Abstract
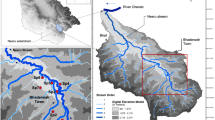
Water contamination with faecal matter is usually the main cause of microbial waterborne diseases. Such diseases are an alarming situation for small cities in developing countries like India. In this research, to check the microbiological status of drinking water in Solan, Himachal Pradesh (India), water samples were collected from baories/stepwells (n = 14), handpumps (n = 9), and the municipal water distribution system (MWDS) (n = 2) in alternative months of the year (covering three main seasons). In 6 months, 150 samples were collected, and they were all examined for the presence of total coliforms and other bacterial pathogens. The associations between the isolates’ ecological and seasonal prevalence were also examined. The coliforms were detected by the Most Probable Number (MPN) method, whose range was noticed from the 2–540/100-ml MPN index. The colony forming unit (CFU) count for different samples at the base log 10 value ranged from 3.03 to 6.19. Different genera isolated and identified were Escherichia coli, Salmonella enteric subsp. enterica, Pseudomonas spp., Klebsiella spp., and Staphylococcus aureus. Overall, 74% of the isolates identified in water samples were from the Enterobacteriaceae family. E. coli was about 42.67% (n = 102), followed by Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica 20.92% (n = 50), Staphylococcus aureus 13.38% (n = 32), Pseudomonas spp. 12.55% (n = 30), and Klebsiella spp. 10.46% (n = 25) amongst the total of 239 isolates. The seasonal impact and the dependency of the occurrence of bacteria on one another were determined to be insignificant in the Spearman correlation test. These results showed that external factors (anthropogenic activities) are mainly responsible for the presence of these bacteria in water resources. The occurrence of bacterial isolates has been noticed in all water samples, irrespective of collecting site or season.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Table 2 is representing the data related to the CFU count. If required in a simple form, then it is attached to this submission.
References
Abdelrahman, A. A., & Eltahir, Y. M. (2011). Bacteriological quality of drinking water in Nyala, South Darfur, Sudan. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 175(1), 37–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-010-1491-7
Agbabiaka, T. O., & Sule, I. O. (2010). Bacteriological assessment of selected borehole water samples in Ilorin metropolis. International Journal of Applied Biological Research, 2(2), 31–37.
Alemayehu, G. K., & Mulugeta, K. A. (2017). Microbiological quality and safety of street vended meat sauce in Bahir Dar Town. Journal of Microbiology and Antimicrobials, 9(2), 14–22. https://doi.org/10.5897/JMA2015.0358
An, Y. J., & Breindenbach, G. P. (2005). Monitoring E. coli and total coliforms in natural spring water as related to recreational mountain areas. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 102(1), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-005-4691-9
APHA-AWWA-WPCF. (2017). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23rd ed.). APHA.
Ashbolt, N. J. (2004). Microbial contamination of drinking water and disease outcomes in developing regions. Toxicology, 198(1–3), 229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2004.01.030
Bain, R., Cronk, R., Wright, J., Yang, H., Slaymaker, T. & Bartram, J. (2014). Fecal contamination of drinking-water in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS medicine, 11(5), e1001644. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001644
Chakraborty, A. K., Poira, K., Saha, D., Halder, C., Das, S., & Nandi, S. K. (2018). Multidrug-resistant bacteria with activated and diversified MDR genes in Kolkata water: Ganga action plan and heterogeneous phyto antibiotics tackling superbug spread in India. American Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, 5(1), 2.
Chauhan, S., & Bhardwaj, S. K. (2017). Inventorization of water resources in Solan block of Himachal Pradesh. India. Current World Environment, 12(2), 456.
Chawla, S. (2017). Role of Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme in eliciting an E. coli 0157:H7 gastroenteritis outbreak at Tribal Girls Hostel, Solan, HP. Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, 5(3A), 717–722.
Edberg, S. C. L., Rice, E. W., Karlin, R. J., & Allen, M. J. (2000). Escherichia coli: The best biological drinking water indicator for public health protection. Journal of applied microbiology, 88(S1), 106S-116S.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2000.tb05338.x
Fardami, A. Y., Mamuda, B. & Kangiwa, I. A., (2019). Bacteriological analysis of drinking water in Zamfara North Senatorial District, Nigeria. Microbiology Research Journal International, 27(5), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.9734/MRJI/2019/v27i530110
Goyal, S. M., Gerba, C. P., & Melnick, J. L. (1977). Occurrence and distribution of bacterial indicators and pathogens in canal communities along the Texas coast. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 34(2), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.34.2.139-149.1977
Gumbo, A., Bangure, D., Gombe, N. T., Tshimanga, M., Hwalima, Z., & Dube, I. (2015). Staphylococcus aureus food poisoning among Bulawayo City Council employees, Zimbabwe, 2014. BMC Research Notes, 8(1), 1–6.
Haque, M. A., Jewel, M. A. S., & Sultana, M. P. (2019). Assessment of physicochemical and bacteriological parameters in surface water of Padma River. Bangladesh. Applied Water Science, 9(1), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0885-5
Koloren, Z., & Kaya, D. (2012). Fecal pollution in rural water supplies of Ordu, at the Mid-Black Sea Coast of Turkey: The effect of climate and environmental elements. EnergEducSciTechnol Part a: Energy Science Research, 28(2), 869–878.
Lapworth, D. J., MacDonald, A. M., Kebede, S., Owor, M., Chavula, G., Fallas, H., Wilson, P., Ward, J. S. T., Lark, M., Okullo, J. J. E. R. L., & Mwathunga, E. (2020). Drinking water quality from rural handpump—Boreholes in Africa. Environmental Research Letters, 15(6), 064020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab8031
Levallois, P., & Villanueva, C. M. (2019). Drinking water quality and human health: An editorial. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(4), 631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16040631
Lukubye, B., & Andama, M. (2017). Bacterial analysis of selected drinking water sources in Mbarara Municipality, Uganda. Journal of Water Resource and Protection, 9(8), 999–1013. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2017.98066
Mukhopadhyay, C., Vishwanath, S., Eshwara, V. K., Shankaranarayana, S. A., & Sagir, A. (2012). Microbial quality of well water from rural and urban households in Karnataka, India: A cross-sectional study. Journal of Infection and Public Health, 5(3), 257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2012.03.004
Naseema, K., Masihur, R., & Husain, K. A. (2013). Study of seasonal variation in the water quality among different ghats of river Ganga, Kanpur, India. Journal of Environmental Research and Development, 8(1), 1.
Nienie, A. B., Sivalingam, P., Laffite, A., Ngelinkoto, P., Otamonga, J. P., Matand, A., Crispin, K., Mulaji, J. I., Mubedi, P. T., & Mpiana, J. P. (2017). Seasonal variability of water quality by physicochemical indexes and traceable metals in suburban area in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 5(2017), 158–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.04.004
Pandit, J., & Bhardwaj, S. K. (2020). Quality characterization of surface water sources using water quality index in urban areas of Solan District of Himachal Pradesh. International Research Journal of Pure & Applied Chemistry, 21(24), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.9734/IRJPAC/2020/v21i2430329
Pouramin, P., Nagabhatla, N., & Miletto, M. (2020). A systematic review of water and gender interlinkages: Assessing the intersection with health. Frontiers in Water, 2, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2020.00006
Pujari, P. R., Nanoti, M., Nitnaware, V. C., Khare, L. A., Thacker, N. P., & Kelkar, P. S. (2007). Effect of on-site sanitation on groundwater contamination in basaltic environment: A case study from India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 134, 271–278.
Qadri, R. & Faiq, M. A. (2020). Freshwater pollution: Effects on aquatic life and human health. Fresh water pollution dynamics and remediation, 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8277-2-2
SD, T., & Panda, A. K. (2012). Laboratory investigation of drinking water sources of Kangra. Himachal Pradesh. J. Commun. Dis, 44(2), 103–108.
Sharma, K. D., Ghosh, N. C., & Singh, R. D. (2008). Scarcity of water in India. Current Science-Bangalore-, 94(12), 1551.
Singh, A. K., Bhardwaj, S. K., & Devi, S. (2021). Microbiological status of drinking water sources and its relationship with human health in Solan. India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 193(1), 32.
Suthar, S., Chhimpa, V., & Singh, S. (2009). Bacterial contamination in drinking water: A case study in rural areas of northern Rajasthan. India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 159(1), 43–50.
Thakur, N., Changotra, H., Shrivastava, R., Grover, N., & Vashistt, J. (2017). Estimation of Vibrio species incidences and antibiotic resistance in diarrhea patients. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 11(1), 369–373. https://doi.org/10.22159/ajpcr.2018.v11i1.22088
World Health Organization. (2011). Guideline for drinking water quality — (3rd ed.). Recommendation WHO.
Yadav, N., Singh, S., & Goyal, S. K. (2019). Effect of seasonal variation on bacterial inhabitants and diversity in drinking water of an office building, Delhi. Air, Soil and Water Research, 12, 1178622119882335. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178622119882335
Yari, A. R., Mohammadi, M. J., Geravandi, S., Doosti, Z., Matboo, S. A., Jang, S. A., & Nazari, S. (2018). Assessment of microbial quality of household water output from desalination systems by the heterotrophic plate count method. Journal of Water and Health, 16(6), 930–937. https://doi.org/10.2166/wh.2018.082
Ye, B., Yang, L., Li, Y., Wang, W., & Li, H. (2013). Water sources and their protection from the impact of microbial contamination in rural areas of Beijing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 10(3), 879–891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph10030879
Varela, A. R., Manageiro, V., Ferreira, E., Guimarães, M. A., da Costa, P. M., Caniça, M., & Manaia, C. M. (2015). Molecular evidence of the close relatedness of clinical, gull and wastewater isolates of quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance, 3(4), 286–289.
Acknowledgements
All authors are thankful to the Vice Chancellor, Shoolini University of Biotechnology and Management Sciences, Solan for providing the necessary facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Mamta Devi Sharma, Saurabh Kulshrestha; Methodology: Mamta Devi Sharma, Payal Gupta; Formal analysis and investigation: Mamta Devi Sharma, Ranjana Panwar; Writing -original draft preparation: Mamta Devi Sharma, Pradeep Kumar, Saurabh Kulshrestha; Writing - review and editing: Mamta Devi Sharma, Sewa Singh, Saurav Chauhan, Pradeep Kumar; Resources, Funding and Supervision: Saurabh Kulshrestha
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical responsibilities of authors
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Ethical approval
The paper does not contain any ethically questionable information.
Consent to participate
The authors mutually agreed that they participated in the preparation of the manuscript.
Consent for publication
The authors declare that the manuscript is their intellectual property and that they want to publish it in the Journal “Environmental Monitoring and Assessment”.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, M.D., Gupta, P., Chauhan, S. et al. Seasonal impact on microbiological quality of drinking water in Solan City of Himachal Pradesh, India. Environ Monit Assess 195, 930 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11510-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11510-4