Abstract
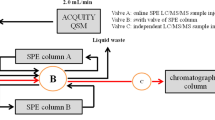
In this study, a pretreatment method based on the QuEChERS method has been applied for simultaneously extracting 27 residual pharmaceuticals from wastewater solids. The extracted compounds have been analyzed using online solid-phase extraction (SPE) coupled to liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS). A recovery test was conducted according to the absorbent type, and buffers were added in the sample extraction step. The highest recovery efficiency could be observed when Na2SO4 was used as an absorbent and Na2EDTA was injected during the extraction process; the recovery efficiencies of the proposed method for the target compounds ranged from 61.3 to 137.2%, and the repeatability was 6.8%. These recovery and repeatability data showed that the proposed method could reliably analyze the 27 target residual pharmaceuticals. The concentrations of the target compounds were all below the limits of quantification: 830 ng g−1 for the target compounds in suspended solids, 2353 ng g−1 in activated sludge, and 1929 ng g−1 in waste sludge. The analytical method established in this study can be applied to quantify residual pharmaceuticals in solid samples and to investigate their behaviors in a municipal wastewater treatment plant.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available for legal/ethical reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Afonso-Olivares, C., Sosa-Ferrera, Z., & Santana-Rodríguez, J. J. (2017). Occurrence and environmental impact of pharmaceutical residues from conventional and natural wastewater treatment plants in gran Canaria (Spain). Science of the Total Environment, 599–600, 934–943
Anastassiades, M., Lehotay, S. J., Stajnbaher, D., & Schenck, F. J. (2003). Fate and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase-extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. Journal of AOAC International, 86(2), 412–431
Ashfaq, M., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Chen, W., Wang, H., Chen, X., et al. (2017). Occurrence, fate, and mass balance of different classes of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in an anaerobic-anoxic-oxic wastewater treatment plant in Xiamen, China. Water Research, 123, 655–667
Association of Analytical communities (AOAC) International. (2011). AOAC Official Method 2007.01 pesticide residues in foods by acetonitrile extraction and partitioning with magnesium sulfate. Official Methods of Analysis AOAC International, 90, 17–26
Behera, S. K., Kim, H. W., Oh, J. E., & Park, H. S. (2011). Occurrence and removal of antibiotics, hormones and several other pharmaceuticals in wastewater treatment plants of the largest industrial city of Korea. Science of the Total Environment, 409, 4351–4360
Bourdat-Deschamps, M., Leang, S., Bernet, N., Daudin, J., & Nelieu, S. (2014). Multi-residue analysis of pharmaceuticals in aqueous environmental samples by online solid-phase extraction-ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: optimisation and matrix effects reduction by quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction. Journal of Chromatography A, 1349, 11–23
Carballa, M., Omil, F., Lema, J. M., Llompart, M., García-Jares, C., Rodríguez, I., et al. (2004). Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Research, 38, 2918–2926
Daughton, C. G., & Ternes, T. A. (1999). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environmental Health Perspectives, 107, 907–938
De Oliveira, M., Frihling, B. E. F., Velasques, J., Magalhães Filho, F. J. C., Cavalheri, P. S., & Migliolo, L. (2020). Pharmaceuticals residues and xenobiotics contaminants: occurrence, analytical techniques and sustainable alternatives for wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 705, 135568
Dorne, J. L. C. M., Ragas, A. M. J., Frampton, G. K., Spurgeon, D. S., & Lewis, D. F. (2007). Trends in human risk assessment of pharmaceuticals. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 387, 1167–1172
Epa, U. S. (2007). Method 1694: pharmaceuticals and personal care products in water, soil, sediment, and biosolids by HPLC/MS/MS, US EPA. Washington D.C.
European Committee for Standardization, (CEN). (2008). Foods of plant origin—determination of pesticide residues using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS following acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and clean-up by dispersive SPE – QuEChERS-method, EN 15662, 24, 1–83
Gabet-Giraud, V., Miège, C., Choubert, J. M., Ruel, S. M., & Coquery, M. (2010). Occurrence and removal of estrogens and beta blockers by various processes in wastewater treatment plants. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 4257–4269
Goh, S. X. L., Duarah, A., Zhang, L., Snyder, S. A., & Lee, H. K. (2016). Online solid phase extraction with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for determination of estrogens and glucocorticoids in water. Journal of Chromatography A, 1465, 1–9
Guo, C., Wang, M., Xiao, H., Huai, B., Wang, F., Pan, G., et al. (2016). Development of a modified QuEChERS method for the determination of veterinary antibiotics in swine manure by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Chromatography B, 1027, 110–118
Han, E. J., & Lee, D. S. (2017). Significance of metabolites in the environmental risk assessment of pharmaceuticals consumed by human. Science of the Total Environment, 592, 600–607
Hwang, Y., Shin, S., & Park, J. (2013). Development of the analytical method for residual pharmaceuticals in raw water using online sample preconcentration with high resolution LC-ESI/Orbitrap MS. Journal of Korean Society on Water Environment, 29,(3) 409–419. [Korean Literature]
Joss, A., Zabczynski, S., Göbel, A., Hoffmann, B., Löffler, D., McArdell, C. S., et al. (2006). Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Research, 40, 1686–1696
Khan, G. A., Lindberg, R., Grabic, R., & Fick, J. (2012). The development and application of a system for simultaneously determining anti-infectives and nasal decongestants using on-line solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis., 66, 24–32
Kim, J.-P., Jin, D. R., Lee, W., Chae, M., & Park, J. (2020). Occurrence and removal of veterinary antibiotics in livestock wastewater treatment plants. South Korea. Processes, 8, 720
Lindsey, M. E., Meyer, M., & Thurman, E. M. (2001). Analysis of trace levels of sulfonamide and tetracycline antimicrobials in groundwater and surface water using solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry, 73, 4640–4646
López-Serna, R., Perez, S., Ginebreda, A., Petrovic, M., & Barcelo, D. (2010). Fully automated determination of 74 pharmaceuticals in environmental and waste waters by online solid phase extraction-liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta, 83, 410–424
Luo, Y., Guo, W., Ngo, H. H., Nghiem, L. D., Hai, F. I., Zhang, J., et al. (2014). A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Science of the Total Environment, 473–474, 619–641
Marshall, A. J., & Piddock, L. J. (1994). Interaction of divalent cations, quinolones and bacteria. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 34(4), 465–483
Narumiya, M., Nakada, N., Yamashita, N., & Tanaka, H. (2013). Phase distribution and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products during anaerobic sludge digestion. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 260, 305–312
National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER). (2012). A study of discharge source and variation for pharmaceuticals in the environment (V), 1–6. Republic of Korea.
Pailler, J.-Y., Krein, A., Pfister, L., Hoffmann, L., & Guignard, C. (2009). Solid phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of sulfonamides, tetracyclines, analgesics and hormones in surface water and wastewater in Luxembourg. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 4736–4743
Panditi, V. R., Batchu, S. R., & Gardinali, P. R. (2013). Online solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-electrospray-tandem mass spectrometry determination of multiple classes of antibiotics in environmental and treated waters. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 405, 5953–5964
Park, J., Yamashita, N., Park, C., Shimono, T., Takeuchi, D. M., & Tanaka, H. (2017a). Removal characteristics of pharmaceuticals and personal care products: comparison between membrane bioreactor and various biological treatment processes. Chemosphere, 179, 347–358
Park, J., Yamashita, N., Wu, G., & Tanaka, H. (2017b). Removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by ammonia oxidizing bacteria acclimated in a membrane bioreactor: contributions and cometabolism and endogenous respiration. Science of the Total Environment, 605–606, 18–25
Park, J., Yamashita, N., & Tanaka, H. (2018). Membrane fouling control and enhanced removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products by coagulation-MBR. Chemosphere, 197, 467–476
Park, J., Kim, C., Hong, Y., Lee, W., Chung, H., Jeong, D.-H., et al. (2020). Distribution and removal of pharmaceuticals in liquid and solid phases in the unit processes of sewage treatment plants. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17, 687
Ponce-Robles, L., Rivas, G., Esteban, B., Oller, I., Malato, S., & Aguera, A. (2017). Determination of pesticides in sewage sludge from an agro-food industry using QuEChERS extraction followed by analysis with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409, 6181–6193
Radjenovic, J., Petrovic, M., & Barcelo, D. (2009). Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Research, 43, 831–841
Rossini, D., Ciofi, L., Ancillotti, C., Checchini, L., Bruzzoniti, M. C., Rivoira, L., et al. (2016). Innovative combination of QuEChERS extraction with on-line solid-phase extract purification and pre-concentration, followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their metabolites in sewage sludge. Analytica Chimca Acta, 935, 269–281
Shrivastava, A., & Gupta, V. B. (2011). Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chronicles of Young Scientists, 2(1), 21–25
Sui, Q., Zhao, W., Cao, X., Lu, S., Qiu, Z., Gu, W., et al. (2015). Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the leachates from a typical landfill reservoir of municipal solid waste in Shanghai, China: occurrence and removal by a full-scale membrane reactor. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 323, 99–108
Ternes, T. A., & Joss, A. (2006). Human pharmaceuticals, hormones and fragrances, IWA 203–206
Trenholm, R. A., Vanderford, B. J., & Snyder, S. A. (2009). On-line solid phase extraction LC-MS/MS analysis of pharmaceutical indicators in water: a green alternative to conventional methods. Talanta, 79, 1425–1432
Vieno, N., Tuhkanen, T., & Kronberg, L. (2007). Elimination of pharmaceuticals in sewage treatment plants in Finland. Water Research, 41, 1001–1012
Wang, Y., Li, Y., Hu, A., Rashid, A., Ashfaq, M., Wang, Y., et al. (2018). Monitoring, mass balance and fate of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in seven wastewater treatment plants in Xiamen City, China. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 354, 81–90
Acknowledgements
The authors also thank Editage (www.editage.co.kr) for providing English language editing guidance.
Funding
This work was supported by National Institute of Environmental Research, Republic of Korea (NIER-2018-01-01-058, NIER-2019-01-01-054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J., Kim, C., Hong, Y. et al. Determination of pharmaceuticals in solid samples in municipal wastewater treatment plants by online SPE LC–MS/MS using QuEChERS extraction. Environ Monit Assess 193, 279 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09069-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09069-z