Abstract
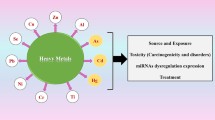
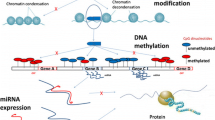
Heavy metals are well-recognised as environmental hazards due to their toxicity, environmental persistence, and bioaccumulation in living organisms. Human health is a crucial concern related to terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems poisoned by harmful heavy metals. Most heavy metals pollute the air, water, and soil, which can be fatal to humans. Humans and other species can be exposed to heavy metals through the food chain if the metals oxidise or combine with other environmental elements (such as water, soil, or air). Their entry into the food chain assures interactions with biological macromolecules in living systems, including humans, resulting in undesirable outcomes. Human poisonings have typically been caused by mercury, lead, chromium, cadmium, and arsenic. The build-up of these metals in living organisms causes various harmful consequences on different organs and tissues. The gravitas of heavy metal toxicity regarding molecular impact and carcinogenesis needs in-depth understanding despite the plethora of available data. Hence, additionally, we attempt to elaborate on the multi-level impact of five heavy metals and emphasise their role in cancer development. The rationale of this essay is thus to understand the role of five heavy metals, viz., lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), arsenic (As), and mercury (Hg), in carcinogenesis. Heavy metals interfere with various biological functions, including proliferation, differentiation, repair of damage, and apoptosis. By comparing their modes of action, we see that these metals share common mechanisms for inducing toxicity, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, antioxidant defence weakening, enzyme inactivation, and oxidative stress.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
A solution to arsenic poisoning in Assam: Water ATMs purify groundwater. (n.d.). https://www.thethirdpole.net/en/pollution/in-assam-atms-purify-arsenic-laced-water/. Accessed 9 June 2022
Achanzar, W. E., Webber, M. M., & Waalkes, M. P. (2002). Altered apoptotic gene expression and acquired apoptotic resistance in cadmium-transformed human prostate epithelial cells. The Prostate, 52(3), 236–244. https://doi.org/10.1002/PROS.10106
Aggarwal, V., Tuli, H. S., Varol, A., Thakral, F., Yerer, M. B., Sak, K., et al. (2019). Role of reactive oxygen species in cancer progression: Molecular mechanisms and recent advancements. Biomolecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110735
Akter, K. F., Owens, G., Davey, D. E., & Naidu, R. (2005). Arsenic speciation and toxicity in biological systems. In Reviews of environmental contamination and toxicology (Vol. 184, pp. 97–149). Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-27565-7_3
Alam, J., Wicks, C., Stewart, D., Gong, P., Touchard, C., Otterbein, S., et al. (2000). Mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 gene activation by cadmium in MCF-7 mammary epithelial cells: Role of p38 kinase and Nrf2 transcription factor. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(36), 27694–27702. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.M004729200
Alert sounded on lead poisoning in Bangalore. (2001). Times of India. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/bengaluru/Alert-sounded-on-lead-poisoning-in-Bangalore/articleshow/1840425823.cms. Accessed 5 May 2023
Andrew, A. S., Mason, R. A., Memoli, V., & Duell, E. J. (2009). Arsenic activates EGFR pathway signaling in the lung. Toxicological Sciences, 109(2), 350–357. https://doi.org/10.1093/TOXSCI/KFP015
Ansari, T. M., Marr, I. L., & Tariq, N. (2003). Heavy metals in marine pollution perspective–A mini review. Journal of Applied Sciences, 4(1), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3923/jas.2004.1.20
Arsenic alarm in villages of Bihar and Jharkhand - Rediff.com India News. (n.d.). https://www.rediff.com/news/report/arsenic-alarm-in-villages-of-bihar-and-jharkhand/20100914.htm. Accessed 9 June 2022
Arsenic. (n.d.). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/arsenic. Accessed 7 June 2022
Aschner, M., & Syversen, T. (2005). Methylmercury: Recent advances in the understanding of its neurotoxicity. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. NIH Public Access. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ftd.0000160275.85450.32
Atsdr. (2002a). Toxicological profile for arsenic. In ATSDR’s Toxicological Profiles. CRC Presshttps://doi.org/10.1201/9781420061888_ch33
Atsdr. (2002b). Toxicological profile for cadmium. In ATSDR’s Toxicological Profiles. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420061888_ch48
Atsdr. (2002c). Toxicological profile for lead. In ATSDR’s Toxicological Profiles. CRC Press.https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420061888_ch106
ATSDR. (2013). Cadmium toxicity: What is the biological fate of cadmium in the body? | Environmental Medicine | ATSDR. https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/csem/cadmium/Biological-Fate.html. Accessed 23 June 2022
Azeh Engwa, G., Udoka Ferdinand, P., Nweke Nwalo, F., & N. Unachukwu, M. (2019). Mechanism and health effects of heavy metal toxicity in humans. In Poisoning in the Modern World - New Tricks for an Old Dog? IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.82511
Bernard, A. (2008). Cadmium & its adverse effects on human health. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 128(4), 557–64. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19106447. Accessed 1st May 2022
Bernhoft, R. A. (2012). Mercury toxicity and treatment: A review of the literature. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, 2012, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/460508
Beyersmann, D., & Hartwig, A. (2008). Carcinogenic metal compounds: Recent insight into molecular and cellular mechanisms. Archives of Toxicology, 82(8), 493–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-008-0313-y
Bhattacharjee, P., Banerjee, M., & Giri, A. K. (2013). Role of genomic instability in arsenic-induced carcinogenicity. A review. Environment International. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.12.004
Bodaghi-Namileh, V., Sepand, M. R., Omidi, A., Aghsami, M., Seyednejad, S. A., Kasirzadeh, S., & Sabzevari, O. (2018). Acetyl-l-carnitine attenuates arsenic-induced liver injury by abrogation of mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 58, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2017.12.005
Boffetta, P., Merler, E., & Vainio, H. (1993). Carcinogenicity of mercury and mercury compounds. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health, 19(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.1510
Boskabady, M. H., Tabatabai, S. A., & Farkhondeh, T. (2016). Inhaled lead affects lung pathology and inflammation in sensitized and control guinea pigs. Environmental Toxicology, 31(4), 452–460. https://doi.org/10.1002/TOX.22058
Brent, J., Burkhart, K., Dargan, P., Hatten, B., Megarbane, B., Palmer, R., & White, J. (2017). Critical care toxicology: Diagnosis and management of the critically poisoned patient. Diagnosis and Management of the Critically Poisoned Patient. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-17900-1
Briffa, J., Sinagra, E., & Blundell, R. (2020). Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon, 6(9), e04691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04691
Brown, H. A., Thomas, P. G., & Lindsley, C. W. (2017). Targeting phospholipase D in cancer, infection and neurodegenerative disorders. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. Nature Publishing Group. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.252
Burford, N., Eelman, M. D., & Groom, K. (2005). Identification of complexes containing glutathione with As(III), Sb(III), Cd(II), Hg(II), Tl(I), Pb(II) or Bi(III) by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry, 99(10), 1992–1997. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JINORGBIO.2005.06.019
BV, L. (2013). Mercury (Hg) - Chemical properties, health and environmental effects. Water Treatment Solutions. https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/hg.htm. Accessed 6 June 2022
Cadmium | toxicological profile | ATSDR. (n.d.). https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=48&tid=15. Accessed 23 June 2022
Cadmium Facts - Periodic Table. (n.d.). https://www.thoughtco.com/cadmium-element-facts-606511. Accessed 23 June 2022
Casalino, E., Sblano, C., Calzaretti, G., & Landriscina, C. (2006). Acute cadmium intoxication induces alpha-class glutathione S-transferase protein synthesis and enzyme activity in rat liver. Toxicology, 217(2–3), 240–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOX.2005.09.020
Chakraborti, D., Singh, E. J., Das, B., Shah, B. A., Hossain, M. A., Nayak, B., et al. (2008). Groundwater arsenic contamination in Manipur, one of the seven North-Eastern Hill states of India: A future danger. EnGeo, 56(2), 381–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00254-007-1176-X
Chang, P., Li, Y., & Li, D. (2011). Micronuclei levels in peripheral blood lymphocytes as a potential biomarker for pancreatic cancer risk. Carcinogenesis, 32(2), 210–215. https://doi.org/10.1093/CARCIN/BGQ247
Chemical And Physical Information - Toxicological profile for lead - NCBI Bookshelf. (n.d.). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK158769/. Accessed 27 June 2022
Chhattisgarh coal block is highly polluted, has unsafe cadmium level in soil, says study. (n.d.). https://scroll.in/latest/846331/cadmium-level-169-times-higher-than-is-safe-found-in-chhattisgarhs-raigarh-district-says-study. Accessed 24 June 2022
Chromium waste remains a threat in Ranipet - The Hindu. (n.d.). https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/tamil-nadu/chromium-waste-remains-a-threat-in-ranipet/article30898352.ece. Accessed 28 June 2022
Chuang, S. M., & Yang, J. L. (2001). Comparison of roles of three mitogen-activated protein kinases induced by chromium(VI) and cadmium in non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 222(1–2), 85–95. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017967408266
Costa, M. (2003). Potential hazards of hexavalent chromate in our drinking water. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 188(1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0041-008X(03)00011-5
Crespo-López, M. E., Macêdo, G. L., Pereira, S. I., Arrifano, G. P., Picanco-Diniz, D. L., do Nascimento, J. L. M., & Herculano, A. M. (2009). Mercury and human genotoxicity: Critical considerations and possible molecular mechanisms. Pharmacological Research, 60(4), 212–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2009.02.011
Cui, X., Wakai, T., Shirai, Y., Hatakeyama, K., & Hirano, S. (2006). Chronic oral exposure to inorganic arsenate interferes with methylation status of p16INK4a and RASSF1A and induces lung cancer in A/J mice. Toxicological Sciences, 91(2), 372–381. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfj159
De Vos, G., Abotaga, S., Liao, Z., Jerschow, E., & Rosenstreich, D. (2007). Selective effect of mercury on Th2-type cytokine production in humans. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology, 29(3–4), 537–548. https://doi.org/10.1080/08923970701690993
Deng, Y., Wang, M., Tian, T., Lin, S., Xu, P., Zhou, L., et al. (2019). The effect of hexavalent chromium on the incidence and mortality of human cancers: A meta-analysis based on published epidemiological cohort studies. Frontiers in Oncology. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00024
Dionisio, K. L., Phillips, K., Price, P. S., Grulke, C. M., Williams, A., & Biryol, D., et al. (2018). Data Descriptor: The Chemical and Products Database, a resource for exposure-relevant data on chemicals in consumer products. Scientific Data, 5. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.125
Dutta, K., Prasad, P., & Sinha, D. (2015). Chronic low level arsenic exposure evokes inflammatory responses and DNA damage. International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health, 218(6), 564–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEH.2015.06.003
Eneman, J. D., Potts, R. J., Osier, M., Shukla, G. S., Lee, C. H., Chiu, J. F., & Hart, B. A. (2000). Suppressed oxidant-induced apoptosis in cadmium adapted alveolar epithelial cells and its potential involvement in cadmium carcinogenesis. Toxicology, 147(3), 215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00215-8
Farmand, F., Ehdaie, A., Roberts, C. K., & Sindhu, R. K. (2005). Lead-induced dysregulation of superoxide dismutases, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and guanylate cyclase. Environmental Research, 98(1), 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2004.05.016
Fatur, T., Lah, T. T., & Filipič, M. (2003). Cadmium inhibits repair of UV-, methyl methanesulfonate- and N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced DNA damage in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mutation Research/fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 529(1–2), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0027-5107(03)00112-X
Fernandes Azevedo, B., Barros Furieri, L., Peçanha, F. M., Wiggers, G. A., Frizera Vassallo, P., Ronacher Simões, M., et al. (2012). Toxic effects of mercury on the cardiovascular and central nervous systems. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 2012, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/949048
Flora, S. J. S. (2009). Nutritional components modify metal absorption, toxic response and chelation therapy. Journal of Nutritional & Environmental Medicine, 12(1), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/13590840220123361
Florea, A. M., & Büsselberg, D. (2006). Occurrence, use and potential toxic effects of metals and metal compounds. BioMetals. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-005-4451-x
Förstermann, U. (2008). Oxidative stress in vascular disease: Causes, defense mechanisms and potential therapies. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine, 5(6), 338–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpcardio1211
Furtak, K., & Gajda, A. M. (2018). Activity and variety of soil microorganisms depending on the diversity of the soil tillage system. In Sustainability of Agroecosystems. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.72966
Garrido, S., Del Campo, G. M., Esteller, M. V., Vaca, R., & Lugo, J. (2005). Heavy metals in soil treated with sewage sludge composting, their effect on yield and uptake of broad bean seeds (Vicia faba L.). Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 166(1–4), 303–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-5269-4
Ghosh, N., & Singh, R. (2009). Groundwater arsenic contamination in India: Vulnerability and scope for remedy. National Institute of Hydrology, Uttarakhand, 1–24. http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:Groundwater+Arsenic+Contamination+in+India+:+Vulnerability+and+Scope+for+Remedy#0. Accessed 9 June 2022
Godt, J., Scheidig, F., Grosse-Siestrup, C., Esche, V., Brandenburg, P., Reich, A., & Groneberg, D. A. (2006). The toxicity of cadmium and resulting hazards for human health. Journal of Occupational Medicine and Toxicology (london, England), 1(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-1-22
Hamelink, J. L., & SETAC (Society). (1994). Bioavailability: physical, chemical, and biological interactions. Lewis Publishers. https://www.routledge.com/Bioavailability-Physical-Chemical-and-Biological-Interactions/Hamelink-Landrum-Bergman-Benson/p/book/9781566700863. Accessed 26 May 2023
Hayes’ principles and methods of toxicology - Google Books. (n.d.). https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=p4fOBQAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&ots=WbAoDLmjMd&sig=Lkh9Ds-nuR4xoa3ubY3bH0Eou4E&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q&f=false. Accessed 27 June 2022
Hazelhoff, M. H., & Torres, A. M. (2018). Gender differences in mercury-induced hepatotoxicity: Potential mechanisms. Chemosphere, 202, 330–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.106
He, Z. L., Yang, X. E., & Stoffella, P. J. (2005). Trace elements in agroecosystems and impacts on the environment. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 19(2–3), 125–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2005.02.010
Heavy metals polluting Kolkata’s groundwater. (n.d.). https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/heavy-metals-polluting-kolkatas-groundwater--6076. Accessed 28 June 2022
Helmenstine, A. M. (2019). Interesting Facts About Arsenic. september 2019. https://www.thoughtco.com/interesting-arsenic-element-facts-603360. Accessed 8 June 2022
High cadmium levels in fly ash at 2 waste plants in Delhi | Delhi News - Times of India. (n.d.). https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/delhi/high-cadmium-levels-in-fly-ash-at-2-waste-plants/articleshow/78373923.cms. Accessed 24 June 2022
Holmes, A. L., Wise, S. S., Sandwick, S. J., & Wise, J. P. (2006). The clastogenic effects of chronic exposure to particulate and soluble Cr(VI) in human lung cells. Mutation Research/genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 610(1–2), 8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2006.06.006
Huy, T., Tuyet-Hanh, T., Johnston, R., & Nguyen-Viet, H. (2014). Assessing health risk due to exposure to arsenic in drinking water in Hanam Province, Vietnam. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(8), 7575–7591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110807575
Idrees, N., Tabassum, B., Abd Allah, E. F., Hashem, A., Sarah, R., & Hashim, M. (2018). Groundwater contamination with cadmium concentrations in some West U.P. Regions, India. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 25(7), 1365. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SJBS.2018.07.005
Järup, L. (2003). Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin, 68(1), 167–182. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldg032
Jensen, T. J., Novak, P., Eblin, K. E., Gandolfi, J. A., & Futscher, B. W. (2008). Epigenetic remodeling during arsenical-induced malignant transformation. Carcinogenesis, 29(8), 1500–1508. https://doi.org/10.1093/CARCIN/BGN102
Jordão, C. P., Nascentes, C. C., Cecon, P. R., Fontes, R. L. F., & Pereira, J. L. (2006). Heavy metal availability in soil amended with composted urban solid wastes. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 112(1–3), 309–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1072-y
Joseph, P., Muchnok, T. K., Klishis, M. L., Roberts, J. R., Antonini, J. M., Whong, W. Z., & Ong, T. M. (2001). Cadmium-Induced cell transformation and tumorigenesis are associated with transcriptional activation of c-fos, c-jun, and c-myc proto-oncogenes: Role of cellular calcium and reactive oxygen species. Toxicological Sciences, 61(2), 295–303. https://doi.org/10.1093/TOXSCI/61.2.295
Joseph, P., O’Kernick, C. M., Othumpangat, S., Lei, Y. X., Yuan, B. Z., & Ong, T. M. (2004). Expression profile of eukaryotic translation factors in human cancer tissues and cell lines. Molecular Carcinogenesis, 40(3), 171–179. https://doi.org/10.1002/MC.20033
Karaca, A., Cetin, S. C., Turgay, O. C., & Kizilkaya, R. (2010). Effects of heavy metals on soil enzyme activities (pp. 237–262). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02436-8_11
Keshav Krishna, A., & Rama Mohan, K. (2016). Distribution, correlation, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface soils around an industrial area, Hyderabad, India. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(5), 411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5151-7
Kitchin, K. T. (2001). Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: Modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 172(3), 249–261. https://doi.org/10.1006/TAAP.2001.9157
Klaassen, C. D., Liu, J., & Diwan, B. A. (2009). Metallothionein protection of cadmium toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 238(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2009.03.026
Klein, C. B., Leszczynska, J., Hickey, C., & Rossman, T. G. (2007). Further evidence against a direct genotoxic mode of action for arsenic-induced cancer. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222(3), 289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2006.12.033
Kligerman, A. D., & Tennant, A. H. (2007). Insights into the carcinogenic mode of action of arsenic. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 222(3), 281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TAAP.2006.10.006
Kretchik, J. T. (2002). Arsenic in drinking water. Chemical Health and Safety, 9(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1074-9098(02)00298-8
Kumar, A., Ali, M., Kumar, R., Kumar, M., Sagar, P., Pandey, R. K., et al. (2021). Arsenic exposure in Indo Gangetic plains of Bihar causing increased cancer risk. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 2376. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81579-9
Kumar, S., Sciences, A., Gupta, R., Sciences, A., Ganguly, A., & Sciences, A. (2019). Status of toxic heavy metals in cattle of haryana, (June). https://www.cabi.org/environmentalimpact/abstract/20193386303. Accessed 29 June 2022
Kumari, S., Jain, M. K., & Elumalai, S. P. (2021). Assessment of pollution and health risks of heavy metals in particulate matter and road dust along the road network of Dhanbad, India. Journal of Health and Pollution, 11(29), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-11.29.210305
Lead, Nickel poisoning may be cause of mystery illness in Southern India. (n.d.). https://www.forbes.com/sites/siladityaray/2020/12/09/lead-nickel-poisoning-may-be-cause-of-mystery-illness-in-southern-india/?sh=571355627ea8. Accessed 27 June 2022
Lech, T., & Sadlik, J. K. (2017). Cadmium concentration in human autopsy tissues. Biological Trace Element Research, 179(2), 172–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12011-017-0959-5
Lee, M. J., Nishio, H., Ayaki, H., Yamamoto, M., & Sumino, K. (2002). Upregulation of stress response mRNAs in COS-7 cells exposed to cadmium. Toxicology, 174(2), 109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00045-8
Lee, C. H., Wu, S. B., Hong, C. H., Chen, G. S., Wei, Y. H., & Yu, H. S. (2013). Involvement of mtDNA damage elicited by oxidative stress in the arsenical skin cancers. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 133(7), 1890–1900. https://doi.org/10.1038/JID.2013.55/ATTACHMENT/447CF2F4-D7BF-41C9-8CC0-688492746E45/MMC1.PDF
Lenntech Water Treatment Solutions. (2017). Lead (Pb) - Chemical properties, health and environmental effects. Lenntech. https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/pb.htm. Accessed 6 June 2022
Lenntech. (2019). Cadmium (Cd) - Chemical properties, health and environmental effects. Lenntech. https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/cd.htm. Accessed 6 June 2022
Levina, A., & Lay, P. A. (2005). Mechanistic studies of relevance to the biological activities of chromium. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 249(3–4), 281–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CCR.2004.02.017
Li, L., Jiang, B., Lai, J., Dai, W. R., Li, X., & Liu, W. F., et al. (2017). [Change in peripheral nervous conduction velocity in patients with occupational chronic mercury poisoning and related influencing factors]. Zhonghua lao dong wei sheng zhi ye bing za zhi = Zhonghua laodong weisheng zhiyebing zazhi = Chinese journal of industrial hygiene and occupational diseases, 35(8), 598–602. https://doi.org/10.3760/CMA.J.ISSN.1001-9391.2017.08.011
Liu, K. J., & Shi, X. (2001). In vivo reduction of chromium (VI) and its related free radical generation. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 222(1–2), 41–47. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017994720562
Liu, J., Qian, S. Y., Guo, Q., Jiang, J. J., Waalkes, M. P., Mason, R. P., & Kadiiska, M. B. (2008). Cadmium generates reactive oxygen- and carbon-centered radical species in rats: Insights from in vivo spin-trapping studies. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 45(4), 475–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.04.041
Martin, S. E., & Griswold, W. (2009a). Environmental science and technology briefs for citizens human health effects of heavy metals. Environmental Science and Technology Briefs for Citizen. www.engg.ksu.edu/CHSR/. Accessed 2 May 2021
Martin, S. E., & Griswold, W. (2009b). Human health effects of heavy metals. Environmental Science and Technology Briefs for Citizens, 15, 5. https://engg.k-state.edu/chsr/files/chsr/outreachresources/15HumanHealthEffectsofHeavyMetals.pdf. Accessed 2 May 2021
Martinez, V. D., Thu, K. L., Vucic, E. A., Hubaux, R., Adonis, M., Gil, L., et al. (2013). Whole-genome sequencing analysis identifies a distinctive mutational spectrum in an arsenic-related lung tumor. Journal of Thoracic Oncology, 8(11), 1451–1455. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0B013E3182A4DD8E
Masindi, V., & Muedi, K. L. (2018). Environmental contamination by heavy metals. In Heavy Metals. InTech. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.76082
Matés, J. M. (2000). Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology, 153(1–3), 83–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00306-1
Mense, S. M., & Zhang, L. (2006). Heme: a versatile signaling molecule controlling the activities of diverse regulators ranging from transcription factors to MAP kinases. Cell Research, 16(8), 681–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7310086
Mercury | Toxicological Profile | ATSDR. (n.d.). https://wwwn.cdc.gov/TSP/ToxProfiles/ToxProfiles.aspx?id=115&tid=24. Accessed 28 June 2022
Mercury facts - Periodic table of the elements. (n.d.). https://www.thoughtco.com/mercury-facts-606560. Accessed 27 June 2022
Mercury pollution of India. (n.d.). https://www.cseindia.org/mercury-pollution-of-india-439. Accessed 28 June 2022
Mishra, B. U. (2019). High levels of arsenic found in groundwater in UP, (May), 1–4. https://www.thehindubusinessline.com/news/science/high-levels-of-arsenic-found-in-groundwater-in-up/article27329332.ece. Accessed 9 June 2022
Misra, U. K., Gawdi, G., Akabani, G., & Pizzo, S. V. (2002). Cadmium-induced DNA synthesis and cell proliferation in macrophages: The role of intracellular calcium and signal transduction mechanisms. Cellular Signalling, 14(4), 327–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00268-6
Mochizuki, H. (2019). Arsenic neurotoxicity in humans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3418. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS20143418
Mohan, V. R., Sharma, S., Ramanujam, K., Babji, S., Koshy, B., Bondu, J. D., et al. (2014). Effects of elevated blood lead levels in preschool children in urban Vellore. Indian Pediatrics, 51(8), 621–625. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13312-014-0464-2
Musilova, J., Arvay, J., Vollmannova, A., Toth, T., & Tomas, J. (2016). Environmental contamination by heavy metals in region with previous mining activity. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 97(4), 569–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1907-3
Namgung, U., & Xia, Z. (2001). Arsenic induces apoptosis in rat cerebellar neurons via activation of JNK3 and p38 MAP kinases. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 174(2), 130–138. https://doi.org/10.1006/TAAP.2001.9200
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2017). Cadmium | Cd - PubChem. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/cadmium#section=Physical-Description. Accessed 23 June 2022
Nelson, L. S., Howland, M. A., Lewin, N. A., Smith, S. W., Goldfrank, L. R., & Hoffman, R. S. (n.d.). Goldfrank’s toxicologic emergencies (11th ed.). McGraw Hill Medical. https://accesspharmacy.mhmedical.com/book.aspx?bookID=2569. Accessed 26 May 2023
Nishijo, M., Nakagawa, H., Suwazono, Y., Nogawa, K., & Kido, T. (2017). Causes of death in patients with Itai-itai disease suffering from severe chronic cadmium poisoning: A nested case-control analysis of a follow-up study in Japan. BMJ Open, 7(7), e015694. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015694
No action as mercury still poisons fish in West Bengal - Reporter At-Large. (n.d.). https://www.reporteratlarge.org/no-action-as-mercury-still-poisons-fish-in-west-bengal/. Accessed 28 June 2022
Nohara, K., Tateishi, Y., Suzuki, T., Okamura, K., Murai, H., Takumi, S., et al. (2012). Late-onset increases in oxidative stress and other tumorigenic activities and tumors with a Ha-ras mutation in the liver of adult male C3H mice gestationally exposed to arsenic. Toxicological Sciences, 129(2), 293–304. https://doi.org/10.1093/TOXSCI/KFS203
Nordberg, G. F., Fowler, B. A., Nordberg, M., & Friberg, L. T. (2007). Handbook on the toxicology of metals. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-369413-3.X5052-6
Ohno, M. (2005). Mercury: chemical properties - Canada.ca. Physical Review B. https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/pollutants/mercury-environment/about/chemical-properties.html. Accessed 27 June 2022
Oliveira, G. B., Fontes, E. D. A., De Carvalho, S., Da Silva, J. B., Fernandes, L. M. P., Oliveira, M. C. S. P., et al. (2014). Minocycline mitigates motor impairments and cortical neuronal loss induced by focal ischemia in rats chronically exposed to ethanol during adolescence. Brain Research, 1561, 23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2014.03.005
P Oppili. (2020). Tamil Nadu: Paints continue to have more lead than prescribed | Chennai News - Times of India. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/chennai/tamil-nadu-paints-continue-to-have-more-lead-than-prescribed/articleshow/76528281.cms. Accessed 27 June 2022
Park, S. H., Araki, S., Nakata, A., Kim, Y. H., Park, J. A., Tanigawa, T., et al. (2000). Effects of occupational metallic mercury vapour exposure on suppressor-inducer (CD4+CD45RA+) T lymphocytes and CD57+CD16+ natural killer cells. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 73(8), 537–542. https://doi.org/10.1007/S004200000173
Patrick, L. (2006). Lead toxicity part II: The role of free radical damage and the use of antioxidants in the pathology and treatment of lead toxicity. Alternative Medicine Review : a Journal of Clinical Therapeutic, 11(2), 114–27. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16813461/. Accessed 16 February 2022
Pearce, J. M. S. (2007). Burton’s line in lead poisoning. European Neurology, 57(2), 118–119. https://doi.org/10.1159/000098100
Pearce, N., Blair, A., Vineis, P., Ahrens, W., Andersen, A., Anto, J. M., et al. (2015). IARC monographs: 40 years of evaluating carcinogenic hazards to humans. Environmental Health Perspectives, 123(6), 507–514. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1409149
Presence of hexavalent chromium: UP pollution control board to undertake detailed groundwater sampling - Hindustan Times. (n.d.). https://www.hindustantimes.com/cities/presence-of-hexavalent-chromium-up-pollution-control-board-to-undertake-detailed-groundwater-sampling/story-Arkk31uBFY8FyRurFBbjKI.html. Accessed 28 June 2022
Properties, P. (2000). Physical Properties of the chromium. Structure and Bonding, 6(Table 1), 1–11. https://www.thoughtco.com/chromium-element-facts-606519. Accessed 28 June 2022
Prozialeck, W. C., Lamar, P. C., & Lynch, S. M. (2003). Cadmium alters the localization of N-cadherin, E-cadherin, and beta-catenin in the proximal tubule epithelium. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 189(3), 180–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0041-008x(03)00130-3
Pulido, M. D., & Parrish, A. R. (2003). Metal-induced apoptosis: Mechanisms. Mutation Research/fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 533(1–2), 227–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRFMMM.2003.07.015
Qin, X. J., Hudson, L. G., Liu, W., Ding, W., Cooper, K. L., & Liu, K. J. (2008). Dual actions involved in arsenite-induced oxidative DNA damage. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 21(9), 1806–1813. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx8001548
Rahman, Z., & Singh, V. P. (2019). The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7528-7
Rani, A., Kumar, A., Lal, A., & Pant, M. (2014). Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: A review. International Journal of Environmental Health Research. Taylor & Francis. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.835032
Ratnaike, R. N. (2003). Acute and chronic arsenic toxicity. Postgraduate Medical Journal, 79(933), 391–396. https://doi.org/10.1136/PMJ.79.933.391
Rin, K., Kawaguchi, K., Oku, N., Okada, S., Yamanaka, K., & Tezuka, M. (1995). DNA-strand breaks induced by dimethylarsinic acid, a metabolite of inorganic arsenics, are strongly enhanced by superoxide anion radicals. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 18(1), 45–48. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.18.45
Sauvé, S. (2014). Time to revisit arsenic regulations: Comparing drinking water and rice. BMC Public Health, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-14-465
Schaefer, H. R., Dennis, S., & Fitzpatrick, S. (2020). Cadmium: Mitigation strategies to reduce dietary exposure. Journal of Food Science, 85(2), 260–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14997
Shah, F. U. R., Ahmad, N., Masood, K. R., Peralta-Videa, J. R., & Ahmad, F. U. D. (2010). Heavy metal toxicity in plants. In Plant Adaptation and Phytoremediation. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-90-481-9370-7_4
Shekhawat, K., Chatterjee, S., & Joshi, B. (2016). Chromium toxicity and its health hazards. International Journal of Advanced Research, 3(July 2016), 167. http://www.journalijar.com/article/5151/chromium-toxicity-and-its-health-hazards/. Accessed 2 May 2021
Shi, H., Shi, X., & Liu, K. J. (2004). Oxidative mechanism of arsenic toxicity and carcinogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MCBI.0000007262.26044.e8
Shih, C. M., Ko, W. C., Wu, J. S., Wei, Y. H., Wang, L. F., Chang, E. E., et al. (2004). Mediating of caspase-independent apoptosis by cadmium through the mitochondria-ROS pathway in MRC-5 fibroblasts. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 91(2), 384–397. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCB.10761
Silbergeld, E. K. (2003). Facilitative mechanisms of lead as a carcinogen. Mutation Research - Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 533(1–2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRFMMM.2003.07.010
Silbergeld, E. K., Waalkes, M., & Rice, J. M. (2000). Lead as a carcinogen: Experimental evidence and mechanisms of action - Silbergeld - 2000 - American Journal of Industrial Medicine - Wiley Online Library. American journal of …, 38(February), 316–323. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0274(200009)38:3%3C316::AID-AJIM11%3E3.0.CO;2-P. Accessed 23 January 2022
Singh, N., Kumar, D., & Sahu, A. P. (2007). Arsenic in the environment: Effects on human health and possible prevention. Journal of environmental biology, 28(2 Suppl), 359–65. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17929751. Accessed 1st May 2022
Smirnova, I. V., Bittel, D. C., Ravindra, R., Jiang, H., & Andrews, G. K. (2000). Zinc and cadmium can promote rapid nuclear translocation of metal response element-binding transcription factor-1 *. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275(13), 9377–9384. https://doi.org/10.1074/JBC.275.13.9377
Smith, A. H., Arroyo, A. P., Guha Mazumder, D. N., Kosnett, M. J., Hernandez, A. L., Beeris, M., et al. (2000). Arsenic-induced skin lesions among Atacameno people in Northern Chile despite good nutrition and centuries of exposure. Environmental Health Perspectives, 108(7), 617–620. https://doi.org/10.1289/EHP.00108617
Snehal Fernandes. (n.d.). Soil around Mumbai’s garbage dumps contains hazardous levels of mercury: Study | mumbai news | Hindustan Times. https://www.hindustantimes.com/mumbai-news/soil-around-mumbai-s-garbage-dumps-contains-hazardous-levels-of-mercury-study/story-qAv4Qds9V4zQmZ2Nq3vssN.html. Accessed 28 June 2022
Tchounwou, P. B., Yedjou, C. G., Patlolla, A. K., & Sutton, D. J. Heavy metal toxicity and the environment. , 101 EXS 133–164 (2012). Springer, Basel.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
The Editors of Encyclopaedia. (Ed.). (n.d.). Cadmium | Uses, Properties, & facts. In Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/science/cadmium. Accessed 23 June 2022
The Poisoning of Punjab | Pulitzer Center. (n.d.). https://pulitzercenter.org/stories/poisoning-punjab. Accessed 24 June 2022
Toxicological Profile for Lead. (2007). Agency for toxic substances and disease registry. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK589538/. Accessed 26 May 2023
Valko, M., Morris, H., & Cronin, M. (2005). Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 12(10), 1161–1208. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867053764635
Ventura, L. M. B., Mateus, V. L., de Almeida, A. C. S. L., Wanderley, K. B., Taira, F. T., Saint’Pierre, T. D., & Gioda, A. (2017). Chemical composition of fine particles (PM2.5): Water-soluble organic fraction and trace metals. Air Quality, Atmosphere & Health, 10(7), 845–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11869-017-0474-Z
Vimercati, L., Santarelli, L., Pesola, G., Drago, I., Lasorsa, G., Valentino, M., et al. (2001). Monocyte-macrophage system and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in workers exposed to low levels of metallic mercury. Science of the Total Environment, 270(1–3), 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(00)00780-4
Waalkes, M. P. (2003). Cadmium carcinogenesis. Mutation Research, 533(1–2), 107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRFMMM.2003.07.011
Waalkes, M. P., Rehm, S., & Cherian, M. G. (2000). Repeated cadmium exposures enhance the malignant progression of ensuing tumors in rats. Toxicological Sciences : An Official Journal of the Society of Toxicology, 54(1), 110–120. https://doi.org/10.1093/TOXSCI/54.1.110
Wang, X.-J., Sun, Z., Chen, W., Eblin, K. E., Gandolfi, J. A., & Zhang, D. D. (2007). Nrf2 protects human bladder urothelial cells from arsenite and monomethylarsonous acid toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 225(2), 206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2007.07.016
Wang, J., Zhu, H., Yang, Z., & Liu, Z. (2013). Antioxidative effects of hesperetin against lead acetate-induced oxidative stress in rats. Indian Journal of Pharmacology, 45(4), 395–398. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.115015
Wani, A. L., Ara, A., & Usmani, J. A. (2015). Lead toxicity: A review. Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 8(2), 55–64. https://doi.org/10.1515/intox-2015-0009
Wasim Aktar, M., Paramasivam, M., Ganguly, M., Purkait, S., & Sengupta, D. (2010). Assessment and occurrence of various heavy metals in surface water of Ganga river around Kolkata: A study for toxicity and ecological impact. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 160(1–4), 207–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-008-0688-5
Wilbur, S., Abadin, H., Fay, M., Yu, D., Tencza, B., & Ingerman, L., et al. (2002). Toxicological profile for chromium. In ATSDR’s Toxicological Profiles (p. 592). CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420061888_ch63
Wild, C. P. (2014). International Agency for Research on Cancer. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology (pp. 1067–1069). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.00402-4
Wise, S. S., Holmes, A. L., & Wise, J. P. (2006). Particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium are cytotoxic and genotoxic to human lung epithelial cells. Mutation Research/genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis, 610(1–2), 2–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MRGENTOX.2006.06.005
Wu, X., Cobbina, S. J., Mao, G., Xu, H., Zhang, Z., & Yang, L. (2016). A review of toxicity and mechanisms of individual and mixtures of heavy metals in the environment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(9), 8244–8259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6333-x
Wynne, B. (2012). Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). In Encyclopedia of Global Health. 2455 Teller Road, Thousand Oaks California 91320 United States: SAGE Publications, Inc. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412963855.n24
Yasutake, A., Sawada, M., Shimada, A., Satoh, M., & Tohyama, C. (2004). Mercury accumulation and its distribution to metallothionein in mouse brain after sub-chronic pulse exposure to mercury vapor. Archives of Toxicology, 78(9), 489–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00204-004-0572-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualisation, research and ideation – Lucky Parida and Trupti N. Patel; construct of manuscript – Lucky Parida and Trupti N. Patel.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All authors have read, understood, and have complied as applicable with the statement on “Ethical responsibilities of Authors” as found in the Instructions for Authors and are aware that with minor exceptions, no changes can be made to authorship once the paper is submitted.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Parida, L., Patel, T.N. Systemic impact of heavy metals and their role in cancer development: a review. Environ Monit Assess 195, 766 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11399-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11399-z