Abstract
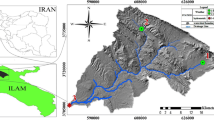
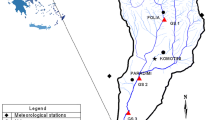
The typology and classification of rivers are highly relevant concepts in the field of limnology and freshwater ecology. Water body typology systematically categorizes water bodies based on their natural attributes, while water body classification groups them based on specific criteria or purposes for management, regulatory, or administrative reasons. Both concepts play important roles in understanding and managing water resources effectively. This scientific article focuses on the ZAT River in Morocco as a model for studying low-flow and intermittent rivers. The objective is to develop an accurate model for the typology and classification of small, low-flow rivers into homogeneous classes based on natural and anthropogenic factors. The study also investigates the impact of human activities on altering the uniformity and reference nature of the water body. The typology of water bodies is carried out according to the European methodology specified in The European Commission’s Water Framework Directive (WFD) in 2000. The classification of water bodies is conducted by assessing their chemical and biological quality using the weighted index (WI), the Iberian Biological Monitoring Working Group (IBMWP) index, and multivariate statistical methods such as principal component analysis (PCA) for confirming water quality assessment. The results indicate the possibility of dividing the basin into four water bodies. Water bodies show homogeneity in terms of chemical quality when human influence is minimal or during periods of high river flow. However, increased human influence and decreased river flows lead to heterogeneity in chemical quality, indicating an unstable state. This study is the first of its kind in arid and semi-arid intermittent rivers, where such an approach could be suggested to determine their typology and classification.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data could be shared upon request.
References
Abessolo, J.-R.Z., Khebiza, M. Y., & Messouli, M. (2021). Réponse des macroinvertébrés benthiques (éphéméroptères, plécoptères, trichoptères) aux pressions anthropiques dans un contexte de changement climatique sur le bassin versant de l’Ourika (Haut-Atlas du Maroc). Hydroécologie Appliquée, 21, 115–155. https://doi.org/10.1051/hydro/2021001
Alvarez Troncoso, R., Gutiérrez, D., Villar, I., Ehlers, S. E., Soto, B., Mato, S., & Garrido, J. (2022). Microplastics in Water, Sediments and Macroinvertebrates in a Small River of Nw Spain. Social Science Research Network, 21, 4079147. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4079147
Arias-Real, R., Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C., Menéndez, M., & Muñoz, I. (2022). Drying niches of aquatic macroinvertebrates identify potential biomonitoring indicators in intermittent and ephemeral streams. Ecological Indicators, 142, 109263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109263
Bellos, D., & Sawidis, T. (2005). Chemical pollution monitoring of the River Pinios (Thessalia—Greece). Journal of Environmental Management, 76, 282–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.01.027
Benaddi, R., Ferkan, Y., Bouriqi, A., & Ouazzani, N. (2022a). Impact of landfill leachate on groundwater quality – A comparison between three different landfills in Morocco. Journal of Ecological Engineering, 23, 89–94. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/153006
Benaddi, R., Bouriqi, A., & Ouazzani, N. (2022b). The environmental problem of olive mill waste water in Morocco: Data analysis and characterization. International Journal of Current Science Research and Review, 5, 1805–1809. https://doi.org/10.47191/ijcsrr/V5-i5-51
Ben-Daoud, M., Mouhaddach, O., Essahlaoui, A., Layachi, A., Kestemont, M.-P., & El Jaafari, S. (2011). Conception d’un SIG pour l’évaluation de l’impact des activités anthropiques sur la qualité des eaux superficielles de la ville de Meknès (Maroc). Cahiers De l’ASEES, 16, 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1051/asees/2011205
Benkirane, M., Laftouhi, N.-E., Mansouri, B. E., Salik, I., Snineh, M., Ghazali, F. E. E., Kamal, S., & Zamrane, Z. (2020). An approach for flood assessment by numerical modeling of extreme hydrological events in the Zat watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). Urban Water Journal, 17, 381–389. https://doi.org/10.1080/1573062X.2020.1734946
Benkirane, M., Laftouhi, N.-E., Khabba, S., & de la Hera-Portillo, Á. (2022). Hydro statistical assessment of TRMM and GPM precipitation products against ground precipitation over a Mediterranean mountainous watershed (in the Moroccan High Atlas). Applied Sciences, 12, 8309. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168309
Bouaida, J., Witam, O., Ibnoussina, M., Delmaki, A. E. F., & Benkirane, M. (2021). Contribution of remote sensing and GIS to analysis of the risk of flooding in the Zat basin (High Atlas-Morocco). Natural Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-021-04758-x
Boudhar, A., Duchemin, B., Hanich, L., Jarlan, L., Chaponnière, A., Maisongrande, P., Boulet, G., Chehbouni, A., (2010). Long-term analysis of snow-covered area in the Moroccan High-Atlas through remote sensing. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, Supplement Issue on “Remote Sensing for Africa – A Special Collection from the African Association for Remote Sensing of the Environment (AARSE)” 12, S109–S115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2009.09.008
Bouimouass, H., Fakir, Y., Tweed, S., & Leblanc, M. (2020). Groundwater recharge sources in semiarid irrigated mountain fronts. Hydrological Processes, 34, 1598–1615. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13685
Brierley, G.J., 2020. The socio-ecological river: Socio-economic, cultural and environmental relations to river systems, in: Brierley, G.J. (Ed.), Finding the voice of the river: Beyond restoration and management. Springer International Publishing, Cham. 29–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-27068-1_2
Camargo, J. A., Alonso, A., & De La Puente, M. (2004). Multimetric assessment of nutrient enrichment in impounded rivers based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 96, 233–249. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EMAS.0000031730.78630.75
Chehbouni, A., Escadafal, R., Duchemin, B., Boulet, G., Simonneaux, V., Dedieu, G., Mougenot, B., Khabba, S., Kharrou, H., Maisongrande, P., Merlin, O., Chaponnière, A., Ezzahar, J., Er-Raki, S., Hoedjes, J., Hadria, R., Abourida, A., Cheggour, A., Raibi, F., … Sobrino, J. A. (2008). An integrated modelling and remote sensing approach for hydrological study in arid and semi-arid regions: The SUDMED Programme. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 29, 5161–5181. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160802036417
Cid, N., Bonada, N., Carlson, S. M., Grantham, T. E., Gasith, A., & Resh, V. H. (2017). High variability is a defining component of Mediterranean-climate rivers and their biota. Water, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010052
Cox, B. A. (2003). A review of dissolved oxygen modelling techniques for lowland rivers. Science of the Total Environment, Land Ocean Interaction: Processes, Functioning and Environmental Management: A UK Perspective, 314–316, 303–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00062-7
Cui, D., Liang, S., & Wang, D. (2021). Observed and projected changes in global climate zones based on Köppen climate classification. Wires Climate Change, 12, e701. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.701
Czerniawska-Kusza, I. (2005). Comparing modified biological monitoring working party score system and several biological indices based on macroinvertebrates for water-quality assessment. Limnologica, 11th Magdeburg Seminar, October 2004 on Waters in Central and Eastern Europe: Assessment. Protection, Management, 35, 169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.limno.2005.05.003
Daniel, M. H. B., Montebelo, A. A., Bernardes, M. C., Ometto, J. P. H. B., de Camargo, P. B., Krusche, A. V., Ballester, M. V., Victoria, R. L., & Martinelli, L. A. (2002). Effects of urban sewage on dissolved oxygen, dissolved inorganic and organic carbon, and electrical conductivity of small streams along a gradient of urbanization in the Piracicaba River Basin. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution, 136, 189–206. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015287708170
Dodkins, I., Rippey, B., Harrington, T. J., Bradley, C., Ni Chathain, B., Kelly-Quinn, M., McGarrigle, M., Hodge, S., & Trigg, D. (2005). Developing an optimal river typology for biological elements within the Water Framework Directive. Water Research, 39, 3479–3486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2005.06.008
Durski, S. M., Barth, J. A., McWilliams, J. C., Frenzel, H., & Deutsch, C. (2017). The influence of variable slope-water characteristics on dissolved oxygen levels in the northern California Current System. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 122, 7674–7697. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017JC013089
El Hmaidi, A., Talhaoui, A., Manssouri, I., Jaddi, H., & Ousmana, H. (2020). Contribution of the pollution index and GIS in the assessment of the physico-chemical quality of the surface waters of Moulouya River (NE, Morocco). La Houille Blanche, 45–54, 2020028. https://doi.org/10.1051/lhb/2020028
Er-Raki, S., Chehbouni, A., Khabba, S., Simonneaux, V., Jarlan, L., Ouldbba, A., Rodriguez, J. C., & Allen, R. (2010). Assessment of reference evapotranspiration methods in semi-arid regions: Can weather forecast data be used as alternate of ground meteorological parameters? Journal of Arid Environments, 74, 1587–1596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2010.07.002
Errochdi, S., El Alami, M., Bennas, N., Belqat, B., Ater, M., & Fdil, F. (2012). Étude de la qualité physicochimique et microbiologique de deux réseaux hydrographiques nord marocains : Laou et Tahaddart. Méditerranée. Journal of Mediterranean Geography, 118, 41–51. https://doi.org/10.4000/mediterranee.6221
Ferreira, J. G., Nobre, A. M., Simas, T. C., Silva, M. C., Newton, A., Bricker, S. B., Wolff, W. J., Stacey, P. E., & Sequeira, A. (2006). A methodology for defining homogeneous water bodies in estuaries – Application to the transitional systems of the EU Water Framework Directive. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 66, 468–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.09.016
Floury, M., Usseglio-Polatera, P., Ferreol, M., Delattre, C., & Souchon, Y. (2013). Global climate change in large European rivers: Long-term effects on macroinvertebrate communities and potential local confounding factors. Global Change Biology, 19, 1085–1099. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.12124
Guellaf, A., & Kettani, K. (2021). Assessing the ecological status using physico-chemical, bacteriological parameters and biotic indices of the Oued Martil River basin in northwestern Morocco. Biologia, 76, 585–598. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00560-5
Gurnell, A. M., Rinaldi, M., Belletti, B., Bizzi, S., Blamauer, B., Braca, G., Buijse, A. D., Bussettini, M., Camenen, B., Comiti, F., Demarchi, L., García de Jalón, D., González del Tánago, M., Grabowski, R. C., Gunn, I. D. M., Habersack, H., Hendriks, D., Henshaw, A. J., Klösch, M., … Ziliani, L. (2016). A multi-scale hierarchical framework for developing understanding of river behaviour to support river management. Aquatic Sciences, 78, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-015-0424-5
Heasley, E. L., Millington, J. D. A., Clifford, N. J., & Chadwick, M. A. (2019). A waterbody typology derived from catchment controls using self-organising maps. Water, 12, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12010078
Julien, F. (2006). Maîtrise de l’eau et développement durable en Afrique de l’ouest : de la nécessité d’une coopération régionale autour des systèmes hydrologiques transfrontaliers. Vertigo, 7, 2402. https://doi.org/10.4000/vertigo.2402
Kagalou, I., & Leonardos, I. (2009). Typology, classification and management issues of Greek lakes: Implication of the Water Framework Directive (2000/60/EC). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 150, 469–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0245-2
Koumba, M., Kevin Mipounga, H., Armel Koumba, A., Zinga Koumba, C. R., Rollinat Mboye, B., Félicien Liwouwou, J., Daniel Mbega, J., & François Mavoungou, J. (2017). Diversité familiale des macroinvertébrés et qualité des cours d’eau du Parc National de Moukalaba Doudou (sud-ouest du Gabon). Entomologie Faunistique -Faunistic Entomology, 70, 3719. https://doi.org/10.25518/2030-6318.3719
Kumar, B., Singh, U. K., & Ojha, S. N. (2019). Evaluation of geochemical data of Yamuna River using WQI and multivariate statistical analyses: A case study. International Journal of River Basin Management, 17, 143–155. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2018.1437743
Lakhloufi, M. Y., Lamchouri, F., El Haissoufi, M., Boulfia, M., Zalaghi, A., & Toufik, H. (2021). Evaluation of anthropic activities impact through the monitoring of aquatic fauna on Oued Lârbaa in Taza City of Morocco. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193, 153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08938-x
Lyche Solheim, A., Globevnik, L., Austnes, K., Kristensen, P., Moe, S. J., Persson, J., Phillips, G., Poikane, S., van de Bund, W., & Birk, S. (2019). A new broad typology for rivers and lakes in Europe: Development and application for large-scale environmental assessments. Science of The Total Environment, 697, 134043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134043
Masese, F., Muchiri, M., & Raburu, P. (2009). Macroinvertebrate assemblages as biological indicators of water quality in the Moiben River, Kenya. African Journal of Aquatic Science, 34, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.2989/AJAS.2009.34.1.2.727
Mourhir, A., Rachidi, T., & Karim, M. (2014). River water quality index for Morocco using a fuzzy inference system. Environmental Systems Research, 3, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-014-0021-y
Munné, A., & Prat, N. (2004). Defining river types in a Mediterranean area: A methodology for the implementation of the EU Water Framework Directive. Environmental Management, 34, 711–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-003-0098-y
Mustapha, M. K. (2008). Assessment of the water quality of Oyun Reservoir, Offa, Nigeria, using selected physico-chemical parameters. TrJFAS, 8, 309–319.
Nahli, A., Oubraim, S., & Chlaida, M. (2022). Application of the biotic indices for water quality and resilience assessment of a disturbed stream (Casablanca, Morocco). Biologia, 77, 2887–2904. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01193-6
Olsen, R. L., Chappell, R. W., & Loftis, J. C. (2012). Water quality sample collection, data treatment and results presentation for principal components analysis – Literature review and Illinois River watershed case study. Water Research, 46, 3110–3122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.028
Pavlidou, A., Anastasopoulou, E., Dassenakis, Μ, Hatzianestis, I., Paraskevopoulou, V., Simboura, N., Rousselaki, E., & Drakopoulou, P. (2014). Effects of olive oil wastes on river basins and an oligotrophic coastal marine ecosystem: A case study in Greece. Science of the Total Environment, 497–498, 38–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.088
Perez, N., Teixell, A., Gómez-Gras, D., & Stockli, D. (2019). Reconstructing extensional basin architecture and provenance in the Marrakech high atlas of Morocco: Implications for rift basins and inversion. Tectonics, 38, 1507–1839. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018TC005413
Prathumratana, L., Sthiannopkao, S., & Kim, K. W. (2008). The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the lower Mekong River. Environment International, 34, 860–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2007.10.011
Qalmoun, A., Bouzrarf, K., & Belqat, B. (2022). Assessment of the ecological status of the Oum Er-rabie River basin (Central Morocco) through physicochemical, bacteriological parameters and biotic indices. Biologia, 77, 2533–2547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01128-1
Rajwa-Kuligiewicz, A., Bialik, R., & Rowiński, P. (2015). Dissolved oxygen and water temperature dynamics in lowland rivers over various timescales. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 63, 353–363. https://doi.org/10.1515/johh-2015-0041
Rego, F., & Rocha, M. S. (2014). Climatic patterns in the Mediterranean region. Ecologia Mediterranea, 40, 49–59. https://doi.org/10.3406/ecmed.2014.1269
Ren, L., Song, C., Wu, W., Guo, M., & Zhou, X. (2020). Reservoir effects on the variations of the water temperature in the upper Yellow River, China, using principal component analysis. Journal of Environmental Management, 262, 110339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110339
Reyjol, Y., Argillier, C., Bonne, W., Borja, A., Buijse, A. D., Cardoso, A. C., Daufresne, M., Kernan, M., Ferreira, M. T., Poikane, S., Prat, N., Solheim, A.-L., Stroffek, S., Usseglio-Polatera, P., Villeneuve, B., & van de Bund, W. (2014). Assessing the ecological status in the context of the European Water Framework Directive: Where do we go now? Science of the Total Environment, 497–498, 332–344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.07.119
Saal, I., Bouchelouche, D., Hamache, C., & Arab, A. (2021). Evaluation of the surface water quality in the Kebir-Rhumel catchment area (northeast Algeria) using biotic indices and physico-chemical analyses. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 46565–46579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10598-2
Schofield, C. L. (1977). Acid snow-melt effects on water quality and fish survival in the Adirondack Mountains of New York State. Cornell University, No. PB-27780. https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5268014
Schourup-Kristensen, V., Maar, M., Larsen, J., Mohn, C., Murawski, J., She, J., & Jakobsen, H. H. (2021). Methodology for defining homogeneous water bodies for management purposes. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 173, 113004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113004
Sehlaoui, H., Hassikou, R., Moussadek, R., Zouahri, A., Douaik, A., Iiach, H., Ghanimi, A., & Dakak, H. (2020). Evaluation of water quality for agricultural suitability in the Benslimane region. Morocco. Environ Monit Assess, 192, 587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08530-9
Sidabutar, N. V., Namara, I., Hartono, D. M., & Soesilo, T. E. B. (2017). The effect of anthropogenic activities to the decrease of water quality. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 67, 012034. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/67/1/012034
Simyrdanis, K., Papadopoulos, N., Soupios, P., Kirkou, S., & Tsourlos, P. (2018). Characterization and monitoring of subsurface contamination from Olive Oil Mills’ waste waters using electrical resistivity tomography. Science of the Total Environment, 637–638, 991–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.348
Skoulikidis, N. T., Sabater, S., Datry, T., Morais, M. M., Buffagni, A., Dörflinger, G., Zogaris, S., del Mar Sánchez-Montoya, M., Bonada, N., Kalogianni, E., Rosado, J., Vardakas, L., De Girolamo, A. M., & Tockner, K. (2017). Non-perennial Mediterranean rivers in Europe: Status, pressures, and challenges for research and management. Science of the Total Environment, 577, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.147
Smeti, E., Kalogianni, E., Karaouzas, I., Laschou, S., Tornés, E., De Castro-Català, N., Anastasopoulou, E., Koutsodimou, M., Andriopoulou, A., Vardakas, L., Muñoz, I., Sabater, S., & Skoulikidis, NTh. (2019). Effects of olive mill wastewater discharge on benthic biota in Mediterranean streams. Environmental Pollution, 254, 113057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113057
Talhaoui, A., El Hmaidi, A., Jaddi, H., Ousmana, H., & Manssouri, I. (2020). Calcul De L’indice De Qualité De L’eau (IQE) Pour L’évaluation De La Qualité Physico-Chimique Des Eaux Superficielles De L’Oued Moulouya (NE, Maroc). European Scientific Journal, 16, 64. https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2020.v16n2p64
Thorp, J. H., Thoms, M. C., & Delong, M. D. (2006). The riverine ecosystem synthesis: Biocomplexity in river networks across space and time. River Research and Applications, 22, 123–147. https://doi.org/10.1002/rra.901
Tripathi, M., & Singal, S. K. (2019). Use of principal component analysis for parameter selection for development of a novel water quality index: A case study of river Ganga India. Ecological Indicators, 96, 430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.09.025
Unda-Calvo, J., Ruiz-Romera, E., Martínez-Santos, M., Vidal, M., & Antigüedad, I. (2020). Multivariate statistical analyses for water and sediment quality index development: A study of susceptibility in an urban river. Science of the Total Environment, 711, 135026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135026
Ustaoğlu, F., & Tepe, Y. (2019). Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 7, 47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2018.09.001
Vatanpour, N., Malvandi, A. M., Hedayati Talouki, H., Gattinoni, P., & Scesi, L. (2020). Impact of rapid urbanization on the surface water’s quality: A long-term environmental and physicochemical investigation of Tajan river, Iran (2007–2017). Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 8439–8450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07477-w
Voudouris, K. (2012). Ecological water quality: Water treatment and reuse. Intechopen, 7, 510. https://doi.org/10.5772/1070
Wetzel, R. G. (2000). Freshwater ecology: Changes, requirements, and future demands. Limnology, 1, 3–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s102010070023
Young, R. G., Quarterman, A. J., Eyles, R. F., Smith, R. A., & Bowden, W. B. (2005). Water quality and thermal regime of the Motueka River: Influences of land cover, geology and position in the catchment. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 39, 803–825. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.2005.9517354
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Tensift Hydraulic Basin Agency (THBA) for providing the data used in this work, and we also appreciate the Erasmus Project for providing the funding necessary to complete this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, writing original draft: Abdelillah Bouriqi; Investigation, Visualization: Hassan Benaissa and Rabia Benaddi; Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, and Writing—Review & Editing: Jean-François Deliège; Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, and Writing—Review & Editing: Naaila Ouazzani. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bouriqi, A., Ouazzani, N., Benaissa, H. et al. Typology and classification of water quality in an intermittent river in a semi-arid Mediterranean climate. Environ Monit Assess 196, 381 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12514-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-024-12514-4