Abstract
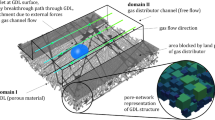
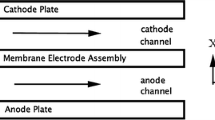
In this paper, we extend a recent one-dimensional isothermal steady-state generalized Darcy model for two-phase flow in the porous cathode gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell, so as to include the effect of heat transfer. As for the isothermal case, we arrive at either a fixed- or free-boundary problem, depending on the main problem parameters: inlet temperature (\(T^\mathrm{in}\)), inlet water saturation (\(s^\mathrm{in}\)), inlet relative humidity (RH), porous medium hydrophobicity and cathode overpotential (\(\eta \)). The inclusion of heat transfer is found to limit the range of values of \(\eta ,T^\mathrm{in}\) and RH over which two-phase flow can occur, as compared to that predicted by the isothermal model. The ensuing non-isothermal two-phase flow model equations are then computed numerically, with particular care being required for the treatment of an integrably singular inter-phase mass transfer term.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noponen M, Birgersson E, Ihonen J, Vynnycky M, Lundblad A, Lindbergh G (2004) A two-phase non-isothermal PEFC model: theory and validation. Fuel Cells 4:365–377
Yuan J, Sundén B (2004) Two-phase flow analysis in a cathode duct of PEFCs. Electrochimica Acta 50:677–683
Yuan J, Sundén B (2004) Three-dimensional analysis of two-phase flow and its effects on the cell performance of PEMFC. Numer Heat Transf 46:669–694
Birgersson E, Noponen M, Vynnycky M (2005) Analysis of a two-phase non-isothermal model for a PEFC. J Electrochem Soc 152:A1021–A1034
Senn SM, Poulikakos D (2005) Multiphase transport phenomena in the diffusion zone of a PEM fuel cell. J Heat Transf 127:1245–1259
Acosta M, Merten C, Eigenberger G, Class H, Helmig R, Thoben B, Müller-Steinhagen H (2006) Modelling non-isothermal two-phase multicomponent flow in the cathode of PEM fuel cells. J Power Sources 159:1123–1141
Song D, Wang Q, Liu Z-S, Huang C (2006) Transient analysis for the cathode gas diffusion layer of PEM fuel cells. J Power Sources 159:928–942
Wang Y, Wang C-Y (2006) A non-isothermal, two-phase model for polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 153:A1193–A1200
Meng H (2007) A two-phase non-isothermal mixed-domain PEM fuel cell model and its application to two-dimensional simulations. J Power Sources 168:218–228
Sadiq Al-Baghdadi MAR, Shahad Al-Janabi HAK (2007) Modeling optimizes PEM fuel cell performance using three-dimensional multi-phase computational fluid dynamics model. Energy Conv Manag 48:3102–3119
Gurau V, Mann JA (2009) A critical overview of computational fluid dynamics multiphase models for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. SIAM J Appl Math 70:410–454
Afshari E, Jazayeri SA (2010) Effects of the cell thermal behavior and water phase change on a proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance. Energy Conv Manag 51:655–662
Min C-H (2010) A novel three-dimensional, two-phase and non-isothermal numerical model for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J Power Sources 195:1880–1887
Wu H, Berg P, Li X (2010) Steady and unsteady 3D non-isothermal modeling of PEM fuel cells with the effect of non-equilibrium phase transfer. Appl Energy 87:2778–2784
Caulk DA, Baker DR (2011) Modeling two-phase water transport in hydrophobic diffusion media for PEM fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 158:B384–B393
Ly H, Birgersson E, Vynnycky M (2011) Computationally efficient multi-phase models for a proton exchange membrane fuel cell: asymptotic reduction and thermal decoupling. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:14573–14589
Yang X-G, Ye Q, Cheng P (2011) Matching of water and temperature fields in proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform distributions. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36:12524–12537
Cindrella L, Kannan AM, Lin JF, Saminathan K, Ho Y, Lin CW, Wertz J (2009) Gas diffusion layer for proton exchange membrane fuel cells—a review. J Power Sources 194:146–160
Arvay A, Yli-Rantala E, Liu C-H, Peng XH, Koski P, Cindrella L, Kauranen P, Wilde PM, Kannan AM (2012) Characterization techniques for gas diffusion layers for proton exchange membrane fuel cells—a review. J Power Sources 213:317–337
Whitaker S (1977) Simultaneous heat, mass, and momentum transfer in porous media: a theory of drying. Adv Heat Transf 13:119–203
Udell KS (1983) Heat transfer in porous media heated from above with evaporation, condensation and capillary effects. J Heat Transf 105:485–492
Udell KS (1985) Heat transfer in porous media considering phase change and capillarity—the heat pipe effect. Int J Heat Mass Transf 28:485–495
Torrance KE (1986) Phase-change heat transfer in porous media. Heat Transf 1:181–188
Baggio P, Bonacina C, Schrefler BA (1997) Some considerations on modeling heat and mass transfer in porous media. Trans Porous Media 28:233–251
Bridge L, Bradean R, Ward MJ, Wetton BR (2003) The analysis of a two-phase zone with condensation in a porous medium. J Eng Maths 45:247–268
Bridge LJ, Wetton BR (2007) A mixture formulation for numerical capturing of a two-phase/vapour interface in a porous medium. J Comput Phys 225:2043–2068
Niessner J, Hassanizadeh SM (2009) Non-equilibrium interphase heat and mass transfer during two-phase flow in porous media—theoretical considerations and modeling. Adv Water Res 32:1756–1766
Wei K, Wang JH, Mao M (2012) Model discussion of transpiration cooling with boiling. Trans Porous Media 94:303–318
Vynnycky M, Gordon A (2013) On the hydrophobicity and hydrophilicity of the cathode gas diffusion layer in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Proc R Soc A 469:20120695
Pasaogullari U, Wang C-Y (2004) Liquid water transport in gas diffusion layer of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 151:A399–A406
Wang Y, Chen KS (2011) Effect of spatially-varying GDL properties and land compression on water distribution in PEM fuel fells. J Electrochem Soc 158:B1292–B1299
Wang Y, Chen KS (2010) Through-plane water distribution in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell: comparison of numerical prediction with neutron radiography data. J Electrochem Soc 157:B1878–B1886
Jordan LR, Shukla AK, Behrsing T, Avery NR, Muddle BC, Forsyth M (2000) Diffusion layer parameters influencing optimal fuel cell performance. J Power Sources 86:250–254
Park GG, Sohn YJ, Yang TH, Yoon YG, Lee WY, Kim CS (2004) Effect of PTFE contents in the gas diffusion media on the performance of PEMFC. J Power Sources 131:182–187
Nakajima H, Konomi T, Kitahara T (2007) Direct water balance analysis on a polymer electrolyte fuel cell (PEFC): Effects of hydrophobic treatment and micro-porous layer addition to the gas diffusion layer of a PEFC on its performance during a simulated start-up operation. J Power Sources 171:457–463
Park S, Lee JW, Popov BN (2008) Effect of PTFE content in microporous layer on water management in PEM fuel cells. J Power Sources 177:457–463
Vynnycky M (2007) On the modelling of two-phase flow in the gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Appl Math Comput 189:1560–1575
Berning T, Djilali N (2003) A 3D, multiphase, multicomponent model of the cathode and anode of a PEM fuel cell. J Electrochem Soc 150:A1589–A1598
Gurau V, Zawodzinski TA, Mann JA (2008) Two-phase transport in PEM fuel cell cathodes. J Fuel Cell Sci Tech 5:021009
Mazumder S, Cole JV (2003) Rigorous 3-D mathematical modeling of PEM fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 150:A1510–1517
Bruggeman DAG (1935) Berechnung verschiedener physikalischer konstanten von heterogenen substanzen. Ann Physik (Leipzig) 24:636–679
Nam JH, Kaviany M (2003) Effective diffusivity and water-saturation distribution in single- and two-layer PEMFC diffusion medium. Int J Heat Mass Trans 46:4595–4611
Hirschfelder JO, Curtiss CF, Bird RB (1954) Theory of gases and liquids. Wiley, New York
Bird RB, Stewart WE, Lightfoot EN (2002) Transport phenomena, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Gawin D, Majorana CE, Schrefler BA (1999) Numerical analysis of hygro-thermal behaviour and damage of concrete at high temperature. Mech Cohesive-Friction Mater 4:37–74
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. American Elsevier, New York
Vargaftik BN, Volkov BN, Voljak LD (1983) International tables of the surface tension of water. J Phys Chem Ref Data 12(3):817–820
Natarajan D, van Nguyen T (2003) Three-dimensional effects of liquid water flooding in the cathode of a PEM fuel cell. J Power Sources 115:66–80
Wang Y, Chen KS (2011) Elucidating two-phase transport in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell, part 1: characterizing flow regimes with a dimensionless group. Chem Eng Sci 66:3557–3567
He W, Yi JS, Nguyen TV (2000) Two-phase flow model of the cathode of PEM fuel cells using interdigitated flow fields. AIChE J 10:2053–2064
Natarajan D, Nguyen TV (2001) A two-dimensional, two-phase, multicomponent, transient model for the cathode of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell using conventional gas distributors. J Electrochem Soc 148:A1324–A1335
Wang Y, Wang C-Y (2007) Two-phase transients of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 154:B636–B643
Jang F, Wang C-Y (2014) Numerical modeling of liquid water motion in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39:942–950
Promislow K, Chang P, Haas H, Wetton B (2008) Two-phase unit cell model for slow transients in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J Electrochem Soc 155:A494–A504
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the Mathematics Applications Consortium for Science and Industry (www.macsi.ul.ie), funded by the Science Foundation Ireland (SFI) Mathematics Initiative grant 06/MI/005 and SFI grant 12/IA/1683. The first author also acknowledges the award of a visiting researcher grant within the Government of Brazil’s “ Science without Borders” programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vynnycky, M., Gordon, A.D. Non-isothermal hydrophobicity-dependent two-phase flow in the porous cathode gas diffusion layer of a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J Eng Math 92, 123–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-014-9748-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10665-014-9748-8