Abstract
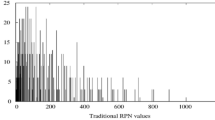
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is one of the most used methods in risk assessment and prioritization. This study was conducted to identify, evaluate, prioritize, and analyze risks associated with the physical processes of Sahand municipal wastewater plant using traditional and fuzzy FMEA methods. The present research was a cross-sectional analytical study that was conducted to prioritize the risks of unit operations of screening and grit removal in Sahand municipal wastewater treatment plant for 6 months. First, a team of five experts was formed and the traditional FMEA worksheet was completed. Then, the fuzzy membership functions were determined according to experts’ opinions and using the MATLAB program, and the severity, occurrence, detection, and risk priority number (RPN) became fuzzy and risks were prioritized according to the fuzzy logic outputs. A total of 53 failure modes were identified for screening (26 failures) and grit removal units (27 failures) using the traditional FMEA risk assessment technique. The results of the traditional FMEA method showed that among the 53 identified failure modes, in physical treatment equipment of Sahand municipal wastewater, 51 failures (96.2%) were in the low-risk levels and two failures (3.8%) were in the medium-risk levels. According to the results of the fuzzy FMEA, 5 failures (9.4%) were in the low-risk levels, 43 failures (81.2%) were in the medium-risk levels, and 5 failures (9.4%) were in the high-risk levels. Based on the traditional FMEA, the highest and lowest level of risk belonged to manual screening clogging and conveyor cutting of mechanical screening with RPN of 540 and 12, respectively, whereas in the fuzzy FMEA, the highest and lowest level of risk were related to manual screening clogging and fracture of pump pipes with RPN of 894 and 105, respectively. The finding showed that risk assessment using fuzzy FMEA provides more accurate and better results than traditional FMEA. In the fuzzy FMEA, the involvement of the experts’ opinions in risk assessment and fuzzy models leads to more realistic results, as well as corrective action prioritization is better performed.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Abbas, M. A., Iqbal, M., Tauqeer, H. M., Turan, V., & Farhad, M. (2022). Microcontaminants in wastewater. In Environmental Micropollutants (pp. 315–329). Elsevier.
Abdelgawad, M., & Fayek, A. R. (2010). Risk management in the construction industry using combined fuzzy FMEA and fuzzy AHP. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 136(9), 1028–1036.
Adegoke, A. A., Amoah, I. D., Stenström, T. A., Verbyla, M. E., & Mihelcic, J. R. (2018). Epidemiological evidence and health risks associated with agricultural reuse of partially treated and untreated wastewater: A review. Frontiers in Public Health, 337.
Alvand, A., Mirhosseini, S. M., Ehsanifar, M., Zeighami, E., & Mohammadi, A. (2021). Identification and assessment of risk in construction projects using the integrated FMEA-SWARA-WASPAS model under fuzzy environment: A case study of a construction project in Iran. International Journal of Construction Management, 1–23.
Anes, V., Henriques, E., Freitas, M., & Reis, L. (2018). A new risk prioritization model for failure mode and effects analysis. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 34(4), 516–528.
Ashley, L., Armitage, G., Neary, M., & Hollingsworth, G. (2010). A practical guide to failure mode and effects analysis in health care: Making the most of the team and its meetings. The Joint Commission Journal on Quality and Patient Safety, 36(8), 351–358.
Azadeh, A., Fam, I. M., Nouri, J., & Azadeh, M. A. (2008). Integrated health, safety, environment and ergonomics management system (HSEE-MS): An efficient substitution for conventional HSE-MS. Journal of Science and Industria Research, 67(6), 403–411.
Balaraju, J., Raj, M. G., & Murthy, C. S. (2019). Fuzzy-FMEA risk evaluation approach for LHD machine–A case study. Journal of Sustainable Mining, 18(4), 257–268.
Boral, S., & Chakraborty, S. (2021). Failure analysis of CNC machines due to human errors: An integrated IT2F-MCDM-based FMEA approach. Engineering Failure Analysis, 130, 105768.
Chanamool, N., & Naenna, T. (2016). Fuzzy FMEA application to improve decision-making process in an emergency department. Applied Soft Computing, 43, 441–453.
Chang, K. H., & Cheng, C. H. (2010). A risk assessment methodology using intuitionistic fuzzy set in FMEA. International Journal of Systems Science, 41(12), 1457–1471.
Chang, K. H., Cheng, C. H., & Chang, Y. C. (2010). Reprioritization of failures in a silane supply system using an intuitionistic fuzzy set ranking technique. Soft Computing, 14(3), 285.
Chen, Z., Wu, X., & Qin, J. (2014). Risk assessment of an oxygen-enhanced combustor using a structural model based on the FMEA and fuzzy fault tree. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 32, 349–357.
Cruz-Rivero, L., Méndez-Hernández, M. L., Mar-Orozco, C. E., Aguilar-Lasserre, A. A., Barbosa-Moreno, A., & Sánchez-Escobar, J. (2022). Functional evaluation using fuzzy FMEA for a non-invasive measurer for methane and carbone dioxide. Symmetry, 14(2), 421.
Damanab, P. S., Alizadeh, S. S., Rasoulzadeh, Y., Moshashaie, P., & Varmazyar, S. (2015). Failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) technique: A literature review. Scientific Journal of Review, 4(1), 1–6.
Eggen, R. I., Hollender, J., Joss, A., Schärer, M., & Stamm, C. (2014). Reducing the discharge of micropollutants in the aquatic environment: The benefits of upgrading wastewater treatment plants. ACS Publications, 7683–7689.
Ehsan, S., Ali, S., Noureen, S., Farid, M., Shakoor, M. B., Aslam, A., & Tauqeer, H. M. (2013). Comparative assessment of different heavy metals in urban soil and vegetables irrigated with sewage/industrial waste water. Ecoterra, 35, 37–53.
Escher, B. I., Baumgartner, R., Koller, M., Treyer, K., Lienert, J., & McArdell, C. S. (2011). Environmental toxicology and risk assessment of pharmaceuticals from hospital wastewater. Water Research, 45(1), 75–92.
Fattahi, R., & Khalilzadeh, M. (2018). Risk evaluation using a novel hybrid method based on FMEA, extended MULTIMOORA, and AHP methods under fuzzy environment. Safety Science, 102, 290–300.
Fytili, D., & Zabaniotou, A. (2008). Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 12(1), 116–140.
Guimarães, A. C. F., & Lapa, C. M. F. (2004). Fuzzy FMEA applied to PWR chemical and volume control system. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 44(3), 191–213.
Hamalainen, P., Saarela, K. L., & Takala, J. (2009). Global trend according to estimated number of occupational accidents and fatal work-related diseases at region and country level. Journal of Safety Research, 40(2), 125–139.
Ivancan, J., & Lisjak, D. (2021). New FMEA risks ranking approach utilizing four fuzzy logic systems. Machines, 9(11), 292.
Jiang, W., Xie, C., Wei, B., & Zhou, D. (2016). A modified method for risk evaluation in failure modes and effects analysis of aircraft turbine rotor blades. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 8(4), 1–16.
Jozi, S., Jafarzadeh Haghighi Fard, N., & Afzali, B. N. (2014). Hazard identification and risk assessment of high voltage power lines in residential areas using failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA). Iranian Journal of Health and Environment, 7(1), 55–64.
Karatop, B., Taşkan, B., Adar, E., & Kubat, C. (2021). Decision analysis related to the renewable energy investments in Turkey based on a Fuzzy AHP-EDAS-Fuzzy FMEA approach. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 151, 106958.
Khalil, M., Iqbal, M., Turan, V., Tauqeer, H. M., Farhad, M., Ahmed, A., & Yasin, S. (2022). Household chemicals and their impact. In Environmental Micropollutants (pp. 201–232). Elsevier.
Kolahdoozi, M., & Halvani, G. (2017). Relationship between prioritized control measures and reducing the risk level in the edible oil factory in Tehran. Occupational Medicine, 47–57.
Kutlu, A. C., & Ekmekçioğlu, M. (2012). Fuzzy failure modes and effects analysis by using fuzzy TOPSIS-based fuzzy AHP. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(1), 61–67.
Li, X., Li, H., Sun, B., & Wang, F. (2018). Assessing information security risk for an evolving smart city based on fuzzy and grey FMEA. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 34(4), 2491–2501.
Liu, H. C., Liu, L., & Liu, N. (2013). Risk evaluation approaches in failure mode and effects analysis: A literature review. Expert Systems with Applications, 40(2), 828–838.
Liu, H. C., Liu, L., Bian, Q. H., Lin, Q. L., Dong, N., & Xu, P. C. (2011). Failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy evidential reasoning approach and grey theory. Expert Systems with Applications, 38(4), 4403–4415.
Liu, H. C., You, J. X., & Duan, C. Y. (2019a). An integrated approach for failure mode and effect analysis under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy environment. International Journal of Production Economics, 207, 163–172.
Liu, H. C., Chen, X. Q., Duan, C. Y., & Wang, Y. M. (2019b). Failure mode and effect analysis using multi-criteria decision making methods: A systematic literature review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 135, 881–897.
Liu, H., Deng, X., & Jiang, W. (2017). Risk evaluation in failure mode and effects analysis using fuzzy measure and fuzzy integral. Symmetry, 9(8), 162.
Maleki, A. R., Zohour, A. R., Ebadifard Azar, F., Rezaie, K., & Ebadian, M. (2010). Health care centers QFD\FMEA design and modeling of an integrated structure. Payesh, 2(9), 117–130.
Mohsenzade, H., Razm Ara, H., Dashti, A., Roosta, H., Nakhaee, H., Tavakoli Aminian, S., Rouhbakhsh, M., & Fazayeli Torabi, A. (2020). Risk assessment for gas chlorination units of water and wastewater treatment with FMEA method. Journal of Water and Wastewater Science and Engineering, 5(4), 31–40.
Niu, Y. M., He, Y. Z., Li, J. H., & Zhao, X. J. (2009). The optimization of RPN criticality analysis method in FMECA. In 2009 International Conference on Apperceiving Computing and Intelligence Analysis, 166–170. IEEE.
Panchal, D., & Kumar, D. (2017). Risk analysis of compressor house unit in thermal power plant using integrated fuzzy FMEA and GRA approach. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 25(2), 228–250.
Pang, J., Dai, J., & Qi, F. (2021). A potential failure mode and effect analysis method of electromagnet based on intuitionistic fuzzy number in manufacturing systems. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021.
Rausand, M. (2005). Preliminary hazard analysis. Norwegian University of Science and Technology. System Reliability Theory, 2nd ed. Wiley.
Roozbahani, A., Zahraie, B., & Tabesh, M. (2013). Integrated risk assessment of urban water supply systems from source to tap. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 27(4), 923–944.
Rozenfeld, O., Sacks, R., Rosenfeld, Y., & Baum, H. (2010). Construction job safety analysis. Safety Science, 48(4), 491–498.
Sardar, K., Ali, S., Hameed, S., Afzal, S., Fatima, S., Shakoor, M. B., & Tauqeer, H. M. (2013). Heavy metals contamination and what are the impacts on living organisms. Greener Journal of Environmental Management and Public Safety, 2(4), 172–179.
Shakoor, M. B., Ali, S., Farid, M., Farooq, M. A., Tauqeer, H. M., Iftikhar, U., & Bharwana, S. A. (2013). Heavy metal pollution, a global problem and its remediation by chemically enhanced phytoremediation: A review. Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences, 3(3), 12–20.
Sharma, R. K., Kumar, D., & Kumar, P. (2005). Systematic failure mode effect analysis (FMEA) using fuzzy linguistic modelling. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management.
Shinta, F. R., Karnaningroem, N., & Mardyanto, M. A. (2019). Risk management of wastewater treatment in the wastewater treatment plant of PT. X. IPTEK. Journal of Proceedings Series, 5, 140–149.
Song, W., Ming, X., Wu, Z., & Zhu, B. (2014). A rough TOPSIS approach for failure mode and effects analysis in uncertain environments. Quality and Reliability Engineering International, 30(4), 473–486.
Tabesh, M., Badali Bavani, E., Asgarian, M., & Roozbahani, A. (2014). An algorithm for risk analysis and management of wastewater treatment plants. Iran-Water Resources Research, 10(3), 53–65.
Tabesh, M., Roozbahani, A., Hadigol, F., & Ghaemi, E. (2021). Risk assessment of water treatment plants using fuzzy fault tree analysis and Monte Carlo simulation. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering, 46, 643–658.
Tauqeer, H. M., Turan, V., Farhad, M., & Iqbal, M. (2022a). Sustainable agriculture and plant production by virtue of biochar in the era of climate change. In Managing Plant Production Under Changing Environment (pp. 21–42). Springer, Singapore.
Tauqeer, H. M., Turan, V., & Iqbal, M. (2022b). Production of safer vegetables from heavy metals contaminated soils: The current situation, concerns associated with human health and novel management strategies. In Advances in Bioremediation and Phytoremediation for Sustainable Soil Management (pp. 301–312). Springer, Cham.
Valipour Khatir, M., & Ghasemnia Arabi, N. (2017). Fuzzy Inference System modeling to assess the potential risks in the medical equipment. Industrial Management Journal, 8(4), 533–554.
Wang, W., Liu, X., Qin, Y., & Fu, Y. (2018). A risk evaluation and prioritization method for FMEA with prospect theory and Choquet integral. Safety Science, 110, 152–163.
Xiao, N., Huang, H. Z., Li, Y., He, L., & Jin, T. (2011). Multiple failure modes analysis and weighted risk priority number evaluation in FMEA. Engineering Failure Analysis, 18(4), 1162–1170.
Yarmohammadian, M. H., Toufighi, S., Saghaeiannezhad, E. S., & Naseri, B. T. (2007). Risks involved in medical records processes of Al-Zahra hospital. Health Information Management, 4, 51–59.
Yucesan, M., Gul, M., & Celik, E. (2021). A holistic FMEA approach by fuzzy-based Bayesian network and best–worst method. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 7(3), 1547–1564.
Zhang, X., Jin, F., & Liu, P. (2013). A grey relational projection method for multi-attribute decision making based on intuitionistic trapezoidal fuzzy number. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(5), 3467–3477.
Zhu, J., Wang, R., & Li, Y. (2018). Failure mode and effects analysis considering consensus and preferences interdependence. Algorithms, 11(4), 34.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the cooperation of the staff of Sahand Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant during this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh, S.S., Solimanzadeh, Y., Mousavi, S. et al. Risk assessment of physical unit operations of wastewater treatment plant using fuzzy FMEA method: a case study in the northwest of Iran. Environ Monit Assess 194, 609 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10248-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10248-9