Abstract
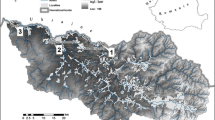
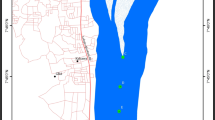
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) contain two or more benzene rings and are categorized as general environmentally harmful pollutants. PAHs occur because of various combustion and pyrolysis processes with different environmental and anthropogenic sources. The Kizilirmak River is one of the major important water sources used for drinking water and irrigation purposes in Turkey. There are important industrial facilities around the river and PAH pollution is important in terms of environmental health. This study was carried out to determine the residues of PAHs in water and sediment samples according to month and to identify the pollution sources. Thus, water and sediment samples were collected from five different stations in the Kirikkale basin of the Kizilirmak River every 15 days for a year. In this way, 120 water and 120 sediment samples were collected over a year and analyzed in terms of 16 priority PAHs according to the Environmental Protection Agency. The monthly average of the water and sediment samples was calculated. Analyses were carried out with high-performance liquid chromatography based on solid phase extraction. GC–MS was used for confirmation. Acenaphthene, acenaphthylene, benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzo[a]pyrene, indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene, and dibenzo[a,h]anthracene were not found in the water samples. The total PAH levels in water and sediment were detected in the range of 0.04 to 1.545 μg/L and 43.15–386.115 μg/kg, respectively. PAHs found in water and sediment samples had pyrogenic and petrogenic origin and pollution changed significantly between autumn and winter. As a result, precautions should be taken in terms of preventing environmental pollution.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supplementary data of this study is given in addition.
References
Arslan, P., Ozeren, S. C. (2021). A case study of 38 micro-organic pollutants contamination in Kirmir Stream, Turkey. Environmental Quality Management. https://doi.org/10.1002/tqem21811
Blahova, J., Divisova, L., Kodes, V., Leontovycova, D., Mach, S., Ocelka, T., Svobodova, Z. (2014). Integrated assessment of PAH contamination in the Czech Rivers using a combination of chemical and biological monitoring. Hindawi Publishing Corporation The Scientific World Journal, 918097, 6.
Chen, Q., Liu, J., Liu, F., Wang, B., Cao, Z. (2014). Biologic risk and source diagnose of 16 PAHs from Haihe River Basin, China. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-014-0717-2
Chen, Y., Sun, C., Zhang, J., & Zhang, F. (2018). Assessing 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocrbons (PAHS) in river basin water and sediment regarding spatial-temporal distribution, partitioning, and ecological risks. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 27(2), 579–589.
Çetindamar, D., Veli, S., Öztürk, T., Arslanbaş, D., Aslan Kilavuz, S., Çetin Doğruparmak, Ş., Can Doğan, E. (2014). Topraklarda PCB ve PAH’ların İncelenmesi: Alikahya Bölgesi. Politeknik Dergisi Cilt: 17 Sayı, 3, 127–133.
Ergönül, P. G., & Kaya, D. (2015). Polisiklik Aromatik Hidrkarbonlar ve Gıdalarda Önemi. CBÜ Fen Bil. Dergisi Cilt 11. Sayı, 2, 143–153.
Honda, M., Suzuki, N. (2020). Toxicities of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons for aquatic animals. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041363
Kafilzadeh, F., Shiva, A. H., & Malekpour, R. (2011). Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediments of the Kor River Iran. Middle-East Journal of Scientific Research, 10(1), 01–07.
Keshavarzifard, M., Zakaria, M. P., Hwai, T. Z., Yusuff, F. M., Mustafa, S., Vaezzadeh, V., Magam, S. M., Masood, N., Alkhader, S. A. A., & Abootalebi-Jahromi, A. (2014). Baseline distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the surface sediments from the Prai and Maalacca Rivers, Peninsular Malaysia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 88, 366–372.
Kuppusamy, S.,Thavamani, P., Megharaj, M., Naidu, R. (2016). Biodegradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHS) by novel bacterial consortia tolerant to diverse physical settings- Assessments in liquid – and slurry –phase systems. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 108, 149–157.
Kuzukiran, Ö., Yurdakök Dikmen, B., Totan, F. E., Çelik, C., Orhan, E. C., Bilir, E. K., Kara, E., & Filazi, A. (2016). Analytical method development and validation for some persistent organic pollutants in water and sediments by gas chromotography and mass spectrometry. International Journal of Environmental Research, 10(3), 401–410.
Nagy, P., Fekete, J., & Sharma, V. K. (2008). Monofluorinated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Surrogate standards for HPLC analysis of surface water and sediment samples. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 31, 240–249.
Palamutoğlu, R., Sariçoban, C., Kasnak, C. (2014). Polisiklik Aromatik Hidrokarbonlar (PAH) ve Et Ürünlerinde Oluşumu. Gıda Teknolojileri Elektronik Dergisi Cilt, 9(3), 47–57.
Pohl, A., Kostecki, M., Jureczko, I., Czaplicka, M., & Lozowski, B. (2018). Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and bottom sediments of a shallow, lowland dammed reservoir (on the example of the reservoir Blachownia, South Poland). Archives of Environmental Protection, 44(1), 10–23.
Sevin, S., Kuzukiran, Ö., Yurdakok-Dikmen, B., Tutun, H., Aydin, F. G., & Filazi, A. (2018). Selected persistent organic pollutants levels in the Ankara River by months. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 705.
Simsek, I., Kuzukiran, Ö., Yurdakok-Dikmen, B., Sireli, U. T., Beykaya, M., & Filazi, A. (2021). Comparison of selected lipophilic compound residues in honey and propolis. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis, 102, 104068.
Sun, C., Zhang, J., Ma, Q., Chen, Y., & Ju, H. (2017). Polycyclic aromatic haydrocarbons (PAHS) in water and sedment from a river basin: Sediment-water partitioning, source identification and environmental health risk assesment. Environ Geochem Healt, 39, 63–74.
Ye, Q., Liang, C., Chen, X., Fang, T., Wang, Y., & Wang, H. (2019). Molecular characterization of methanogenic microbial communities for degrading various types of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 86, 97–106.
Zhao, X., Ding, J., & You, H. (2014). Spatial distribution and temporal trends of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water and sediment from Songhua River, China. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36, 131–143.
Zhao, Z., Gong, X., Zhang, L., Jin, M., Cai, Y., & Wang, X. (2021). Riverine transport and water-sediment exchange of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) along the middle-lower Yangtze River China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 403, 123973.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Ankara University Scientific Research Projects Directorate with project number 16L0239001. We are thankful for their support. We thank Associate Professor Özgür Kuzukıran and Professor Dr. Ayhan Filazi for their assistance with laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
İS: conceptualization, methodology, material collection, investigation, performing analysis, writing; AB: conceptualization, methodology, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Şimşek, İ., Bilgili, A. Investigation of monthly residues of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and sediment samples from Kirikkale Kizilirmak River Basin. Environ Monit Assess 194, 683 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10344-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10344-w