Abstract
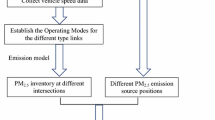
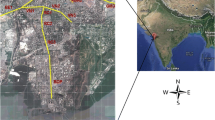
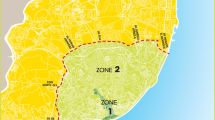
Motor vehicle emissions especially occur at signalized intersections during idling, acceleration, and deceleration phases. The reduction of exhaust emissions from motor vehicles is on the focus of environmental studies. The main targets of this paper are the modeling of motor vehicle particulate matter (PM10) emissions by American Meteorological Society/Environmental Protection Agency Regulatory Model (AERMOD) and California Line Source for Queuing and Hot Spot Calculations (CAL3QHCR) models and investigating the effectiveness of a hypothetical green wave scenario as a pollution reduction strategy. The portion of D010 State Road in Zonguldak (Turkey) is selected. Vehicle counting is applied for determining the traffic volume. Then, the PM10 emission inventory is prepared. After that, PM10 pollution distribution maps at signalized intersections are created by running air quality models. Next, the CAL3QHCR model is run again for the green wave scenario which assumes free flow at signalized intersections. The maximum PM10 concentrations predicted by AERMOD and CAL3QHCR models are 16.8 µg/m3 and 14.9 µg/m3, respectively. Although these values are below the threshold value, it can be said that air quality may pose a threat to public health in the existence of other sources. With the implementation of signal optimization, the PM10 pollution is reduced by 10–50% at intersections. Cumulative model validation is employed including other PM10 sources in the study area. PM10 contribution of other sources at Zonguldak air quality monitoring station is determined by the AERMOD model. Finally, the sum of model outputs is validated against measured concentrations. According to the validation, both models are found as satisfactory and AERMOD performed better than CAL3QHCR.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdul-Wahab, S. A. (2004). An application and evaluation of the CAL3QHC model for predicting carbon monoxide concentrations from motor vehicles near a roadway intersection in Muscat, Oman. Environmental Management, 34(3), 372–382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00267-004-0146-2
Akay, M. E., & Akgüngör, A. P. (2008). Modeling of traffic signals syncronisation effect for vehicle emission reduction. Journal of Polytechnic, 11(1), 51–56.
Al-jeelani, H. A. (2013). The ımpact of traffic emission on air quality in an urban environment. Journal of Environmental Protection, 4(February), 205–217. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2013.42025
Amoatey, P., Omidvarborna, H., Affum, H. A., & Baawain, M. (2018). Performance of AERMOD and CALPUFF models on SO2 and NO2 emissions for future health risk assessment in Tema Metropolis. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 7039(2), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1451745
Anjos, M., Lopes, A., & Alves, E. (2018). Using the CAL3QHC and I-Tree Canopy for air quality assessment in Aracaju: Estimates of the concentrations of PM10 in roadways of intensive traffic of cars. Geousp - Espaço e Tempo (Online), 22(3), 707–728. https://doi.org/10.11606/issn.2179-0892.geousp.2018.139515
Askariyeh, M. H., Kota, S. H., Vallamsundar, S., Zietsman, J., & Ying, Q. (2017). AERMOD for near-road pollutant dispersion: Evaluation of model performance with different emission source representations and low wind options. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 57, 392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2017.10.008
Behera, S. N., Sharma, M., Dikshit, O., & Shukla, S. P. (2011). GIS-based emission inventory, dispersion modeling, and assessment for source contributions of particulate matter in an urban environment. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 218(1–4), 423–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0656-x
Çetin, Ş, & ̧, Karademir, A., Pekey, B., & Ayberk, S. (2007). Inventory of emissions of primary air pollutants in the city of Kocaeli. Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 128(1–3), 165–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-9302-x
Chang, J. C., & Hanna, S. R. (2004). Air quality model performance evaluation. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics, 87(1–3), 167–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-003-0070-7
Chart-asa, C., Sexton, K. G., & Gibson, J. M. (2013). Traffic ımpacts on fine particulate matter air pollution at the urban project scale: A quantitative assessment. Journal of Environmental Protection, 04(12), 49–62. https://doi.org/10.4236/jep.2013.412a1006
Chew, S., Kolosowska, N., Saveleva, L., Malm, T., & Kanninen, K. M. (2020). Impairment of mitochondrial function by particulate matter: Implications for the brain. Neurochemistry International, 135, 104694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104694
Cimorelli, A. J., Perry, S. G., Venkatram, A., Weil, J. C., Paine, R. J., Wilson, R. B., et al. (2005). AERMOD: A Dispersion model for ındustrial source applications. Part I: General model formulation and boundary layer characterization. Journal of Applied Meteorology, 44(5), 682–693. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAM2227.1
Claggett, M. (2014). Comparing predictions from the CAL3QHCR and AERMOD models for highway applications. Transportation Research Record, 2428(1), 18–26. https://doi.org/10.3141/2428-03
Cruz, A. M. J., Sarmento, S., Almeida, S. M., Silva, A. V., Alves, C., Freitas, M. C., & Wolterbeek, H. (2015). Association between atmospheric pollutants and hospital admissions in Lisbon. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 5500–5510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3838-z
De Coensel, B., Can, A., Degraeuwe, B., De Vlieger, I., & Botteldooren, D. (2012). Effects of traffic signal coordination on noise and air pollutant emissions. Environmental Modelling and Software, 35, 74–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2012.02.009
Demirarslan, K. O., & Çetin Doğruparmak, Ş. (2018). Dispersion modeling of traffic Emissions originated from Mining: The case of Artvin. Journal of Natural Hazards and Environment, 90(462), 11–21. https://doi.org/10.21324/dacd.420274
Demirel Bayik, G., Polat Alpan, M., Zeydan, O., Tanis, M., & Bayik, C. (2018). Vehicle emissions at ıntersections before and after signal ımprovement: Zonguldak example. International Journal of Advances in Mechanical and Civil Engineering, 5(5), 33–37.
Dhyani, R., & Sharma, N. (2018). Vehicular pollution dispersion modelling along roads using CALINE4 model - A review. International Journal of Environmental Technology and Management, 21(1–2), 91–110. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJETM.2018.092565
EEA. (2019a). Turkey - Air pollution country fact sheet 2019. https://www.eea.europa.eu/themes/air/country-fact-sheets/2019-country-fact-sheets/turkey. Accessed 20 July 2020
EEA. (2019b). EMEP/EEA air pollutant emission inventory guidebook 2019. https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/emep-eea-guidebook-2019. Accessed 14 July 2020
Faria, M. V., Duarte, G. O., Baptista, P. C., & Farias, T. L. (2017). Scenario-based analysis of traffic-related PM2.5 concentration: Lisbon case study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(13), 12026–12037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5556-6
Forehead, H., & Huynh, N. (2018). Review of modelling air pollution from traffic at street-level - The state of the science. Environmental Pollution, 241, 775–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.019
Gokhale, S., & Raokhande, N. (2008). Performance evaluation of air quality models for predicting PM10and PM2.5concentrations at urban traffic intersection during winter period. Science of the Total Environment, 394(1), 9–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.01.020
Greco, S. L., Wilson, A. M., Hanna, S. R., & Levy, J. I. (2007). Factors influencing mobile source particulate matter emissions-to-exposure relationships in the Boston urban area. Environmental Science and Technology, 41(22), 7675–7682. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062213f
Gubadlı, S., & Kocabas, S. (2019). Zonguldak Limanı Gemi Faaliyetlerinden Kaynaklanan Emisyonların Hesaplanması. In 3rd Engineers of Future International Student Symposium (pp. 149–152). Zonguldak.
Heist, D., Isakov, V., Perry, S., Snyder, M., Venkatram, A., Hood, C., et al. (2013). Estimating near-road pollutant dispersion: A model inter-comparison. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 25, 93–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2013.09.003
Jacomino, V., Tavares, F., Barreto, A., & Dutra, E. (2009). Study of the dispersion process of vehicular emissions at a specific site in Belo Horizonte using numerical simulation. WIT Transactions on Biomedicine and Health, 14, 23–34. https://doi.org/10.2495/EHR090031
Jo, E. J., Lee, W. S., Jo, H. Y., Kim, C. H., Eom, J. S., Mok, J. H., et al. (2017). Effects of particulate matter on respiratory disease and the impact of meteorological factors in Busan, Korea. Respiratory Medicine, 124, 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2017.02.010
Kampa, M., & Castanas, E. (2008). Human health effects of air pollution. Environmental Pollution, 151, 362–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.012
Kiers, M., & Visser, C. (2017). The effect of a green wave on traffic emissions. In Forschungsforum Der Österreichischen Fachhochschulen (pp. 1–6). http://ffhoarep.fh-ooe.at/handle/123456789/997
Kim, E., Park, H., Park, E. A., Hong, Y. -C., Ha, M., Kim, H. -C., & Ha, E. -H. (2016). Particulate matter and early childhood body weight. Environment International, 94, 591–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.021
Kravchenko, J., Akushevich, I., Abernethy, A. P., Holman, S., Ross, W. G., & Kim Lyerly, H. (2014). Long-term dynamics of death rates of emphysema, asthma, and pneumonia and improving air quality. International Journal of COPD, 9, 613–627. https://doi.org/10.2147/COPD.S59995
Macêdo, M. F. M., & Ramos, A. L. D. (2020). Vehicle atmospheric pollution evaluation using AERMOD model at avenue in a Brazilian capital city. Air Quality, Atmosphere and Health, 13(3), 309–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00792-z
Madireddy, M., De Coensel, B., Can, A., Degraeuwe, B., Beusen, B., De Vlieger, I., & Botteldooren, D. (2011). Assessment of the impact of speed limit reduction and traffic signal coordination on vehicle emissions using an integrated approach. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 16(7), 504–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2011.06.001
Mishra, V. K., & Padmanabhamutry, B. (2003). Performance evaluation of CALINE3, CAL3QHC and PART5 in predicting lead concentration in the atmosphere over Delhi. Atmospheric Environment, 37(22), 3077–3089. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(03)00272-3
Misra, A., Roorda, M. J., & MacLean, H. L. (2013). An integrated modelling approach to estimate urban traffic emissions. Atmospheric Environment, 73, 81–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2013.03.013
Moriasi, D. N., Arnold, J. G., Van Liew, M. W., Bingner, R. L., Harmel, R. D., & Veith, T. L. (2007). Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Transactions of the ASABE, 50(3), 885–900.
Nagendra, S. M. S., & Khare, M. (2002). Line source emission modelling. Atmospheric Environment, 36(13), 2083–2098. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00177-2
NCEP. (2019). NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR). https://rda.ucar.edu/pub/cfsr.html
Nesmachnow, S., Massobrio, R., Arreche, E., Mumford, C., Olivera, A. C., Vidal, P. J., & Tchernykh, A. (2019). Traffic lights synchronization for Bus Rapid Transit using a parallel evolutionary algorithm. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 8(1), 53–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijtst.2018.10.002
Onay, T. T., Copty, N. K., Gökçe, H. B., Aydın-Sarıkurt, D., Mumcu, M., & Arıoğlu, E. (2019). Air quality impact assessment for the Eurasia Tunnel in Istanbul, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7340-4
Pascal, M., Falq, G., Wagner, V., Chatignoux, E., Corso, M., Blanchard, M., et al. (2014). Short-term impacts of particulate matter (PM10, PM10-2.5, PM2.5) on mortality in nine French cities. Atmospheric Environment, 95, 175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2014.06.030
Polichetti, G., Cocco, S., Spinali, A., Trimarco, V., & Nunziata, A. (2009). Effects of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5 and PM1) on the cardiovascular system. Toxicology, 261, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.04.035
Ritner, M., Westerlund, K. K., Cooper, C. D., & Claggett, M. (2013). Accounting for acceleration and deceleration emissions in intersection dispersion modeling using MOVES and CAL3QHC. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 63(6), 724–736. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2013.778220
Sharma, N., Chaudhry, K. K., & Chalapati Rao, C. V. (2007). Vehicular pollution prediction modelling: A review of highway dispersion models. Transport Reviews: A Transnational Transdisciplinary Journal, 24(4), 409–435.
Song, J., Qiu, Z., Ren, G., & Li, X. (2020). Prediction of pedestrian exposure to traffic particulate matters (PMs) at urban signalized intersection. Sustainable Cities and Society, 60(May), 102153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102153
Tezel-Oguz, M. N., Sari, D., Ozkurt, N., & Keskin, S. S. (2020). Application of reduction scenarios on traffic-related NOx emissions in Trabzon, Turkey. Atmospheric Pollution Research, (June), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.06.014
The, J. L., The, C. L., & Johnson, M. A. (2016). CALRoads view user guide.
TUIK. (2019). Number of road motor vehicles by model years, 2018. http://www.tuik.gov.tr/PreIstatistikTablo.do?istab_id=357. Accessed 14 July 2020
TUIK. (2020). Distribution of cars registered to the traffic according to fuel type, 2004 - 2020. http://www.tuik.gov.tr/PreIstatistikTablo.do?istab_id=1582. Accessed 20 September 2019
Uherek, E., Halenka, T., Borken-Kleefeld, J., Balkanski, Y., Berntsen, T., Borrego, C., et al. (2010). Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Land transport. Atmospheric Environment, 44(37), 4772–4816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2010.01.002
USEPA. (1995). AP 42, Fifth Edition Compilation of air pollutant emissions factors, Volume 1: Stationary point and area sources. https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-factors-and-quantification/ap-42-compilation-air-emissions-factors. Accessed 14 July 2020
USEPA. (2008). Idling Vehicle Emissions for Passenger Cars, Light-Duty Trucks, and Heavy- Duty Trucks. http://www.epa.gov/otaq/consumer/420f08025.pdf
Wang, A., Fallah-Shorshani, M., Xu, J., & Hatzopoulou, M. (2016). Characterizing near-road air pollution using local-scale emission and dispersion models and validation against in-situ measurements. Atmospheric Environment, 142(2), 452–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2016.08.020
Wei, Y., Zhang, J. J., Li, Z., Gow, A., Chung, K. F., Hu, M., et al. (2016). Chronic exposure to air pollution particles increases the risk of obesity and metabolic syndrome: Findings from a natural experiment in Beijing. FASEB Journal, 30, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201500142
Wen, D., Zhai, W., Xiang, S., Hu, Z., Wei, T., & Noll, K. E. (2017). Near-roadway monitoring of vehicle emissions as a function of mode of operation for light-duty vehicles. Journal of the Air and Waste Management Association, 67(11), 1229–1239. https://doi.org/10.1080/10962247.2017.1330713
Woodcock, J., Edwards, P., Tonne, C., Armstrong, B. G., Ashiru, O., Banister, D., et al. (2009). Public health benefits of strategies to reduce greenhouse-gas emissions: Urban land transport. The Lancet, 374, 1930–1943. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61714-1
Zhou, H., & Sperling, D. (2001). Traffic emission pollution sampling and analysis on urban streets with high-rising buildings. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 6(4), 269–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1361-9209(00)00029-8
Zhu, F., Lo, H. K., & Lin, H. Z. (2013). Delay and emissions modelling for signalised intersections. Transportmetrica B, 1(2), 111–135. https://doi.org/10.1080/21680566.2013.821689
Acknowledgements
The preliminary findings were presented and discussed at the 18th World Clean Air Congress organized by the Turkish National Committee for Air Pollution Control (TUNCAP) and the International Union of Air Pollution Prevention Associations (IUAPPA) held in Istanbul Turkey in September 2019.
Funding
This study was funded by Zonguldak Bülent Ecevit University Scientific Research Fund (Grant No. 2018–77047330-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeydan, Ö., Öztürk, E. Modeling of PM10 emissions from motor vehicles at signalized intersections and cumulative model validation. Environ Monit Assess 193, 619 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09410-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09410-6