Abstract
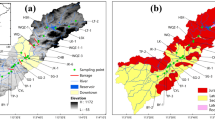
Estuaries have very complex mechanisms because they are influenced by seawater intrusion, which causes enrichment of contaminants in the maximum turbidity area. Magnetic susceptibility measurements have been used for monitoring a wide variety of environments. However, there have been few studies of the magnetic properties of surface sediments from estuaries in volcanic environments in the tropics. This study investigates the magnetic properties and their correlations with the geochemistry of surface sediments in estuaries in volcanic areas and was conducted in the Krueng Aceh River, Indonesia. Measurements consist of magnetic susceptibility measurements, chemical analysis, and mineralogical analysis. Measurements of magnetic susceptibilities were performed using a Bartington MS2 instrument with an MS2B sensor using frequencies of 460 and 46 kHz. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) were used to identify elements in the sediments. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis was used to analyze sediment grains. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was used to determine mineral contents. For the first time, χLF/χFD ratios were found to be an obvious parameter for identifying areas of sediment traps and metal enrichment in the estuary turbidity maxima (ETM) zone. The magnetic properties carried by volcanic rock minerals consist of pigeonite and enstatite. These two minerals have not been previously considered as carriers of sediments with magnetic properties when monitoring heavy metal enrichment in urban rivers. These results provide an extension of the use of magnetic susceptibility measurements in environmental studies, particularly in estuary river environments in volcanic areas such as the Krueng Aceh River, Indonesia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data for figures are provided with the paper.
Change history
17 August 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10053-4
References
Adib, A., & Javdan, F. (2015). Interactive approach for determination of salinity concentration in tidal rivers (Case study: The Karun River in Iran). Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 6(3), 785–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2015.02.005
Ananthapadmanabha, A. L., Shankar, R., & Sandeep, K. (2014). Rock magnetic properties of lateritic soil profiles from southern India: Evidence for pedogenic processes. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 111, 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2014.10.009
Artiola, J. F., & Brusseau, M. L. (2019). Environmental and pollution science (Third Edition) 2019, Chapter 10-The role of environmental monitoring in pollution science, 149–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814719-1.00010-0
Badesab, F., von Dobeneck, T., Bryan, K. R., Müller, H., Briggs, R. M., Frederichs, T., & Kwoll, E. (2012). Formation of magnetite-enriched zones in and offshore of a mesotidal estuarine lagoon: An environmental magnetic study of Tauranga Harbor and Bay of Plenty, New Zealand. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012gc004125
Bao, L. J., Hu, C. F., Hui, C. J., Sheng, X. D., & Hai, X. Q. (2011). Humid Medieval warm period recorded by magnetic characteristics of sediments from Gonghai Lake, Shanxi, North China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56, 2464–2474.
Bennett, J. D., Cameon, N. R., Bride, D. M. C., Clarke, M. C. G., Djunuddin, A., Ghazali, S. A., Harahap, H., Jeffry, D. H., Kartawa, W., Keats, W., Ngabito, H., Rock, N. M. S., Thompson, S. J. (1983): Peta geologi lembar Banda Aceh, Sumatera, skala 1:250.000. Center for Geological Research and Development. Bandung.
Biedermann, A. R., Pettke, T., Bender Koch, C., & Hirt, A. M. (2015). Magnetic anisotropy in clinopyroxene and orthopyroxene single crystals. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 120(3), 1431–1451. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014jb011678
Burchard, H., Schuttelaar, H. M., & Ralston, D. K. (2018). Sediment trapping in estuaries. Annual Review of Marine Science, 10(1), 371–395. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060535
Canbay, M., Aydin, A., & Kurtulus, C. (2010). Magnetic susceptibility and heavy-metal contamination in topsoils along the Izmit Gulf coastal area and IZAYTAS (Turkey). Journal of Applied Geophysics, 70(1), 46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2009.11.002
Chandrasekaran, S., Sankaran Pillai, G., & Venkatraman, B. (2020). Spatial and heavy metal assessment in beach sands of east coast of Tamil Nadu India. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100324
Chen, Z., Kostaschuk, R., & Yang, M. (2001). Heavy metals on tidal flats in the Yangtze Estuary. China. Environmental Geology, 40(6), 742–749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540000241
Chu, B., Chen, X., Li, Q., Yang, Y., Mei, X., He, B., He, Y., Hui, L., & Tan, L. (2014). Effects of salinity on the transformation of heavy metals in tropical estuary wetland soil. Chemistry and Ecology, 31(2), 186–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2014.917174
De Souza Machado, A. A., Spencer, K., Kloas, W., Toffolon, M., & Zarfl, C. (2016). Metal fate and effects in estuaries: A review and conceptual model for better understanding of toxicity. Science of the Total Environment, 541, 268–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.045
Dearing, J. A. (1999). Environmental magnetic susceptibility: Using the Bartington MS2 System. Chi Pub, Kenilworth.
Dessai, D. V. G., Nayak, G. N., & Basavaiah, N. (2009). Grain size, geochemistry, magnetic susceptibility: Proxies in identifying sources and factors controlling distribution of metals in a tropical estuary, India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 85(2), 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2009.08.020
Esteller, M. V., Kondratenko, N., Expósito, J. L., Medina, M., & Martin del Campo, M. A. (2017). Hydrogeochemical characteristics of a volcanic-sedimentary aquifer with special emphasis on Fe and Mn content: A case study in Mexico. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 180, 113–126.
Fabre, S., Jeandel, C., Zambardi, T., Roustan, M., & Almar, R. (2019). An overlooked silica source of the modern oceans: Are sandy beaches the key? Frontiers in Earth Science. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2019.00231
Fujimori, T., & Takigami, H. (2013). Pollution distribution of heavy metals in surface soil at an informal electronic-waste recycling site. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 36(1), 159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9526-y
Hamdan, A. M., Bijaksana, S., Tjoa, A., Dahrin, D., & Kirana, K. H. (2019). Magnetic characterizations of nickel hyperaccumulating plants (Planchonella oxyhedra and Rinorea bengalensis) from Halmahera. Indonesia. International Journal of Phytoremediation. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1524839
Hamdan, A. M., Bijaksana, S., Tjoa, A., Dahrin, D., Fajar, S. J., & Kirana, K. H. (2020). Use and validation of magnetic properties for differentiating nickel hyperaccumulators and non-nickel hyperaccumulators in ultramafic regions. Journal of Geochemical Exploration. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106581
Haris, H., Looi, L. J., Aris, A. Z., Mokhtar, N. F., Ayob, N. A. A., Yusoff, F. M., Salleh, A. B., & Praveena, S. M. (2017). Geo-accumulation index and contamination factors of heavy metals (Zn and Pb) in urban river sediment. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 39(6), 1259–1271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-017-9971-0
Hopwood, M. J., Statham, P. J., Skrabal, S. A., & Willey, J. D. (2015). Dissolved iron(II) ligands in river and estuarine water. Marine Chemistry, 173, 173–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2014.11.004
Jin, B., Wang, M., Yue, W., Zhang, L., & Wang, Y. (2019). Heavy mineral variability in the Yellow River sediments as determined by the multiple-window strategy. Minerals, 9(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9020085
Jilbert, T., Asmala, E., Schröder, C., Tiihonen, R., Myllykangas, J. -P., Virtasalo, J. J., Kotilainen, A., Peltola, P., Ekholm, P., & Hietanen, S. (2018). Impacts of flocculation on the distribution and diagenesis of iron in boreal estuarine sediments. Biogeosciences, 15, 1243–1271. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-15-1243-2018
Kanu, M. O., Meludu, O. C., & Oniku, S. A. (2014). Comparative study of topsoil magnetic susceptibility variation based on some human activities. Geofísica Internacional, 53(4), 411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7169(14)70075-3
Kowalska, J. B., Skiba, M., & Maj-Szeliga, K. (2021). Does calcium carbonate influence clay mineral transformation in soils developed from slope deposits in Southern Poland? Journal of Soils and Sediments, 21, 257–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02764-3
Kumar, R., Srivastava, P. K., & Srivastava, S. P. (1994). Leaching of heavy metals (Cr, Fe, and Ni) from stainless steel utensils in food simulants and food materials. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00192042
Kumari, S., Amit, Jamwal, R., Mishra, N., & Singh, D. K. (2020). Recent developments in environmental mercury bioremediation and its toxicity: A review. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management, 100283.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100283
Labrada-Delgado, G., Aragon-Pina, A., Campos-Ramos, A., Castro-Romero, T., Amador-Munoz, O., & Villalobos-Pietrini, R. (2012). Chemical and morphological characterization of PM2.5 collected during MILAGRO campaign using scanning electron microscopy. Atmospheric Pollution Research, 3(3), 289–300. https://doi.org/10.5094/apr.2012.032
Li, M., Zhu, S., Ouyang, T., Tang, J., & He, C. (2020). Magnetic fingerprints of surface sediment in the Bohai Sea, China. Marine Geology, 106226.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2020.106226
Mariyanto, M., Amir, M. F., Utama, W., Hamdan, A. M., Bijaksana, S., Pratama, A., Yunginger, R., & Sudarningsih, S. (2019). Heavy metal contents and magnetic properties of surface sediments in volcanic and tropical environments from Brantas River, Jawa Timur Province, Indonesia. Science of the Total Environment. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.244
Meng, W., Qin, Y., Zheng, B., & Zhang, L. (2008). Heavy metal pollution in Tianjin Bohai Bay, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 20(7), 814–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1001-0742(08)62131-2
Moechtar, H., Subiyanto, S., & Sugianto, D. (2009): Geologi Aluvium dan Karakter Endapan Pantai/Pematang Pantai di Lembah Krueng Aceh, Aceh Besar (Provinsi. Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam). Journal of Geology and Mineral Resources, 19(4).
Monteil, C. L., Benzerara, K., Menguy, N., Bidaud, C. C., Michot-Achdjian, E., Bolzoni, R., Mathon, F. P., Coutaud, M., Alonso, B., Garau, C., Jézéquel, D., Viollier, E., Ginet, N., Floriani, M., Swaraj, S., Sachse, M., Busigny, V., Duprat, E., Guyot, F., & Lefevre, C. T. (2020). Intracellular amorphous Ca-carbonate and magnetite biomineralization by a magnetotactic bacterium affiliated to the Alphaproteobacteria. The ISME Journal: Multidisciplinary Journal of Microbial Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-00747-3
Nakanishi, R., Baba, A., Tsuyama, T., Ikemi, H., & Mitani, Y. (2019). Examination of sediment dynamics based on the distribution of silica fluxes and flood sediments in the Otoishi River related to the Northern Kyushu heavy rain disaster, July 2017. Geosciences, 9(2), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9020075
Naseh, M. R. V., Karbassi, A., Ghazaban, F., Baghvand, A., & Mohammadizadeh, M. J. (2012). Magntic susceptibility as a proxy to heavy metal content in the sediments of Anzali wetland, Iran. Iranian Journal of Environmental Health Science & Engineering, 9(1), 34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1735-2746-9-34
Novala, G. C., Fitriani, D., Susanto, K., & Kirana, K. H. (2016). Magnetic properties of soils from Sarimukti landfill as proxy indicators of pollution (Case Study: Desa Sarimukti, Kabupaten Bandung Barat). IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science., 29, 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/29/1/012015
Oldham, V. E., Miller, M. T., Jensen, L. T., & Luther, G. W. (2017). Revisiting Mn and Fe removal in humic rich estuaries. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 209, 267–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.04.001
Peter, P. O., Rashid, A., Hou, L., Nkinahamira, F., Kiki, C., Sun, Q., Yu, C. P., & Hu, A. (2020). Elemental contaminants in surface sediments from Jiulong River Estuary, China: Pollution level and ecotoxicological risk assessment. Water, 12(6), 1640. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061640
Priya, K. L., Jegathambal, P., & James, E. J. (2016). Salinity and suspended sediment transport in a shallow estuary on the east coast of India. Regional Studies in Marine Science, 7, 88–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2016.05.015
Reitermajer, D., Celino, J. J., & Queiroz, A. F. D. S. (2011). Heavy metal distribution in the sediment profiles of the Sauípe River Estuary, north seashore of the Bahia State, Brazil. Microchemical Journal, 99(2), 400–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2011.06.015
Reyes, A. B., Bautista, F., Goguitchaichvili, A., Contreras, A. J. J., Battu, J., Quintana Owen, P., & Carvallo, C. (2013). Rock-magnetic properties of topsoils and urban dust from Morelia (>800,000 inhabitants), Mexico: Implications for anthropogenic pollution monitoring in Mexico’s medium size cities. Geofísica Internacional, 52(2), 121–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7169(13)71467-3
Sudarningsih, S., Bijaksana, S., Hafidz, A., Pratama, A., Widodo, W., Iskandar, I., Dahrin, D., Fajar, S. J., & Santoso, N. A. (2017). Variations in the concentration of magnetic minerals and heavy metals in suspended sediments from Citarum River and its tributaries, West Java. Indonesia. Geosciences, 7(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences7030066
Togibasa, O., Bijaksana, S., & Novala, G. (2018). Magnetic properties of iron sand from the Tor River Estuary, Sarmi, Papua. Geosciences, 8(4), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8040113
Wu, J., Liu, J. T., & Wang, X. (2012). Sediment trapping of turbidity maxima at the Changjiang estuary. Marine Geology., 303–306, 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2012.02.011
Xu, Q., Xing, R., Sun, M., Gao, Y., & An, L. (2020). Microplastics in sediments from an interconnected river-estuary region. Science of the Total Environment, 729, 139025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139025
Yang, L., Song, X., Zhang, Y., & Han, D. (2012). Characterizing interactions between surface water and groundwater in the Jialu River basin using major ion chemistry and stable isotopes. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 9(5), 5955–5981.
Yi, Q., Dou, X. D., Huang, Q. R., & Zhao, X. Q. (2012). Pollution characteristics of Pb, Zn, As, Cd in the Bijiang River. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2012.01.004
Yunginger, R., Bijaksana, S., Dahrin, D., Zulaikah, S., Hafidz, A., Kirana, K., & Fajar, S. (2018). Lithogenic and anthropogenic components in surface sediments from Lake Limboto as shown by magnetic mineral characteristics, trace metals, and REE geochemistry. Geosciences, 8(4), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8040116
Zhao, G., Ye, S., Yuan, H., Ding, X., & Wang, J. (2016). Surface sediment properties and heavy metal pollution assessment in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(3), 2966–2979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8003-4
Zhu, X., Zhang, R., Wu, Y., Zhu, J., Bao, D., & Zhang, J. (2018). The remobilization and removal of Fe in estuary-A case study in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 123(4), 2539–2553. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jc013671
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hamdan, A.M., Kirana, K.H., Hakim, F. et al. Magnetic susceptibilities of surface sediments from estuary rivers in volcanic regions. Environ Monit Assess 194, 239 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09891-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-09891-z