Abstract
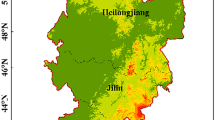
This study uses the daily product data of the concentration of ozone in the atmospheric column (ozone column concentration) collected by the Aura satellite’s Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI), to evaluate the ozone pollution status of the Fenwei Plain in east-central China, by employing pixel-based spatial analysis, an θslope trend index, a Hurst index, and grey correlation. The following results were found. (1) The spatial distribution of ozone in the atmosphere of the Fenwei Plain was higher in the north and lower in the south, with high values appearing in Jinzhong, Lvliang, and other cities. (2) The changes in ozone column concentration periodically and seasonally in the Fenwei Plain. Seasonally, the ozone column concentration was highest in spring, followed by summer, winter, and autumn. (3) The pixel-based trend change of the ozone slope (θslope) indicated that the ozone concentration in the region was in a downward trend, while the long-term correlation of the time series trend Hurst index found that the region should expect to see a weak rebound in the ozone column concentration in the future, so that routine monitoring should be strengthened. (4) The present study on the factors influencing the ozone concentration found that the concentration is relatively closely related to temperature, air pressure, humidity, grain sowing area, highway mileage, and secondary industry.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Archibald, A. T., Levine, J. G., Abraham, N. L., Cooke, M. C., Edwards, P. M., Heard, D. E., Jenkin, M. E., Karunaharan, A., Pike, R. C., Monks, P. S., Shallcross, D. E., Telford, P. J., Whalley, L. K., & Pyle, J. A. (2011). Impacts of HOx regeneration and recycling in the oxidation of isoprene: Consequences for the composition of past, present and future atmospheres. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(5), 1–6. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1029/2010GL046520
Balis, D., Kroon, M., Koukouli, M. E., Brinksma, E. J., Labow, G., Veefkind, J. P. & Mcpeters, R. D. (2007). Validation of Ozone Monitoring Instrument total ozone column measurements using Brewer and Dobson spectrophotometer ground-based observations. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(D24), D24S46. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD008796
Bao, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, M., Tang, W., & Meng, F. (2017). Characteristics of ozone pollution and typical daily causes of pollution in Dalian. China Environmental Monitoring, 33(04), 167–178. https://doi.org/10.19316/j.issn.1002-6002.2017.04.21
Bracher, A., Weber, M., Bramstedt, K., Coldewey-Egbers, M., & Burrows, J. P. (2005). Global satellite validation of SCIAMACHY O3 columns with GOME WFDOAS. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 5(1), 795–813. https://doi.org/10.5194/acpd-5-795-2005
Deng, X. J., Zhou X. J., Wu, D., Tie, X. X., Tan, H. B., Li, F., Bi, X. Y., Deng, T., & Jiang, D. H. (2011). Effect of atmospheric aerosol on surface ozone variation over the Pearl River Delta region. Scientia Sinica(Terrae), 41(1), 93–102. https://doi.org/10.1360/zd-2011-41-1-93
Fishman, J., & Crutzen, P. J. (1978). The origin of ozone in the troposphere. Nature, 274(5674), 855–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/274855a0
Hong, H., Lee, H., Kim, J., & Lee, Y. G. (2015). First comparison of OMI-DOAS total ozone using ground-based observations at a megacity site in East Asia: Causes of discrepancy and improvement in OMI-DOAS total ozone during summer. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 119(16), 10058–10067. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JD021829
Ito, K., De Leon, S. F., & Lippmann, M. (2005). Associations between ozone and daily mortality: Analysis and meta-analysis. Epidemiology, 16(4), 446–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(95)00407-6
Jiang, W. M., Cai, C. X., & Li, X. (2001). Simulation of the forming of ozone in the low layer air of urban area. Journal of the Meteorological Sciences., 21(2), 154–161. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1009-0827.2001.02.004
Jin, X. M., & Holloway, T. (2015). Spatial and temporal variability of ozone sensitivity over China observed from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 120(14), 7229–7246. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JD023250
Kong X. Q., Liu G. R., & Li G. C. (1999). Surface ozone concentration variation and possible influences on human health. Climatic and Environmental Research, 4(1),61–66. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=QHYH199901013&DbName=CJFQ1999
Lacis, A. A., Wuebbles, D. J., & Logan, J. A. (1990). Radiative forcing of climate by changes in the vertical distribution of ozone. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 95(D7), 9971–9981. https://doi.org/10.1029/JD095iD07p09971
Lee, D. S., Holland, M. R., & Falla, N. (1996). The potential impact of ozone on materials in the U.K. Atmospheric Environment, 30(7), 1053–1065. https://doi.org/10.1016/1352-2310(95)00407-6
Li, L., Wang, L., Liu, X., Wang, K., Xu, Y., Li, S., & Jiang, J. (2020). The temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of ozone and the relationship between meteorological elements in Harbin. China Environmental Science, 40(05), 1991–1999. https://doi.org/10.19674/j.cnki.issn1000-6923.2020.0225
Liu, F., Zhu, Y. G., & Wang, X. K. (2008). Surface ozone pollution and its eco-environmental effects in China. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, (04), 1674–1679. https://doi.org/10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2008.04.046.
Li, Y., Chang, L. M., Lv, P. C., Yang, Y. M., Wang, Z. X., Ge, H. P., Gao, H., Huang, T., Mao, X. X., & Ma, J. M. (2021). Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(05),1628–1639. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2020.0460
Mansfield, M. L., & Hall, C. F. (2018). A survey of valleys and basins of the western United States for the capacity to produce winter ozone. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association (1995), 68(9), 909–919. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2018.1454356
Mielniczuk, J., & Wojdyłło, P. (2007). Estimation of Hurst exponent revisited. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 51(9), 4510–4525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csda.2006.07.033
Monks, P. S., Archibald, A. T., Colette, A., Cooper, O., Coyle, M., Derwent, R., Fowler, D., Granier, C., Law, K. S., Mills, G. E., Stevenson, D. S., Tarasova, O., Thouret, V., von Schneidemesser, E., Sommariva, R., Wild, O., & Willians, M. L. (2015). Tropospheric ozone and its precursors from the urban to the global scale from air quality to short-lived climate forcer. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 15(15), 8889–8973. http://www.atmos-chem-phys-discuss.net/14/32709/2014/acp-2014-881-manuscript-version2.pdf
Nisperuza, D., Alex Rúa, Avendao-Tamayo, E., Vásquez, L., & Grajales, H. (2021). Tropospheric O3 model from climatological approaches in the Colombian Andes. The Professional Geographer (2), 775–784. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2021.1922295
Pan, S., Choi, Y., Roy, A., & Jeon, W. (2017). Allocating emissions to 4 km and 1 km horizontal spatial resolutions and its impact on simulated NOx and O3 in Houston, TX. Atmospheric Environment, 164(sep.), 398–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.06.026
Qin, Z. F., Liao, H., Chen, L., Zhu, J. & Qian, J. (2021). Fenwei Plain air quality and the dominant meteorological parameters for its daily and interannual variations. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 45(6), 1273–1291. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2021&filename=DQXK202106009&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=YVYF6jucPDDIBPHU-zoFV_VaUb7PozrG9VNsTZOyHLqZzn7xmadhMObQHg7hKLCc
Qu, Y., & An, J. L. (2009). Total and synergistic impacts of anthropogenic and biogenic emissions on ozone-examples in East Asia in spring and summer. China Environmental Science., 4, 337–344. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6923.2009.04.001
Ran, L., Zhao, C. S., Xu, W. Y., Lu, X. Q., Han, M., & Lin, W. L. (2011). VOC reactivity and its effect on ozone production during the HaChi summer campaign. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 11(10), 4657–4667. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-11-4657-2011
Senff, C. J., Alvarez, R. J., Hardesty, R. M., Banta, R. M., & Langford, A. O. (2010). Airborne lidar measurements of ozone flux downwind of Houston and Dallas. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(D20), D20307. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD013689
Shan, W. P., Yin, Y. Q., Du, S. Y., Yan, H. Z., Lv, B., & Hou, L. J. (2006). Ozone pollution, influence factors and their correlation at urban area in summer. Environmental Science, 27(7), 1276–1281. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2006.07.004
Strode, S. A., Ziemke, J., & R., Oman, L, D., Lamsal, L. N. Olsen, M. A. & Liu, J. (2019). Global changes in the diurnal cycle of surface ozone. Atmospheric Environment, 199, 323–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2018.11.028.
Wang, S., Xu, J. X., Sun, X. L., Hu, Z. X., & Zhao, X. Y. (2019). Spatial-temporal variation characteristics of air pollution in Fenwei Plain during heating and non-heating seasons. Environmental Pollution and Control, 41(12), 1451−1458. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&dbname=CJFDLAST2020&filename=HJWR201912013&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=OmkoaqwAQHFd_H5tvdGOzCHFlBdubrWEcu1s69-KO-ndrFc2WbLoJWZmE_PjU5_B
Wang, X. S., & Li, J. L. (2003). A case study of ozone source identification in Beijing. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 39(2), 244–253. https://doi.org/10.13209/j.0479-8023.2003.036
Xie, X., Shao, M., Ying, L., & Lu, S. H. (2009). Diurnal variation characteristics of atmospheric volatile organic compounds and their role in ozone generation: A case study of Guangzhou in summer, Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae (1), 54–62. https://doi.org/10.13671/j.hjkxxb.2009.01.030
Xu, X. B., Lin, W. L., Wang, T., Meng, Z. Y., & Wang, Y. (2006). Long-term trend of tropospheric ozone over the Yangtze Delta Region of China. Climate Change Research, 2(5), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2007.z1.012
Yin, Y., & Q., Li, C. M., Ma, G. X. & Cui, Z. J. (2004). Ozone concentration distribution of urban. Environmental Science, 25(6), 16–20. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2004.06.004
Zhang, Y. H., Shao, K. S., Tang, X. Y., & Li, J. L. (1998). The study of urban photochemical smog pollution in China. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 34(2), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.13209/j.0479-8023.1998.116
Zhu, S., Ma, J. Z., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2006). Numerical simulation of abnormal high value of ozone in spring in the Yangtze River Delta. Research of Environmental Sciences, 19(6),1–8. https://doi.org/10.13198/j.res.2006.06.3.zhush.001
Ziemke, J. R., Oman, L. D., Strode, S. A., Douglass, A. R., & Taylor, S. L. (2019). Trends in global tropospheric ozone inferred from a composite record of TOMS/OMI/MLS/OMPS satellite measurements and the MERRA-2 GMI simulation. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 19(5), 3257–3269. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-19-3257-2019
Zong, X. M., Wang, G. C., Chen, H. B., Wang, P. C., & Xuan, Y. J. (2007). Analysis on concentration variety characteristics of atmospheric ozone under the boundary layer in Beijing. Environmental Science, 28(11), 2615–2619. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.2007.11.036
Acknowledgements
The ozone column concentration data were all from an OMI sensor loaded on Aura satellite, and were obtained from https://www.nasa.gov/. The socioeconomic and human activity data, such as total energy production, GDP, and car ownership, were all from the National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S., Ju, T., Liang, Z. et al. Analysis of atmospheric ozone in Fenwei Plain based on remote sensing monitoring. Environ Monit Assess 194, 412 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10082-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10082-z