Abstract
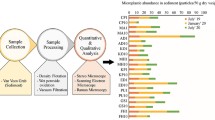
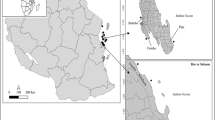
Microplastics (MPs) and their impacts have been extensively studied in the Mediterranean region. However, more research has yet to be conducted on assessing the extent of microplastic (MP) pollution in the eastern Aegean Sea, specifically in Izmir Bay. This study aims to evaluate the current state of MP pollution in surface water and sediment samples collected from Izmir Bay. Ten sampling stations were specifically selected, including locations near stream discharge points, maritime transportation piers, and port areas. Surface water samples were collected using a manta trawl net, while sediment samples were obtained using a Van Veen grab. The mean MP abundances in surface water ranged from 1,083,882 to 8,091,684 items/km2. Fragment type MPs were dominant. In terms of size category, it was found that MP s of 500µm size were dominant. The dominant color of MPs was white. ATR-FTIR analyses revealed that polyethylene and polypropylene were the dominant polymer types. MP concentrations in sediment ranged from 2,125 to 4,925 items/m2, with fiber-type MPs being the most abundant. Black-colored MPs were found to dominate in sediment samples. Overall, the MP levels in Izmir Bay were higher than previous studies findings. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct long-term monitoring studies to obtain more consistent and reliable data on MP pollution levels in Izmir Bay.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during the study are included in this manuscript and its supplementary information file. Additional raw data available upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Adamopoulou, A, Zeri, C, Garaventa, F., Gambardella, C., Ioakeimidis, C., & Pitta, E. (2021). Distribution patterns of floating microplastics in open and coastal waters of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea (Ionian, Aegean, and Levantine Seas). Frontiers in Marine Science, 8:699000. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.699000
Alomar, C., & Deudero, S. (2017). Evidence of microplastic ingestion in the shark Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 in the continental shelf of the western Mediterranean Sea. Environmental Pollution, 223, 223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.015
Alomar, C., Estarellas, F., & Deudero, S. (2016). Microplastics in the Mediterranean Sea: deposition in coastal shallow sediments, spatial variation and preferential grain size. Marine Environmental Research, 115, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.01.005
Andrady, A. L. (2011). Microplastics in the marine environment. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 62, 1596–1605.
Aytan, Ü., Şentürk, Y., Esensoy, F. B., Öztekin, A., Ağırbaş, E., & Valente, A. (2020). Microplastic pollution along the southeastern Black Sea. In Aytan, Ü., Pogojeva, M., Simeonova, A. (Eds.,), Marine Litter in the Black Sea. (pp. 192-207). Turkish Marine Research Foundation (TUDAV) Publication No: 56, Istanbul, Turkey.
Baalkhuyur, F. M., Bin Dohaish, E. J. A., Elhalwagy, M. E. A., Alikunhi, N. M., AlSuwailem, A. M., Røstad, A., & Duarte, C. M. (2018). Microplastic in the gastrointestinal tract of fishes along the Saudi Arabian Red Sea coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 131, 407–415.
Belioka, M.-P., & Achilias, D. S. (2023). Microplastic Pollution and Monitoring in Seawater and Harbor Environments: A Meta-Analysis and Review. Sustainability, 15, 9079. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15119079
Bellas, J., Martínez-Armental, J., Martínez-Cámara, A., Besada, V., & Martínez-Gómez, C. (2016). Ingestion of microplastics by demersal fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 109(1), 55–60.
Borrelle, S. B., Ringma, J., Law, K. L., Monnahan, C. C., Lebreton, L., McGivern, A., Murphy, E., Jambeck, J., Leonard, G. H., Hilleary, M. A., Eriksen, M., Possingham, H. P., De Frond, H., Gerber, L. R., Polidoro, B., Tahir, A., Bernard, M., Mallos, N., Barnes, M., & Rochman, C. M. (2020). Predicted growth in plastic waste exceeds efforts to mitigate plastic pollution. Science, 369(6510), 1515–1518.
Bošković, N., Joksimović, D., Peković, M., Perošević-Bajĉeta, A., & Bajt, O. (2021). Microplastics in surface sediments along the Montenegrin coast, Adriatic Sea: Types, occurrence, and distribution. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9080841
Brown, E., MacDonald, A., Allen, S., & Allen, D. (2023). The potential for a plastic recycling facility to release microplastic pollution and possible filtration remediation effectiveness. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 10, 100309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100309
Clunies-Ross, P. J., Smith, G. P. S., Gordon, K. C., & Gaw, S. (2016). Synthetic shorelines in New Zealand? Quantification and characterisation of microplastic pollution on Canterbury’s coastlines. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research, 50(2), 317–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.2015.1132747
Corona, E., Martin, C., Marasco, R., & Duarte, C. M. (2020). Passive and active removal of marine microplastics by a mushroom coral (Danafungia scruposa). Frontiers in Marine Science, 7, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2020.00128
da Rocha, F. O. C., Martinez, S. T., Campos, V. P., da Rocha, G. O., & de Andrade, J. B. (2021). Microplastic pollution in Southern Atlantic marine waters: review of current trends, sources, and perspectives. Science of the Total Environment, 782, 146541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146541
Erkan, H. S., Turan, N. B., Albay, M., & Engin, G. O. (2021). A preliminary study on the distribution and morphology of microplastics in the coastal areas of Istanbul, the metropolitan city of Turkey: The effect of location differences. Journal of Cleaner Production, 307, 127320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127320
Eronat, C. (2017). An overview on İzmir Bay physical oceanography. Ege Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 34(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.12714/egejfas.2017.34.1.01
Filgueiras, A. V., Gago, J., Campillo, J. A., & Leòn, V. M. (2019). Microplastic distribution in surface sediments along the Spanish Mediterranean continental shelf. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 21264–21273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05341-5
Garcı́a-Gómez, J. C., Garrigós, M., & Garrigós, J. (2021). Plastic as a Vector of Dispersion for Marine Species With Invasive Potential. A Review. Frontiers in Ecology & Evolution, 9, 208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2021.629756
GESAMP. (2016). “Sources, fate and effects of microplastics in the marine environment: part two of a global assessment” (Kershaw, P.J., and Rochman, C.M., eds). (IMO/FAO/UNESCO-IOC/UNIDO/WMO/IAEA/UN/UNEP/UNDP Joint Group of Experts on the Scientific Aspects of Marine Environmental Protection). Rep. Stud. GESAMP No. 93, 220.
Gündoğdu, S. (2017). High level of micro-plastic pollution in the Iskenderun Bay NE Levantine coast of Turkey. Ege Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 34(4), 401–408.
Gündoğdu, S., & Çevik, C. (2017). Micro- and mesoplastics in Northeast Levantine coast of Turkey: The preliminary results from surface samples. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 118(1), 341–347.
Gündoğdu, S., Çevik, C., Ayat, B., Aydoğan, B., & Karaca, S. (2018). How microplastics quantities increase with flood events? An example from Mersin Bay NE Levantine coast of Turkey. Environmental Pollution, 239, 342–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.042
Gürkan, Y., & Yüksek, A. (2022). Microplastics in Turkish Straits system: a case study of the bays and straits. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 22(7). https://doi.org/10.4194/TRJFAS20603
Güven, O., Gökdağ, K., Jovanović, B., & Kıdeyş, A. E. (2017). Microplastic litter composition of the Turkish territorial waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and its occurrence in the gastrointestinal tract of fish. Environmental Pollution, 223, 286–294.
Hanke, G., Galgani, F., Werner, S., Oosterbaan, L., Nilsson, P., Fleet, D., ... & Liebezeit, G. (2013). Guidance on Monitoring of Marine Litter in European Seas: a guidance document within the Common Implementation Strategy for the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. https://doi.org/10.2788/99816
Hidalgo-Ruz, V., Gutow, L., Thompson, R. C., & Thiel, M. (2012). Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environmental Science & Technology., 46, 3060–3075. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2031505
Jambeck, J. R., Geyer, R., Wilcox, C., Siegler, T. R., Perryman, M., Andrady, A., & Law, K. L. (2015). The ocean. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Part B: Regional Aspects: Working Group II Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on. Climate Change, 347, 1655–1734.
Kalcíkova, G. (2023). Beyond ingestion: Adhesion of microplastics to aquatic organisms. Aquatic Toxicology, 258, 106480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2023.106480
Kashiwabara, L. M., Kahane-Rapport, S. R., King, C., DeVogelaere, M., Goldbogen, J. A., & Savoca, M. S. (2021). Microplastics and microfibers in surface waters of monterey Bay National marine sanctuary, California. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 165, 112148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112148
Kedzierski, M., Villain, J., Falcou-Préfol, M., Kerros, M. E., Henry, M., Pedrotti, M. L., & Bruzaud, S. (2019). Microplastics in Mediterranean Sea: A protocol to robustly assess contamination characteristics. PLoS One, 14(2), e0212088. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0212088
Lusher, A. L., Welden, N. A., Sobral, P., & Cole, M. (2017). Sampling, isolating and identifying microplastics ingested by fish and invertebrates. Analytical Methods, 9, 1346–1360.
Masura, J., Baker, J., Foster, G., & Arthur, C. (2015). Laboratory Methods for the Analysis of Microplastics in the Marine Environment: Recommendations for quantifying synthetic particles in waters and sediments. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS-OR&R-48. https://doi.org/10.25607/OBP-604
MEUCC (Republic of Türkiye, Ministry of Environment, Urbanisation and Climate Change). (2017). Integrated Marine Pollution Monitoring Business 2014-2016 Aegean Sea Summary Report in Turkish. ISBN 978-605-5294-69-4, Ankara, 68p. https://webdosya.csb.gov.tr/db/ced/editordosya/2014-2016%20YILI%20EgeDenizi_Ozet_Raporu.pdf
MEVBIS. (2022). Republic of Türkiye, Ministry of Environment, Urbanisation and Climate Change, Meteorological Data Information Sales and Presentation System. Retrieved November 12, 2022, from https://mevbis.mgm.gov.tr/mevbis/ui/index.html#/Workspace
Mistri, M., Scoponi, M., Granata, T., Moruzzi, L., Massara, F., & Munari, C. (2020). Types, occurrence and distribution of microplastics in sediments from the northern Tyrrhenian Sea. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 153, 111016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111016
Mohsen, M., Lin, C., Liu, S., & Yang, H. (2022). Existence of microplastics in the edible part of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Chemosphere, 287, 132062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132062
Murphy, F., Russell, M., Ewins, C., & Quinn, B. (2017). The uptake of macroplastic & microplastic by demersal & pelagic fish in the Northeast Atlantic around Scotland. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 122(1–2), 353–359.
Nadal, M. A., Alomar, C., & Deudero, S. (2016). High levels of microplastic ingestion by the semipelagic fish bogue Boops boops (L.) around the Balearic Islands. Environmental Pollution, 214, 517–523.
Neves, D., Sobral, P., Ferreira, J. L., & Pereira, T. (2015). Ingestion of microplastics by commercial fish off the Portuguese coast. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 101(1), 119–126.
Olivatto, G. P., Martins, M. C. T., Montagner, C. C., Henry, T. B., & Carreira, R. S. (2019). Microplastic contamination in surface waters in Guanabara Bay, Rio de Janeiro. Brazil. Marine Pollution Bullettin, 139, 157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.12.042
Ozguler, U., Demir, A., Kayadelen, G., & Kideyş, A. (2022). Riverine microplastic loading to mersin bay, Turkey on the north-eastern mediterranean. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 22(7). https://doi.org/10.4194/TRJFAS20253
Oztekin, A., & Bat, L. (2017). Microlitter Pollution in Sea Water: A Preliminary Study from Sinop Sarikum Coast of the Southern Black Sea. Turkish Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 17, 1431–1440. https://doi.org/10.4194/1303-2712-v17_6_37
Palatinus, A., Viršek, M. K., & Kaberi, E. (2015). DeFishGear protocols for sea surface and beach sediment sampling and sample analysis. Adriatic IPA. Retrieved February 5, 2021, from https://mio-ecsde.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/12/Protocols-sea-surfacebeach-sediments-Feb15.pdf
Plastics Europe. (2021). Plastics – the Facts 2018. Retrieved June 8, 2022, from https://plasticseurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/2018-Plastics-the-facts.pdf
Ridall, A., & Ingels, J. (2021). Suitability of free-living marine nematodes as bioindicators: Status and future considerations. Frontiers in Marine Science, 8, 685327. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.685327
Rochman, C. M., Hoh, E., Kurobe, T., & Teh, S. J. (2013). Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Scientific Reports, 3(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03263
Sagawa, N., Kawaai, K., & Hinata, H. (2018). Abundance and size of microplastics in a coastal sea: Comparison among bottom sediment, beach sediment, and surface water. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 133, 532–542.
Sayed, A. E. D. H., Hamed, M., Badrey, A. E., Ismail, R. F., Osman, Y. A., Osman, A. G., & Soliman, H. A. (2021). Microplastic distribution, abundance, and composition in the sediments, water, and fishes of the Red and Mediterranean seas, Egypt. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 173, 112966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112966
Suaria, G., Avio, C. G., Mineo, A., Lattin, G. L., Magaldi, M. G., Belmonte, G., Moore, C. J., Regoli, F., & Aliani, S. (2016). The Mediterranean plastic soup: synthetic polymers in Mediterranean surface waters. Scientific Reports, 6, 37551. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37551
Sutton, R., Mason, S. A., Stanek, S. K., Willis-Norton, E., Wren, I. F., & Box, C. (2016). Microplastic contamination in the San Francisco Bay, California, USA. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 109, 230–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.05.077
Terzi, Y., Gedik, K., Eryaşar, A. R., Öztürk, R. Ç., Şahin, A., & Yılmaz, F. (2022). Microplastic contamination and characteristics spatially vary in the southern Black Sea beach sediment and sea surface water. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 174, 113228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.113228
Van Cauwenberghe, L., Claessens, M., Vandegehuchte, M. B., & Janssen, C. R. (2015). are taken up by mussels (Mytilus edulis) and lugworms (Arenicola marina) living in natural habitats. Environmental Pollution, 199, 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2015.01.008bellaal
Xiao, C., Lang, M., Wu, R., Zhang, Z., & Guo, X. (2023). A Review of the distribution, characteristics and environmental fate of microplastics in different environments of China. Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 261, 3.
Yelekci, O., Ibello, V., Fach, B. A., Kucuksezgin, F., Yumruktepe, C., Sayin, E., Salihoglu, B., & Tugrul, S. (2021). Assessing the impact of nutrient loads on eutrophication in the semi-enclosed Izmir Bay combining observations and coupled hydrodynamic-ecosystem modelling. Mediterranean Marine Science, 22(3), 677–696. https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.23294
Zayen, A., Sayadi, S., Chevalier, C., Boukthir, M., Ben I. S., & Tedetti, M. (2020). in surface waters of the Gulf of Gabes, southern Mediterranean Sea: Distribution, composition and influence of hydrodynamics. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 242. 106832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2020.106832
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank the R/V Egederin and R/V Egesüf crew for their support during the sample collection. Authors also would like thank Dr. Levent Yurga for his help preparing supplementary Fig. S1.
Funding
This study was funded by Ege University, Office of Scientific Research Projects. Project no: 21064.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aslı Başaran: conceived the study, collected the samples, performed laboratory analysis, analyzed the results, wrote the manuscript, edited, and reviewed the text. Mehmet Aksu: conceived the study, collected the samples, performed laboratory analysis, analyzed the results, wrote the manuscript, edited, and reviewed the text. Uğur Sunlu: conceived the study, collected the samples, edited, and reviewed the text. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclaimer
In addition, we declare that “All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on "Ethical responsibilities of Authors" as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.”
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Aksu, M., Başaran, A. & Sunlu, U. Spatio-temporal distribution of microplastic abundances in Izmir Bay (eastern Aegean Sea). Environ Monit Assess 195, 1116 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11790-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11790-w