soils along a toposequence proximal to River Donga in Wukari area of Northeast Nigeria. International Journal of Agricultural and Rural Development, 20(2), 3150–3158.
IPCC. (2007). Climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability, Contribution of Working Group II to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, M.L., Parry, O.F., Canziani, J.P., Palutikof, P.J., van der Linden & Hanson C.E., Eds. (p. 976). Cambridge University Press.
Karlen, D. L. (1997). Soil quality: A concept, definition, and framework for evaluation (a guest editorial). Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61, 4–10.
Kharal, S., Khanal, B. R., & Panday, D. (2018). Assessment of soil fertility under different land-use systems in Dhading District of Nepal. Soil Systems, 2(57), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems2040057
Khresat, S., Al-Bakri, J., & Al-Tahnan, R. (2008). Impacts of land use/cover change on soil properties in the Mediterranean region of northwestern Jordan. Land Degradation and Development, 19(4), 397–407.
Kirkby, M. J., Le Bissonais, Y., Coulthard, T. J., Daroussin, J., & McMahon, M. D. (2000). The development of land quality indicator for soil degradation by water erosion. Agricultural Ecosystem Environment, 81, 125–135.
Kroetsch, D., & Wang, C. (2007). Particle size distribution. In M. R. Carter & E. G. Gregorich (Eds.), Soil Sampling and methods of analysis (2nd ed., pp. 713–726). CRC Press.
Larson, W. E. & Pierce, F. J. (1991). Conservation and enhancement of soil quality. In: Dumanski, J. (Ed.), Evaluation for Sustainable Land Management in the Developing World. In Proceedings of the International Workshop. Chiang Rai, Thailand, 15–21. Technical papers, vol. 2. Int, Board for Soil Res. and management Bangkok, Thailand, pp: 175–203.
Lemenih, M. (2004). Effects of land use changes on soil quality and native flora degradation and restoration in the highlands of Ethiopia, Doctoral Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Uppsala, Sweden
Lindsay, W. L. (1979). Chemical equilibria in soils. Wiley.
Magaji, J. Y. & Shat, A. T. (2019). Indigenous Knowledge of Integrated Soil Fertility Management in Kafanchan and its Environs, Jema’a Local Government, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Journal of Environment Design & Constructions Management, 19 (4): 1–16. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344430304
Majaliwa, J. G., Twongyirwe, R., Nyenje, R., Oluka, M., Ongom, B., Sirike, J., Mfitumukiza, D., Azanga, E., Natumanya, R., Mwerera, R., & Barasa, B. (2010). The effect of land cover change on soil properties around Kibale national park in south western Uganda. Applied and Environmental Soil Science, 10, 1–7.
McCauley, A., Jones, C. & Jacobsen, J. (2009). Nutrient Management. Module No. 8, Montana State University Extension Publications. http://www.msuextension.org
Mclean, E. O. (1982). Soil pH and lime requirement, In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeny, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Agronomy Monograph No. 9. Second ed. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp. 199–234.
Mojiri, A., Emami, N., & Ghafari, N. (2011). Effects of land use changes on soil quality attributes (A review). American-Eurasian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 5(1), 42–45.
Nelson, D. W. & Sommers, L. E. (1982). Total organic carbon, organic matter. In: Pages, A.L., Miller R.H and Kenney, D.R. (Eds). Methods of Soil Analysis: part 2 Ameri. Soc. Agron., Madison, Wis., pp. 539–579.
Obidike-Ugwu, E. O., Nwafor, E. O., Okunade, A. A., Maful, A. M., & Eze, C. J. (2021). Landuse management impact assessment on soil fertility status of Bokkos Local Government Area of Plateau State, Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Soil Science, 31(2), 102–109.
Olsen, S. R. (1982). Phosphorus, In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeny, D.R. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part-2. Agronomy monograph No. 9. 2nd Edn. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp. 403–430.
Osujieke, D. N., Imadojemu, P. E., Angyu, M. D., & Ibeh, K. (2020). Characterization and classification of soils of Wukari Urban Northeast Nigeria. International Journal of Forest, Soil, and Erosion, 10(4), 47–56.
Pacheco, F. A. L., Sanches Fernandes, L. F., Valle Junior, R. F., Valera, C. A., & Pissarra, T. C. T. (2018). Land degradation: Multiple environmental consequences and routes to neutrality. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 5, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2018.07.002
R Core Team (2022). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. URL https://www.R-project.org/
Richard G., Boizard H., Roger-Estrade J., Boiffin J., & Guérif J. (1999). Field study of soil compaction due to traffic: pore space and morphological analysis. Soil and Tillage Research, 51, 151–160.
Richardson, A. E., Barea, J. M., McNeill, A. M., & Prigent-Combaret, C. (2009). Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant and Soil, 321, 305–339.
Tchienkoua, M., & Zech, W. (2004). Organic carbon and plant nutrient dynamics under three land uses in the highlands of West Cameroon. Agricultural Ecosystem Environment, 104, 673–679.
Thomason, W. (2002). Understanding Phosphorus Behavior in Soils. Noble Research Institute: Ardmore, OK, USA
World Bank (2001). A Revised Forestry Strategy for the World Bank Group.
Yakubu, M., Abdullahi, I., Ibrahim, B. & Noma, S. S. (2008). Characterization of upland and floodplain soils for management implications in Dundaye District, Sokoto, Nigeria. In Proceedings of the 32nd Annual Conference of the Soil Science Society of Nigeria, Federal Univ. of Tech., Yola, Nigeria: 44–63.
Yao, M. K., Angui, P. K. T., Konaté, S., Tondoh, J. E., Tano, Y., Abbadie, L., & Benest, D. (2010). Effects of land use types on soil organic carbon and nitrogen dynamics in mid-west Côte d’Ivoire. European Journal of Scientific Research, 40(2), 211–222.
Yimer, F., Ledin, S., & Abdelkadir, A. (2007). Changes in soil organic carbon and total nitrogen contents in three adjacent landuse types in the Bale Mountains, Southeastern highlands of Ethiopia. Forest Ecology and Management, 242(2–3), 337–342.
Young, A. (1976). Tropical soils and soil survey (p. 46). Cambridge University Press.
Yousefifard, M., Khademi, H., & Jalalian, A. (2007). Decline in soil quality as a result of land use change in Cheshmeh Ali region (IRAN). Agricultural Science and Natural Resource, 14(1), 425–436.
Yuksek, T., Ceyhun, G., Filiz, Y., & Esin, E. Y. (2009). The effects of land use changes on soil properties: The conversion of Alder coppice to tea plantations in the humid Northern Black Sea region. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 4(7), 665674.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization to assist with the preparation of submitted manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by EOOU, BB, OEN and JOA. The first draft of the manuscript was written by EOOU, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Obidike-Ugwu, E.O., Bege, B., Ariwaodo, J.O. et al. Land-use changes and management impact on soil quality indicators in tropical ecosystem. Environ Dev Sustain (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04026-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-04026-x