Abstract
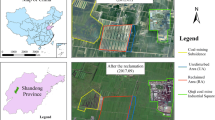
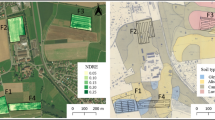
Underground coal mining leads to land subsidence, and the situation is particularly serious in the Coal-Grain Complex in eastern China, causing the crop production to be reduced or to be taken out. Backfilling with Yellow River sediment is one of the effective methods to solve the land subsidence in this area, but a key issue is how to select the optimal soil reconstruction profile so that the crop yield after backfilling and reclamation is unaffected. The main purpose of this study is to verify the feasibility of selecting the optimal soil reconstruction profile by rapid monitoring of crop growth and judging soil quality with the aid of unmanned aerial vehicle systems (UAVs). A control treatment and 13 experimental treatments were established for the study area. The control treatment consisted of using 30 cm topsoil and 90 cm subsoil and the topsoil is a proxy for native (undisturbed) soil from the study sites. All other treatments consisted of using varying combinations of subsoil and sediment overlain by 30 cm of topsoil. The vegetation indices from the UAV multispectral images, and the plant height and vegetation coverage from the UAV RGB images were used for estimation of the winter wheat biomass in a random forest regression. The results showed that the random forest regression model yielded accurate estimation of the aboveground biomass. Furthermore, knowledge of plant height and vegetation coverage improved the accuracy of prediction such that crop growth was well characterized. The optimal soil profile consisted of 0.3 m topsoil + 0.2 m subsoil + 0.2 m sediment + 0.2 m subsoil + 0.3 m sediment. A fast and effective airborne monitoring method for soil quality was established, thus providing greatly improved monitoring efficiency.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available because the data may also be used by other persons in our laboratory but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahirwal, J., Maiti, S. K., & Singh, A. K. (2017). Changes in ecosystem carbon pool and soil CO2 flux following post-mine reclamation in dry tropical environment, India. Science of the Total Environment, 583, 153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.043
Ashapure, A., Jung, J., Chang, A., Oh, S., Yeom, J., Maeda, M., ... & Smith, W. (2020). Developing a machine learning based cotton yield estimation framework using multi-temporal UAS data. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 169, 180-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.09.015
Banerjee, B. P., Spangenberg, G., & Kant, S. (2020). Fusion of spectral and structural information from aerial images for improved biomass estimation. Remote Sensing, 12(19), 3164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12193164
Barkley, Z. R., Lauvaux, T., Davis, K. J., Deng, A., Fried, A., Weibring, P., Richter, D., Walega, J. G., DiGangi, J., Ehrman, S. H., Ren, X., & Dickerson, R. R. (2019). Estimating methane emissions from underground coal and natural gas production in southwestern Pennsylvania. Geophysical Research Letters. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019gl082131
Bendig, J., Yu, K., Aasen, H., Bolten, A., Bennertz, S., Broscheit, J., ... & Bareth, G. (2015). Combining UAV-based plant height from crop surface models, visible, and near infrared vegetation indices for biomass monitoring in barley. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 39, 79-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2015.02.012
Blackburn, G. A. (1998). Quantifying chlorophylls and caroteniods at leaf and canopy scales: An evaluation of some hyperspectral approaches. Remote Sensing of Environment, 66(3), 273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(98)00059-5
Cheng, L., Jiang, P. H., Chen, W., Li, M. C., Wang, L. Y., Gong, Y., Pian, Y. Z., Xia, N., Duan, Y. W., & Huang, Q. H. (2015). Farmland protection policies and rapid urbanization in China: A case study for Changzhou City. Land Use Policy, 48, 552–566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2015.06.014
Duo, L. H., & Hu, Z. Q. (2018). Soil quality change after reclaiming subsidence land with Yellow River sediments. Sustainability, 10(11), 4310. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114310
El-Hendawy, S. E., Alotaibi, M., Al-Suhaibani, N., Al-Gaadi, K., Hassan, W., Dewir, Y. H., ... & Schmidhalter, U. (2019). Comparative performance of spectral reflectance indices and multivariate modeling for assessing agronomic parameters in advanced spring wheat lines under two contrasting irrigation regimes. Frontiers in plant science, 10, 1537. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01537
Fan, H., Wang, L., Wen, B., & Du, S. (2021). A new model for three-dimensional Deformation extraction with single-track InSAR based on mining subsidence characteristics. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 94, 102223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2020.102223
Fang, L., Xinju, L., Le, H., & Anran, S. (2020). A long-term study on the soil reconstruction process of reclaimed land by coal gangue filling. Catena, 195, 104874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104874
Fern, R. R., Foxley, E. A., Bruno, A., & Morrison, M. L. (2018). Suitability of NDVI and OSAVI as estimators of green biomass and coverage in a semi-arid rangeland. Ecological Indicators,94, 16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.06.029
Filgueiras, R., Almeida, T. S., Mantovani, E. C., Dias, S. H. B., Fernandes-Filho, E. I., da Cunha, F. F., & Venancio, L. P. (2020). Soil water content and actual evapotranspiration predictions using regression algorithms and remote sensing data. Agricultural Water Management, 241, 106346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106346
Fu, Y., Yang, G., Li, Z., Song, X., Li, Z., Xu, X., ... & Zhao, C. (2020). Winter wheat nitrogen status estimation using UAV-based RGB imagery and gaussian processes regression. Remote Sensing, 12(22), 3778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12223778
Gao, G., Xiao, K., & Jia, Y. (2020). A spraying path planning algorithm based on colour-depth fusion segmentation in peach orchards. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 173, 105412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2020.105412
Gebremedhin, A., Badenhorst, P., Wang, J., Giri, K., Spangenberg, G., & Smith, K. (2019). Development and validation of a model to combine NDVI and plant height for high-throughput phenotyping of herbage yield in a perennial ryegrass breeding program. Remote Sensing, 11(21), 2494. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11212494
Gilliot, J. M., Michelin, J., Hadjard, D., & Houot, S. (2021). An accurate method for predicting spatial variability of maize yield from UAV-based plant height estimation: a tool for monitoring agronomic field experiments. Precision Agriculture, 22(3), 897-921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-020-09764-w
Grinberg, N. F., Orhobor, O. I., & King, R. D. (2019). An evaluation of machine-learning for predicting phenotype: studies in yeast, rice, and wheat. Machine Learning, 109, 251-277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-019-05848-5
Gong, Y. L., Hu, Z. Q., & McSweeney, K. (2020). Reclaiming subsidized land: An evaluation of coal gangue interlayers. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2020(2020), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5740659
Günlü, A., Ercanlı, I., Keleş, S., & Anlar, H. C. (2015). Modelling of stand volume and tree density using Spot-4 satellite image: A case study in Devrez planning unit. International Journal of Global Warming, 7(4), 454. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijgw.2015.070047
Guo, Y., Fu, Y., Hao, F., Zhang, X., Wu, W., Jin, X., Robin Bryant, C., Senthilnath, J. (2021). Integrated phenology and climate in rice yields prediction using machine learning methods. Ecological Indicators, 120, 106935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106935
Gupta, D. K., Rai, U. N., Tripathi, R. D., & Inouhe, M. (2002). Impacts of fly-ash on soil and plant responses. Journal of Plant Research, 115(6), 401-409.
Hamuda, E., Glavin, M., & Jones, E. (2016). A survey of image processing techniques for plant extraction and segmentation in the field. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 125, 184–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.04.024
Hosseini, M., McNairn, H., Mitchell, S., Dingle Robertson, L., Davidson, A., & Homayouni, S. (2019). Synthetic aperture radar and optical satellite data for estimating the biomass of corn. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 83, 101933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2019.101933
Hu, Z. Q., Duo, L. H., & Shao, F. (2018). Optimal thickness of soil cover for reclaiming subsided land with Yellow River sediments. Sustainability, 10(11), 3853. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10113853
Hu, Z. Q., Shao, F., & McSweeney, K. (2017). Reclaiming subsided land with Yellow River sediments: Evaluation of soil-sediment columns. Geoderma, 307, 210–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.06.027
Jordan, C. F. (1969). Derivation of leaf area index from quality of light on the forest floor. Ecology, 50(4), 663–666.
Kim, S. C., Hong, Y. K., Lee, S. P., Oh, S. M., Lim, K. J., Yang, J. E. (2017). Calculating soil quality index for biomass production based on soil chemical properties. 한국토양비료학회지, 50(1), 56–64. https://doi.org/10.7745/KJSSF.2017.50.1.056
Kumar, D., & Singh, B. (2003). The use of coal fly ash in sodic soil reclamation. Land Degradation & Development, 14(3), 285–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.557
Li, G., Wang, J. L., Wang, Y. J., Wei, H. S., Ochir, A., Davaasuren, D., Chonokhuu, S., & Nasanbat, E. (2019). Spatial and temporal variations in grassland production from 2006 to 2015 in Mongolia along the China-Mongolia railway. Sustainability, 11(7), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072177
Liu, H., Zhu, H., & Wang, P. (2016). Quantitative modelling for leaf nitrogen content of winter wheat using UAV-based hyperspectral data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(8–10), 2117–2134. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2016.1253899
Liu, N., Liu, G., & Sun, H. (2020). Real-time detection on spad value of potato plant using an in-field spectral imaging sensor system. Sensors, 20(12), 3430. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20123430
Liu, X. Y., Bai, Z. K., Zhou, W., Cao, Y. G., & Zhang, G. J. (2017). Changes in soil properties in the soil profile after mining and reclamation in an opencast coal mine on the Loess Plateau, China. Ecological Engineering, 98, 228–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.10.078
Maesano, M., Khoury, S., Nakhle, F., Firrincieli, A., Gay, A., Tauro, F., & Harfouche, A. (2020). UAV-Based LiDAR for High-Throughput Determination of Plant Height and Above-Ground Biomass of the Bioenergy Grass Arundo donax. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203464
Maiti, S. K. (2013). Ecorestoration of the coalmine degraded lands. Springer.
Milas, A. S., Romanko, M., Reil, P., Abeysinghe, T., & Marambe, A. (2018). The importance of leaf area index in mapping chlorophyll content of corn under different agricultural treatments using UAV images. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39(15–16), 5415–5431. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1455244
Mukhopadhyay, S., Masto, R. E., Yadav, A., George, J., Ram, L. C., & Shukla, S. P. (2016). Soil quality index for evaluation of reclaimed coal mine spoil. Science of the Total Environment, 542, 540–550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.035
Myneni, R. B., Hall, F. G., Sellers, P. J., & Marshak, A. L. (1995). The interpretation of spectral vegetation indexes. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 33(2), 481–486. https://doi.org/10.1109/36.377948
Pölönen, I., Saari, H., Kaivosoja, J., Honkavaara, E., & Pesonen, L. (2013). Hyperspectral imaging based biomass and nitrogen content estimations from light-weight UAV. In Remote Sensing for Agriculture, Ecosystems, and Hydrology XV (Vol. 8887, p. 88870J). International Society for Optics and Photonics. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2028624
Qu, J. F., Hou, Y. L., Ge, M. Y., Wang, K., Liu, S., Zhang, S. L., Li, G., & Chen, F. (2017). Carbon dynamics of reclaimed coal mine soil under agricultural use: A chronosequence study in the Dongtan Mining Area, Shandong Province. China. Sustainability, 9(4), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9040629
Ren, H., Xiao, W., Zhao, Y. L., & Hu, Z. Q. (2020). Land damage assessment using maize aboveground biomass estimated from unmanned aerial vehicle in high groundwater level regions affected by underground coal mining. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27, 21666–21679.
Ren, H., Zhao, Y. L., Xiao, W., & Hu, Z. Q. (2019). A review of UAV monitoring in mining areas: Current status and future perspectives. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 6(3), 320–333.
Schirrmann, M., Hamdorf, A., Garz, A., Ustyuzhanin, A., & Dammer, K. H. (2016). Estimating wheat biomass by combining image clustering with crop height. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 121, 374–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.01.007
Tang, Q., Li, L., Zhang, S., Zheng, L., & Mao, C. H. (2018). Characterization of heavy metals in coal gangue-reclaimed soils from a coal mining area. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 186, 1–11.
Tunca, E., Köksal, E. S., Çetin, S., Ekiz, N. M., & Balde, H. (2018). Yield and leaf area index estimations for sunflower plants using unmanned aerial vehicle images. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 190(11), 1-1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7064-x
Varela, S., Assefa, Y., Prasad, P. V. V., Peralta, N. R., & Ciampitti, I. A. (2017). Spatio-temporal evaluation of plant height in corn via unmanned aerial systems. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 11(3), 1.
Walter, J. D., Edwards, J., McDonald, G., & Kuchel, H. (2019). Estimating biomass and canopy height with LiDAR for field crop breeding. Frontiers in plant science, 10, 1145. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.01145
Wang, G., Liu, S., Liu, T., Fu, Z., Yu, J., & Xue, B. (2019). Modelling above-ground biomass based on vegetation indexes: a modified approach for biomass estimation in semi-arid grasslands. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 40(10), 3835-3854. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2018.1553319
Wang, P. J., Hu, Z. Q., Shao, F., Jiang, Z. D., Qiao, Z. Y., Liu, D. W., & Chen, Y. K. (2014). Feasibility analysis of Yellow River sediment used as the filling reclamation material of mining subsidence land. Journal of China Coal Society, 39, 1133–1139.
Wang, P., Hu, Z., Yost, R. S., Shao, F., Liu, J., & Li, X. (2016). Assessment of chemical properties of reclaimed subsidence land by the integrated technology using Yellow River sediment in Jining, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(12), 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5848-2
Wang, X. T., Hu, Z. Q., & Liang, Y. S. (2020). Impact of interlayer on moisture characteristics of reclaimed soil backfilled with yellow river sediments. International Journal of Agricultural and Biological Engineering, 13(1), 153–159.
Wang, Y. H., Xin, L. J., Zhang, H. Z., & Li, Y. Q. (2019). an estimation of the extent of rent-free farmland transfer and its driving forces in rural China: A multilevel logit model analysis. Sustainability, 11(11), 3161. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113161
Wu, H., Xiong, D. H., Xiao, L., Zhang, S., Yuan, Y., Su, Z. A., ... & Yang, D. (2018). Effects of vegetation coverage and seasonal change on soil microbial biomass and community structure in the dry-hot valley region. Journal of Mountain Science, 15(7), 1546-1558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-017-4650-2
Xiao, W., Fu, Y. H., Wang, T., & Lv, X. J. (2018). Effects of land use transitions due to underground coal mining on ecosystem services in high groundwater table areas: A case study in the Yanzhou coalfield. Land Use Policy, 71, 213–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.11.059
Xiao, W., & Hu, Z. Q. (2014). GIS-based pre-mining land damage assessment for underground coal mines in high groundwater area. International Journal of Mining & Mineral Engineering, 5(3), 245–255.
Xiao, W., Hu, Z. Q., Yoginder, P. C., & Zhao, Y. L. (2014). Dynamic subsidence simulation and topsoil removal strategy in high-groundwater table and underground coal mining area- a case study in Shandong Province. International Journal of Mining, Reclamation and Environment, 28(4), 250–263.
Yang, G. H., Hu, Z. Q., Zhao, Y. L., Yang, Y. Q., & Yu, Y. (2014). Proposals on countermeasures of reclamation control in coal mining subsidence land with high underground water level. Coal Eng, 46, 91–95.
Yang, R., Wang, Y., & Ding, C. (2016). Laboratory study of wave propagation due to explosion in a jointed medium. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 81, 70–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.10.014
Yoginder, P. C. (2018). Concurrent mining and reclamation for underground coal mining subsidence impacts in China. International Journal of Coal Science & Technology, 5(1), 18–35.
Yuan, M., Burjel, J. C., Isermann, J., Goeser, N. J., & Pittelkow, C. M. (2019). Unmanned aerial vehicle–based assessment of cover crop biomass and nitrogen uptake variability. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 74(4), 350–359. https://doi.org/10.2489/jswc.74.4.350
Yue, J. B., Feng, H. K., Jin, X. L., Yuan, H. H., Li, Z. H., Zhou, C. Q., Yang, G. J., & Tian, Q. J. (2018). A comparison of crop parameters estimation using images from UAV-mounted snapshot hyperspectral sensor and high-definition digital camera. Remote Sensing, 10(7), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10071138
Yue, J. B., Yang, G. J., Tian, Q. J., Feng, H. K., Xu, K. J., & Zhou, C. Q. (2019). Estimate of winter-wheat above-ground biomass based on UAV ultrahigh-ground-resolution image textures and vegetation indices. ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 150, 226–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.02.022
Zhang, H., Sun, Y., Chang, L., Qin, Y., Chen, J., Qin, Y., Du, J. X., Yi, S. H., Wang, Y. (2018). Estimation of grassland canopy height and aboveground biomass at the quadrat scale using unmanned aerial vehicle. Remote sensing, 10(6), 851. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060851
Zhang, K., Xu, L. J., Huang, G. D., Meng, X. Y., Yao, J. X., & Jiang, B. X. (2020). Coupled variations of soil temperature and moisture in reclaimed fields filled with coal gangue of different grain size distributions. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 20(4), 2248–2259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02579-2
Zhang, S. M., Zhao, G. X., Lang, K., Su, B. W., Chen, X. N., Xi, X., & Zhang, H. B. (2019). Integrated satellite, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) and ground inversion of the SPAD of winter wheat in the reviving stage. Sensors, 19(7), 1485. https://doi.org/10.3390/s1907148
Zhang, Y., & Shao, Z. F. (2021). Assessing of urban vegetation biomass in combination with lidar and high-resolution remote sensing images. International Journal of Remote Sensing. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431161.2020.1820618
Zhao, Y., Zheng, W., Xiao, W., Zhang, S., Lv, X., & Zhang, J. (2020). Rapid monitoring of reclaimed farmland effects in coal mining subsidence area using a multi-spectral UAV platform. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(7), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08453-5
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Technology Research and Development Program (2012BAC04B03) during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan Period, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41771542), Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Approval No. 42071250, National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 41807511).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Lyu, X., Xiao, W. et al. Evaluation of the soil profile quality of subsided land in a coal mining area backfilled with river sediment based on monitoring wheat growth biomass with UAV systems. Environ Monit Assess 193, 576 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09250-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09250-4