Abstract
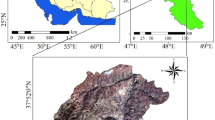
In order to facilitate the decision making in spatial applications, several methods are available to aggregate the performance of decision-makers. The multitude of these methods makes it difficult to choose one method over another. Two main types of methods are used, the outranking methods which are based on bottom-up approach and the hierarchical analysis methods which are based on top-down approach. These methods can be adapted to this kind of applications and can be integrated into GIS which is an essential tool in spatial management and decision making. Methods developed according to the first approach are different from those developed in accordance with the second one. This study aims to present a comparison between two multicriteria decision-making methods ELECTRE (Elimination Et Choix Traduisant la REalité) Tri and AHP (Analytic Hierarchy Process) to assess land suitability for agriculture. Twelve criteria [water reserve easily utilizable, drainage, permeability, potential of hydrogen (pH), electrical conductivity, active limestone, cation exchange capacity, soil texture, soil useful depth, slope, availability of labor, proximity (roads)] grouped in five factors (agronomic, planning, land enhancement and improvement, soil conservation and environment protection, and socioeconomic conditions) were used in this study. An application has been carried out on the area of Mleta in Algeria. Two land suitability maps for durum wheat have been produced by the two procedures (optimistic and pessimistic) available in ELECTRE Tri, and another map has been obtained by AHP. After the comparison between the obtained results, it was apparent that ELECTRE Tri is more appropriate for the land suitability assessment for agriculture despite its complexity given the large number of required parameters. The subjective parameters available in ELECTRE Tri make it possible to take into account imprecise data. Another advantage of this method lies in the way of the decision-makers' preferences aggregation and the assignment of the land units to classes of predefined categories.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelfattah, M. A. (2013). Integrated suitability assessment: A way forward for land use planning and sustainable development in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Arid Land Research and Management, 27(1), 41–64.
Abdelkawy, O. R., Ismail, H. A., Rod, J. K., & Suliman, A. S. (2010). A developed GIS-based land evaluation model for agricultural land suitability assessments in arid and semi arid regions. Research Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 6(5), 589–599.
Akinci, H., Özalp, A. Y., & Turgut, B. (2013). Agricultural land use suitability analysis using GIS and AHP technique. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 97, 71–82.
Akpoti, K., Kabo-bah, A. T., & Zwart, S. J. (2019). Agricultural land suitability analysis: State-of-the-art and outlooks for integration of climate change analysis. Agricultural Systems, 173(C), 172–208.
Almeida-Dias, J., Figueira, J. R., & Roy, B. (2010). ELECTRE Tri-C: A multiple criteria sorting method based on characteristic reference actions. European Journal of Operational Research, 204(3), 565–580.
Chakhar, S., & Mousseau, V. (2008). Multicriteria spatial decision support systems. In S. Shekar & H. Xiong (Eds.), Encyclopedia of GIS (Vol. 6, pp. 753–758).
Delli, G., Martucci, A., & Sarfatti, P. (1996). Land suitability evaluation for winter wheat in Tiaret region (Algeria). In R. Escadafal, M. A. Mulders, & L. Thiombiano (Eds.) Monitoring soils in the environment with remote sensing and GIS(pp. 531–542). Paris: ORSTOM.
FAO. (1989). Evaluation des Terres pour l'Agriculture Irriguée: Directives. Rome: Bulletin Pédologique de la FAO.
FAO. (2007). Land evaluation. Towards a revised framework. Land and water discussion paper, n° 6. FAO, Rome.
Girish, P. B., & Tushar, D. (2018). Multi criteria decision making (MCDM) methods and its applications. International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET), 6(V), 899–915.
INSID (INstitut Supérieur de l’Irrigation et du Drainage). (2005). Le classement des terres agricoles. Disponible sur: www.insid-algerie.com.
Jafari, S., & Zaredar, N. (2010). Land suitability analysis using multi attribute decision making approach. International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, 1(5), 441–445.
Jayasinghe, P. K. S. C., & Mashida, T. (2010). Web based GIS online consulting system with crop-land suitability identification. Agricultural Information Research, 17(1), 13–19.
Joerin, F., Thériault, M., & Musy, A. (2001). Using GIS and outranking multicriteria analysis for landuse suitability assessment. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 15(2), 153–174.
Khoi, D. D., & Murayama, Y. (2010). Delineation of suitable cropland areas using a GIS based multi-criteria evaluation approach in the Tam Dao National Park Region, Vietnam. Sustainability, 2(7), 2024–2043.
Malczewski, J. (1999). GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Hoboken: Wiley.
Malczewski, J. (2004). GIS-based land-use suitability analysis: A critical overview. Journal of Progress in Planning, 62, 3–65.
Mendas, A., & Delali, A. (2012). Integration of multicriteria decision analysis in GIS to develop land suitability for agriculture: Application to durum wheat cultivation in the region of Mleta in Algeria. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 83(2012), 117–126.
Mendas, A., Errih, M., Benahmed Daho, S. A., Hamadouche, M. A., & Saidi, A. (2010). Water impoundment location—approach using GIS and multicriteria decision making. Revue internationale de Géomatique, 20(1), 87–103.
Mendas, A., Hamadouche, M. A., Nechniche, H., & Djilali, A. (2007). Elaboration d’un système d’aide à la décision spatiale—application à la dangerosité de l’infrastructure routière. Journal of Decision Systems, 16(3), 369–391.
Mousseau, V., Slowinski, R., & Zielniewicz, P. (1999). ELECTRE Tri 2.0a, Methodological guide and user's manual. Document n° 111 of Lamsade.
Prakash, T. N. (2003). Land suitability analysis for agricultural crops: A fuzzy multicriteria decision making approach. Thesis, ITC, Netherlands.
Reshmidevi, T. V., Eldho, T. I., & Jana, R. (2009). A GIS-integrated fuzzy rule-based inference system for land suitability evaluation in agricultural watersheds. Agricultural Systems, 101(1–2), 101–109.
Rovai, M., & Andreoli, M. (2018). Integrating AHP and GIS techniques for rural landscape and agricultural activities planning.In J. Berbel, T. Bournaris, B. Manos, N. Matsatsinis, & D. Viaggi (Eds.), Multicriteria analysis in agriculture. current trends and recent applications (pp 69–98).
Roy, B., & Vincke, P. (1984). Relational systems of preferences with one or more pseudo-criteria: Some news concepts and results. Management Science, 30(11), 1323–1334.
Saaty, T. L. (1977). A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 15(3), 234–281.
Saaty, T. L. (1996). The analytic network process. Pittsburgh: RWS Publications.
Saaty, T. L. (2002). Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Scientia Iranica, 9(3), 215–229.
Saaty, T. L. (2008). Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. International Journal of Services Sciences, 1(1), 83–98.
Saaty, T. L., & Tran, L. T. (2007). On the invalidity of fuzzifying numerical judgments in the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 46(7), 962–975.
Saaty, T. L., & Vargas, L. G. (1991). Prediction, projection and forecasting (p. 251). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
SCET-Tunisia / ENHYD-Algeria. (2007). Hydro-agricultural improvements study of Mleta - Oran,Algeria.
Schärlig, A. (1996). Pratiquer ELECTRE et Promethee: un complément à décider sur plusieurs critères. Lausanne: Presses Polytechniques et Universitaires Romandes.
Shahram, A. (2010). Land suitability analysis for wheat using multicriteria evaluation and GIS method. Research Journal of Biological Sciences, 5(9), 601–605.
Shepande, C. (2002). Soils and land use with particular attention to land evaluation for selected land use types in the Lake Naivasha Basin, Kenya. MSc in Soil Information for Sustainable Land Management. Netherland: ITC, 100p.
Tovar-Perilla, N. J., Bermeo-Andrade, H. P., Torres-Delgado, J. F., & Gómez, M. I. (2018). Methodology to support decision-making in prioritization improvement plans aimed at agricultural sector: Case study. DYNA, 85(204), 352–359.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendas, A., Mebrek, A. & Mekranfar, Z. Comparison between two multicriteria methods for assessing land suitability for agriculture: application in the area of Mleta in western part of Algeria. Environ Dev Sustain 23, 9076–9089 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01012-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-020-01012-5