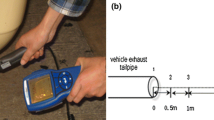
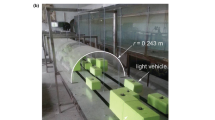
Abstract
In recent years, investigation of the dispersion of exhaust gas from vehicles has received increasing attention in various studies using various approaches, including on-field measurements, experimental laboratory models, and software simulations. This study aimed to investigate the effects of changes in vehicle traffic conditions, fuel type used in an engine, and vehicle size on the emission and dispersion of gaseous pollutants from the exhaust pipe in a wind tunnel. The results showed that pollutant concentration decreases along the tailpipe centerline as the exhaust gas moves backward and the flow pattern changes significantly from 11.5 to 15 m/s. However, for the passenger car, the small recirculation region in the near-wake region at an inflow air velocity of 11.5 m/s carries away more particles compared to an incoming velocity of 15 m/s, resulting in lower gaseous concentrations in both longitudinal and transverse directions. The gaseous dispersion behind the truck and the car is wider for an inflow air velocity of 11 m/s, especially for NO, NO2, and SO2. The results also showed that the pollutant concentrations of the truck exhaust plume were higher than those of the passenger car in lower inflow air velocity in both longitudinal and transverse directions. The lower concentration of dispersed gaseous pollutants behind the passenger car model compared to the truck model may be attributed to the shape and height of the truck model, which can trap more particles behind the vehicle. Finally, the dispersion pattern of SO2 is almost identical to that of NO2, and the dispersion of the exhaust gas plume related to CO and NO pollutants is more prolonged than that of CO2 and NO2 particles along the tailpipe centerline. The findings of this study may help in estimating the concentration of pollutants along urban highways.

































Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study were included in this published article. In addition, the datasets used or analyzed during the current study were available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Adar, S. D., & Kaufman, J. D. (2007). Cardiovascular Disease and Air Pollutants: Evaluating and ImprovingEpidemiological Data Implicating Traffic Exposure. Inhalation Toxicology, 19(sup1), 135–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958370701496012
Baik, J.-J., & Kim, J.-J. (2002). On the escape of pollutants from urban street canyons. Atmospheric Environment, 36(3), 527–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(01)00438-1
Banerjee, T., & Christian, R. A. (2017). On-field and laboratory measurement of nanoparticle emission in the wake of gasoline vehicle. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 8(6), 1179–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2017.05.007
Cui, P.-Y., Li, Z., & Tao, W.-Q. (2016). Wind-tunnel measurements for thermal effects on the air flow and pollutant dispersion through different scale urban areas. Building and Environment, 97, 137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.12.010
Deng, B., Chen, Y., Duan, X., Li, D., Li, Q., Tao, D., . . . Hou, K. (2020). Dispersion behaviors of exhaust gases and nanoparticle of a passenger vehicle under simulated traffic light driving pattern. Science of The Total Environment, 740, 140090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140090
He, H.-D., Shi, W., & Lu, W.-Z. (2017). Investigation of exhaust gas dispersion in the near-wake region of a light-duty vehicle. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 31(3), 775–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-016-1208-8
Hucho, W. H. (1998). Aerodynamics of Road Vehicles: From Fluid Mechanics to Vehicle Engineering Butterworth-Heinemann
Kanda, I., Uehara, K., Yamao, Y., Yoshikawa, Y., & Morikawa, T. (2006). A wind-tunnel study on exhaust-gas dispersion from road vehicles—Part II: Effect of vehicle queues. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 94(9), 659–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2006.06.002
Kanda, I., Uehara, K., Yamao, Y., Yoshikawa, Y., & Morikawa, T. (2006). A wind-tunnel study on exhaust gas dispersion from road vehicles—Part I: Velocity and concentration fields behind single vehicles. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 94(9), 639–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jweia.2005.12.003
Mehel, A., & Murzyn, F. (2015). Effect of air velocity on nanoparticles dispersion in the wake of a vehicle model: Wind tunnel experiments. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 6(4), 612–617. https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2015.069
Men, Y., Lai, Y., Dong, S., Du, X., & Liu, Y. (2017). Research on CO dispersion of a vehicular exhaust plume using Lattice Boltzmann Method and Large Eddy Simulation. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 52, 202–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2017.03.012
Oettl, D., Sturm, P. J., Bacher, M., Pretterhofer, G., & Almbauer, R. A. (2002). A simple model for the dispersion of pollutants from a road tunnel portal. Atmospheric Environment, 36(18), 2943–2953. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00254-6
Rao, K. S., Hosker Jr, R. P., Gunter, R. L., Nappo, C. J., Meyers, T. P., Birdwell, K. R., & White, J. R. (2003). Issues Affecting Dispersion Near Highways: Light Winds, Intra-Urban Dispersion, Vehicle Wakes, and the Roadway-2 Dispersion Model [Tech Report]. https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/49982. Accessed 1 Feb 2003
Salam, M. T., Islam, T., & Gilliland, F. D. (2008). Recent evidence for adverse effects of residential proximity to traffic sources on asthma. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine, 14(1), 3–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCP.0b013e3282f1987a
Shi, X., Sun, D., Fu, S., Zhao, Z., & Liu, J. (2019). Assessing on-road emission flow pattern under car-following induced turbulence using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) numerical simulation. Sustainability, 11(23), 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11236705
Shi, X., Sun, D., Zhang, Y., Xiong, J., & Zhao, Z. (2020). Modeling emission flow pattern of a single cruising vehicle on urban streets with cfd simulation and wind tunnel validation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4557. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124557
Sun, D., & Zhang, Y. (2018). Influence of avenue trees on traffic pollutant dispersion in asymmetric street canyons: Numerical modeling with empirical analysis. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 65, 784–795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2017.10.014
Sun, D., Shi, X., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, L. (2021). Spatiotemporal distribution of traffic emission based on wind tunnel experiment and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation. Journal of Cleaner Production, 282, 124495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124495
Sun, D., Wu, S., Shen, S., & Xu, T. (2021). Simulation and assessment of traffic pollutant dispersion at an urban signalized intersection using multiple platforms. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 12(7), 101087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2021.101087
Yu, J., Tian, L., Zhuang, W., & Yang, J. (2014). Prediction of the pollutant diffusion discharged from wind tower of the city traffic tunnel. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 42, 112–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2014.02.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Majid Shirazi Basiri, Mohammad Hojaji and Alireza Shirneshan. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Alireza Shirneshan and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
All the authors mentioned in the manuscript have given consent for submission and subsequent publication of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
All authors agree with publication in this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Basiri, M.S., Shirneshan, A. & Hojaji, M. The dispersion of various pollutants emitted from truck and passenger vehicles: a wind-tunnel study. Environ Monit Assess 195, 1417 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12007-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-12007-w