Abstract
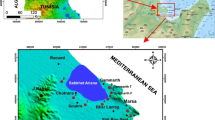
The natural environment, as well as human production and survival, is intrinsically dependent on soil. This study comprehensively assessed the pollution status, health risks, and sources of trace metals in the middle reaches of the River Gui Basin (MRGB) utilizing the geoaccumulation index, potential ecological risk index (PERI), and human health risk evaluation method. The findings of this study provide the following key insights: (1) only Cu and Pb levels in the MRGB soils did not exceed the background values established for soils in Weifang City (WFC). (2) The geoaccumulation status in most areas of the MRGB ranged from non-polluted to mildly polluted, with the overall ecological risk classification ranging from mild to moderate. (3) The cumulative non-carcinogenic risk for humans in the MRGB remained within acceptable limits, whereas the carcinogenic risk indices fell within tolerable levels. Oral ingestion emerged as the primary exposure pathway for both non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic health risks. (4) Cu, Zn, Ni, and Cr concentrations in MRGB soils primarily stemmed from natural sources associated with parent rocks, with Zn exhibiting additional influence from anthropogenic factors. In contrast, Pb, Cd, Hg, and As concentrations were predominantly driven by anthropogenic sources. Although the soils in the MRGB typically exhibited mild-to-moderate contamination levels, the contamination levels of Hg and Cd were notably more severe. As and Cr were significant health hazards. Most soil contamination sources are attributed to anthropogenic factors, warranting heightened attention from the relevant authorities.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Agency. (2001). Supplemental Guidance for Developing Soil Screening Levels for Superfund Sites. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response US Environment Protection Agency Washington, DC 20460.OSWER 9355.4-24.
Bhupander, K., Gargi, G., Richa, G., Dev, P., & Shekhar, S. C. (2012). Distribution, composition profiles and source identification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in roadside soil of Delhi, India. Journal of Environment & Earth Science, 2(1), 10–22.
Chen, T. B., Zheng, Y. M., Lei, M., Huang, Z. C., & Tian, Q. Z. (2005). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing. China. Chemosphere, 60(4), 542–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.12.072
Dai, J. R., Pang, X. G., Yu, C., Wang, C. L., & Hu, X. P. (2011). Geochemical baselines and background values and element enrichment characteristics in soils in Eastern Shandong Province. Geochimica, 40(6), 577–581. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-011-2067-x
Delavar, M., & Safari, Y. (2016). Spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils and plants in Zinc Town, Northwest Iran. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 13(1), 297–306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-015-0868-0
Din, I. U., Muhammad, S., & Rehman, I. U. (2022). Heavy metal(loid)s contaminations in soils of Pakistan: A review for the evaluation of human and ecological risks assessment and spatial distribution. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 45(5), 1991–2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-022-01312-x
Ferreira-Baptista, L., & Miguel, E. D. (2005). Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: A tropical urban environment. Atmospheric Environment, 39(25), 4501–4512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.03.026
Flora, A., Emma, F., Beatriz, C., & María, L. (2009). Enrichment of marsh soils with heavy metals by effect of anthropic pollution. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(2–3), 1056–1063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.074
Gasiorek, M., Kowalska, J., Mazurek, R., & Pajak, M. (2017). Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution in topsoil of historical urban park on an example of the Planty Park in Krakow (Poland). Chemosphere, 179(Jul), 148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.106
Govil, P. K., Sorlie, J. E., Murthy, N. N., Sujatha, D., Reddy, G. L. N., Rudolph-Lund, K., Krishna, A. K., & Mohan, K. R. (2008). Soil contamination of heavy metals in the Katedan Industrial Development Area, Hyderabad. India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 140(1–3), 313–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9869-x
Guseva, A. S., & Petrov, V. A. (2023). Assessment of soil pollution by heavy metals in certain areas of New Moscow. Doklady Earth Sciences, 510(1), 353–357. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1028334X23600202
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hall, R. K., Wolinsky, G. A., & Husby, P. (2000). Status of aquatic bioassessment in U.S. EPA Region IX. Environmental Monitoring & Assessment, 64(1), 17–30. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006430231539
Hossain, M. A., Ali, N. M., Islam, M. S., & Hossain, H. M. Z. (2015). Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils of Gebeng Industrial City. Malaysia. Environmental Earth Sciences, 73(1), 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3398-z
Izah, S. C., Bassey, S. E., & Ohimain, E. I. (2017). Assessment of pollution load indices of heavy metals in cassava mill effluents contaminated soil: A case study of small-scale processors in a rural community in the Niger Delta. Nigeria. Bioscience Methods, 8(1), 542–551. https://doi.org/10.5376/bm.2017.08.0001
Jadoon, S., Muhammad, S., Hilal, Z., Ali, M., Khan, S., & Khattak, N. U. (2020). Spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in urban soils of Abbottabad City, (N Pakistan): Evaluation for potential risk. Microchemical Journal, 153, 104489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104489
Khan, S. A., Muhammad, S., Nazir, S., & Shah, F. A. (2020). Heavy metals bounded to particulate matter in the residential and industrial sites of Islamabad, Pakistan: Implications for non-cancer and cancer risks. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 19, 100822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100822
Lee, H. G., Kim, H. K., Noh, H. J., Byun, Y. J., Chung, H. M., & Kim, J. I. (2020). Source identification and assessment of heavy metal contamination in urban soils based on cluster analysis and multiple pollution indices. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21(5), 1947–1961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02716-x
Lin, J., Zhang, Z. C., & Qiu, Q. (2001). Assessment on pollution of heavy metal in soil along road with method of the index of geoaccumulation. Practical Preventire Medicine, 8(5), 339–340.
Mohammed, L., Benhaddya, M., & Hadjel, M. (2014). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in surface soils of Hassi Messaoud Algeria. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(3), 1473–1486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2552-3
Muhammad, S. (2022). Evaluation of heavy metals in water and sediments, pollution, and risk indices of Naltar Lakes Pakistan. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(10), 28217–28226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24160-9
Naveedullah, Hashmi, M. Z. , Yu, C. , Shen, H. , Duan, D. , Shen, C.,Lou, L., &Chen, Y. (2013). Risk assessment of heavy metals pollution in agricultural soils of Siling reservoir watershed in Zhejiang Province, China. BioMed Research International,2013(0), 590306. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/590306
Reimann, C., & Caritat, P. (2005). Distinguishing between natural and anthropogenic sources for elements in the environment: Regional geochemical surveys versus enrichment factors. Science of the Total Environment, 337(1–3), 91–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.06.011
Sun, Y., Zhou, Q., Xie, X., & Liu, R. (2010). Spatial, sources and risk assessment of heavy metal contamination of urban soils in typical regions of Shenyang. China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 174(1–3), 455–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.074
Taghipour, H., Mosaferi, M., Armanfar, F., & Gaemmagami, S. J. (2013). Heavy metals pollution in the soils of suburban areas in big cities: A case study. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 10(2), 243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-012-0143-6
Tian, K., Huang, B., Xing, Z., & Hu, W. Y. (2017). Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai. China. Ecological Indicators, 72(1), 510–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.037
Ullah, R., & Muhammad, S. (2020). Heavy metals contamination in soils and plants along with the Mafic-ultramafic Complex (Ophiolites), Baluchistan, Pakistan: Evaluation for risk and phytoremediation potential. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 19, 100931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100931
USEPA. (1996). Exposure Factors Handbook. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC. EPA/600/P-95/002F a-c.
Xu, X., Han, J., Pang, J., Wang, X., & Qiu, G. (2020). Methylmercury and inorganic mercury in Chinese commercial rice: Implications for overestimated human exposure and health risk. Environmental Pollution, 258, 113706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113706
Yang, Z., Di, W. U., Xiang, Z., Kang, C., Wang, F., Huang, Z., & Zhang, L. (2016). Evaluation on potential ecological risk of heavy metals in soil from Penglai Fairyland Park. Asian Agricultural Research, 8(6), 75–86.
Yang, H., Dong, C., Zhang, H., Luo, H., Li, J., Yin, J., Dong, X., Wei, Z., Zhang, N., & Bao, L. (2022). Characteristics and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution in a mining area. Journal of Geoscience and Environment Protection, 10(3), 159–176. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2022.103012
Zhang, H., Li, Q., Ji, H., & Lu, K. (2019). Evaluation of heavy metal pollution in farmland soil of Henan Province based on bibliometrics. Hans Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 9(1), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.12677/HJAS.2019.91010
Funding
This study received support from the Geological Exploration and Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (202005) and the Research on Major Geological Environmental Issues in the Coastal Zone of Shandong Province (KY201911).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zongjun Gao: supervision, writing—original draft.
Menghan Tan: formal analysis, software, methodology, writing—original draft.
Jiutan Liu: research, conceptualization, methodology, writing review, resource acquisition.
Yuqi Zhang: investigation, resource acquisition.
Yiru Niu: investigation.
Bing Jiang: investigation, resource acquisition.
All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and complied with the Instructions for Authors’ statement on “Ethical Responsibilities of Authors” as necessary.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Tan, M., Liu, J. et al. Characterization of soil trace metal pollution, source identification, and health risk assessment in the middle reaches of the Guihe River Basin. Environ Monit Assess 196, 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12280-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12280-9