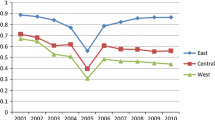
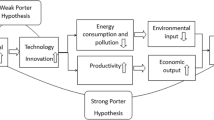
Abstract
Production assumptions play dominant roles in the modeling of data envelopment analysis (DEA). Few studies systematically investigate how the production assumptions in DEA influence the environmental efficiency and technology inequality measurements. This study aims to fill this research gap. The representative categories of production assumptions are considered, that is, disposability and returns to scale (RTS). Based on the given disposability and RTS, the corresponding DEA models are proposed. The proposed models are then applied to measure the environmental efficiency and technology inequality of Chinese cities. Fixed effects panel models are further adopted to explore the effect mechanism of production assumptions. The main findings are summarized as follows: (1) disposability and RTS have significant influences on the environmental efficiency of Chinese cities. Managerial disposability considers innovation efficiency and variable RTS captures scale efficiency; (2) disposability affects the technology inequality measurement, while the RTS has no significant impact. Managerial disposability is more sensitive to technological progress compared with natural and weak disposability; (3) the average efficiency is less than 0.803 and the efficiency Theil index is less than 0.04, indicating the environmental efficiency and technology inequality of Chinese cities are at low levels; (4) To improve efficiency, Chinese cities should decrease labor and increase capital. To mitigate technology inequality, the cities should decrease energy under managerial disposability, and decrease capital and labor under weak disposability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, Y., Deng, X., Jiang, S., Zhang, Q., & Wang, Z. (2018). Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 195, 1487–1496.
Banker, R. D., Cooper, W. W., Seiford, L. M., Thrall, R. M., & Zhu, J. (2004). Returns to scale in different DEA models. European Journal of Operational Research, 154(2), 345–362.
Basso, A., & Funari, S. (2014). Constant and variable returns to scale DEA models for socially responsible investment funds. European Journal of Operational Research, 235(3), 775–783.
Bian, J., Ren, H., & Liu, P. (2020). Evaluation of urban ecological well-being performance in China: A case study of 30 provincial capital cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 254, 120109.
Cai, B., Guo, H., Ma, Z., Wang, Z., Dhakal, S., & Cao, L. (2019). Benchmarking carbon emissions efficiency in Chinese cities: A comparative study based on high-resolution gridded data. Applied Energy., 242, 994–1009.
Charnes, A., Cooper, W. W., & Rhodes, E. (1978). Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. European Journal of Operational Research, 2, 429–444.
Chen, W., Ning, S., Chen, W., Liu, E., Wang, Y., & Zhao, M. (2020). Spatial–temporal characteristics of industrial land green efficiency in China: Evidence from prefecture-level cities. Ecological Indicators., 113, 106256.
Dhakal, S. (2009). Urban energy use and carbon emissions from cities in China and policy implications. Energy Policy, 37, 4208–4219.
Färe, R., Grosskopf, S., Lovel, C. A. K., & Pasurka, C. (1989). Multilateral productivity comparison when some outputs are undesirable: A nonparametric approach. Review of Economics and Statistics, 71, 90–98.
Feng, Y., Dong, X., Zhao, X., & Zhu, A. (2020). Evaluation of urban green development transformation process for Chinese cities during 2005–2016. Journal of Cleaner Production, 266, 121707.
Hart, W. E., Laird, C. D., Watson, J.-P., Woodruff, D. L., Hackebeil, G. A., Nicholson, B. L., & Siirola, J. D. (2017). Pyomo–optimization modeling in python (2nd ed, vol. 67). Springer. https://www.pyomo.org/
He, Z., Xiao, L., Guo, Q., Liu, Y., Mao, Q., & Kareiva, P. (2020). Evidence of causality between economic growth and vegetation dynamics and implications for sustainability policy in Chinese cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 251, 119550.
Hu, M., Zhang, J., & Chao, C. (2019). Regional financial efficiency and its non-linear effects on economic growth in China. International Review of Economics & Finance, 59, 193–206.
Huang, Y., Li, L., & Yu, Y. (2018). Does urban cluster promote the increase of urban eco-efficiency? Evidence from Chinese cities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 197, 957–971.
Jiang, H., Hua, M., Zhang, J., Cheng, P., Ye, Z., Huang, M., & Jin, Q. (2020). Sustainability efficiency assessment of wastewater treatment plants in China: A data envelopment analysis based on cluster benchmarking. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, 118729.
Kao, C., & Hwang, S. (2021). Measuring the effects of undesirable outputs on the efficiency of production units. European Journal of Operational Research., 292(3), 996–1003.
Kuosmanen, T. (2005). Weak disposability in nonparametric production analysis with undesirable outputs. American Journal of Agricultural Economics, 87(4), 1077–1082.
Li, B., Mohiuddin, M., & Liu, Q. (2019a). Determinants and differences of township. Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(9), 1601.
Li, H., He, H., Shan, J., & Cai, J. (2019b). Innovation efficiency of semiconductor industry in China: A new framework based on generalized three-stage DEA analysis. Socio-Economic Planning Sciences, 66, 136–148.
Li, K., & Lin, B. (2018). How to promote energy efficiency through technological progress in China? Energy, 143, 812–821.
Li, Q., Wei, J., Jiang, F., Zhou, G., Jiang, R., Chen, M., Zhang, X., & Hu, W. (2020). Equity and efficiency of health care resource allocation in Jiangsu Province, China. International Journal for Equity in Health, 19(1), 211.
Li, W., & Yi, P. (2020). Assessment of city sustainability-coupling coordinated development among economy, society and environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 256, 120453.
Li, Z., Deng, X., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Evaluation and convergence analysis of socio-economic vulnerability to natural hazards of Belt and Road Initiative countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 282, 125406.
Li, Z., Ouyang, X., Du, K., & Zhao, Y. (2017). Does government transparency contribute to improved eco-efficiency performance? An empirical study of 262 cities in China. Energy Policy, 110, 79–89.
Lin, B., & Fei, R. (2015). Regional differences of CO2 emissions performance in China’s agricultural sector: A Malmquist index approach. European Journal of Agronomy, 70, 3–40.
Lin, B., & Zhu, J. (2019). Impact of energy saving and emission reduction policy on urban sustainable development: Empirical evidence from China. Applied Energy, 239, 12–22.
Liu, Q., Li, B., & Mohiuddin, M. (2018). Prediction and decomposition of efficiency differences in Chinese provincial community health services. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15, 2265.
Liu, T., Li, J., Chen, J., & Song, Y. (2020). Regional Differences and Influencing Factors of Allocation Efficiency of Rural Public Health Resources in China. Healthcare., 8(3), 270.
Liu, X., Li, A., Qu, J., & Xie, C. (2022b). Measuring environmental efficiency and technology inequality of China’s power sector: Methodological comparisons among data envelopment analysis, free disposable hull, and super free disposable hull models. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(32), 48607–48619.
Liu, X., Liu, Y., & Wang, B. (2022a). Evaluating the sustainability of Chinese cities: Indicators based on a new data envelopment analysis model. Ecological Indicators, 137, 108779.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. (2009–2017). China city statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press.
Ren, Y., Fang, C., & Li, G. (2020). Spatiotemporal characteristics and influential factors of eco-efficiency in Chinese prefecture-level cities: A spatial panel econometric analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production., 260, 120787.
Shen, Y., Sun, S., Yue, S., & Sun, X. (2020). Ecological development efficiency index of tropics and subtropics in China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(2), 14160–14174.
Sueyoshi, T., & Goto, M. (2012). Weak and strong disposability vs. natural and managerial disposability in DEA environmental assessment: Comparison between Japanese electric power industry and manufacturing industries. Energy Economics, 34(3), 686–699.
Sueyoshi, T., & Goto, M. (2018). Environmental assessment on energy and sustainability by data envelopment analysis. Wiley.
Sueyoshi, T., Liu, X., & Li, A. (2020). Evaluating the performance of Chinese fossil fuel power plants by data environment analysis: An application of three intermediate approaches in a time horizon. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277, 121992.
Sun, C., Liu, X., & Li, A. (2018a). Measuring unified efficiency of Chinese fossil fuel power plants: Intermediate approach combined with group heterogeneity and window analysis. Energy Policy, 123, 8–18.
Sun, J., Wang, Z., & Li, G. (2018b). Measuring emission-reduction and energy-conservation efficiency of Chinese cities considering management and technology heterogeneity. Journal of Cleaner Production, 175, 561–571.
Sun, X., Liu, X., Li, F., Tao, Y., & Song, Y. (2017). Comprehensive evaluation of different scale cities’ sustainable development for economy, society, and ecological infrastructure in China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, S329–S337.
Tan, Y., Jiao, L., Shuai, C., & Shen, L. (2018). A system dynamics model for simulating urban sustainability performance: A China case study. Journal of Cleaner Production., 199, 1107–1115.
Tan, Y., Xu, H., Jiao, L., Ochoa, J. J., & Shen, L. (2017). A study of best practices in promoting sustainable urbanization in China. Journal of Environmental Management, 193, 8–18.
Tang, M., Li, Z., Hu, F., & Wu, B. (2020). How does land urbanization promote urban eco-efficiency? The mediating effect of industrial structure advancement. Journal of Cleaner Production, 272, 122798.
Theil, H. (1967). Economics and information theory. North-Holland.
Wang, J., Lv, K., Bian, Y., & Cheng, Y. (2017). Energy efficiency and marginal carbon dioxide emission abatement cost in urban China. Energy Policy, 105, 246–255.
Wang, R., & Feng, Y. (2020). Research on China’s agricultural carbon emission efficiency evaluation and regional differentiation based on DEA and Theil models. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 6, 66.
Wu, J., Kang, Z., & Zhang, N. (2017). Carbon emission reduction potentials under different polices in Chinese cities: A scenario-based analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production., 161, 1226–1236.
Xiao, H., Shan, Y., Zhang, N., Zhou, Y., Wang, D., & Duan, Z. (2019). Comparisons of CO2 emission performance between secondary and service industries in Yangtze River Delta cities. Journal of Environmental Management, 252, 109667.
Yan, Y., Wang, C., Quan, Y., Wu, G., & Zhao, J. (2018). Urban sustainable development efficiency towards the balance between nature and human well-being: Connotation, measurement, and assessment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 178, 67–75.
Yang, J., & Lin, Y. (2020). Driving factors of total-factor substitution efficiency of chemical fertilizer input and related environmental regulation policy: A case study of Zhejiang Province. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114541.
Zeng, L., Li, X., & Ruiz-Menjivar, J. (2020). The effect of crop diversity on agricultural eco-efficiency in China: A blessing or a curse? Journal of Cleaner Production, 276, 124243.
Zhai, D., Shang, J., Yang, F., & Ang, S. (2019). Measuring energy supply chains’ efficiency with emission trading: A two-stage frontier-shift data envelopment analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 210, 1462–1474.
Zhang, B., Lu, D., He, Y., & Chiu, Y. (2018a). The efficiencies of resource-saving and environment: A case study based on Chinese cities. Energy, 150, 493–507.
Zhang, J., Zeng, W., Wang, J., Yang, F., & Jiang, H. (2017). Regional low-carbon economy efficiency in China: Analysis based on the Super-SBM model with CO2 emissions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 163, 202–211.
Zhang, L., Xu, Y., Yeh, C., Liu, Y., & Zhou, D. (2016). City sustainability evaluation using multi-criteria decision making with objective weights of interdependent criteria. Journal of Cleaner Production, 131, 491–499.
Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., Jiang, T., & Wang, J. (2018b). Equity and efficiency of primary health care resource allocation in mainland China. International Journal for Equity Health, 17, 140.
Zhou, P., Ang, B. W., & Poh, K. L. (2008). A survey of data envelopment analysis in energy and environmental studies. European Journal of Operational Research, 189(1), 1–18.
Zhou, X., Song, M., & Cui, L. (2020). Driving force for China’s economic development under Industry 4.0 and circular economy: Technological innovation or structural change? Journal of Cleaner Production, 271, 122680.
Zhou, X., Zhang, J., & Li, J. (2013). Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy, 57, 43–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the anonymous referees for their valuable suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Qu, J. & Wang, B. Understanding the factors affecting environmental efficiency and technology inequality of Chinese cities: insights from production assumptions in data envelopment analysis. Environ Dev Sustain 25, 14661–14692 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02683-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02683-y