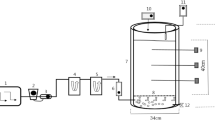
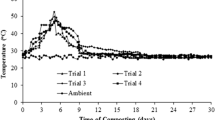
Abstract
As the composting industry develops rapidly in the world, the compost producers have focused on the efficiency of energy utilization in production without restricting the quality of compost in the forced ventilation systems. Therefore, this experimental study quantified the impacts of initial C/N ratio on aeration requirement and energy consumption due to aeration for reactor composting of rose pomace through kinetics of the process using fifteen 100-l composting reactors. The results of the study showed that initial C/N ratio significantly affected decomposition rate, compost maturity, and dry matter losses and organic matter losses (P < 0.05). The maximum decomposition rate (0.072 day−1) and the highest degree of progression of the composting process existed at the mixture with initial C/N ratio of 24.26. The results underlined the importance of the initial C/N of composting of rose pomace in terms of energy consumption due to aeration. In particular, more mature compost within a short time can be obtained when composting was operated with a C/N ratio of 23.7–25.8 in the expense of requiring more airflow rate, fan power, and energy consumption by aeration fan per composting material.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khateeb, A. J., Al-Sari, M. I., Al-Khatib, I. A., & Anayah, F. (2017). Factors affecting the sustainability of solid waste management system—the case of Palestine. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(2), 93.
Al-Madbouh, S., Al-Khatib, I. A., Al-Sari, M. I., Salahat, J. I., Jararaa, B. Y., & Ribbe, L. (2019). Socioeconomic, agricultural, and individual factors influencing farmers’ perceptions and willingness of compost production and use: an evidence from Wadi al-Far’a Watershed-Palestine. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(4), 209.
Al-Sari, M. I., Sarhan, M. A. A., & Al-Khatib, I. A. (2018). Assessment of compost quality and usage for agricultural use: A case study of Hebron, Palestine. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190, 223.
Araujo, A. S. F., Miranda, A. R. L., Oliveira, M. L. J., Santos, V. M., Nunes, L. A. P. L., & Melo, W. J. (2015). Soil microbial properties after 5 years of consecutive amendment with composted tannery sludge. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(1), 4153.
Arias, O., Viña, S., Uzal, M., & Soto, M. (2017). Composting of pig manure and forest green waste amended with industrial sludge. Science of the Total Environment, 586, 1228–1236.
Bernal, M. P., Alburquerque, J. A., & Moral, R. (2009). Composting of animal manures and chemical criteria for compost maturity assessment: a review. Bioresource Technology, 100, 5444–5453.
Ekinci, K. (1997). Evaluation of decomposition rate, airflow rate and ammonia control of sort paper fiber with broiler litter and additives - alum and sulfuric acid. Master’s Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, USA.
Ekinci, K., Keener, H. M., & Elwell, D. L. (2002). Composting short paper fiber with broiler litter and additives: II- evaluation and optimization of decomposition rate versus mixing ratio. Compost Science and Utilization, 10(1), 16–28.
Ekinci, K., Keener, H. M., Elwell, D. L., & Michel, F. C. (2004). Effects of four aeration strategies on the composting process. Part I - Experimental Studies, Transaction of the ASAE, 47(5), 1697–1708.
Ekinci, K., Tosun, İ., Bıtrak, B., Kumbul, B. S., Şevik, F., & Sülük, K. (2019). Effects of initial C/N ratio on organic matter degradation of composting of rose oil processing solid wastes. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 16(9), 5131–5140.
Epstein, E. (1997). The science of composting. Lanchester: Technomic Publishing Co..
Evangelou, A., Gerassimidou, S., Mavrakis, N., & Komilis, D. (2016). Monitoring the performances of a real scale municipal solid waste composting and a biodrying facility using respiration activity indices. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 188, 302.
Finstein, M. S., Miller, F. C., & Strom, P. F. (1986). Monitoring and evaluating composting process performance. Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation), 272–278.
Forján, R., Rodríguez-Vila, A., Cerqueira, B., Covelo, E. F., Marcet, P., & Asensio, V. (2018). Comparative effect of compost and technosol enhanced with biochar on the fertility of a degraded soil. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(10), 610.
Guo, R., Li, G., Jiang, T., Schuchardt, F., Chen, T., Zhao, Y., & Shen, Y. (2012). Effect of aeration rate, C/N ratio and moisture content on the stability and maturity of compost. Bioresource Technology, 112, 171–178.
Guo, H., Zhao, Y., Damgaard, A., Wang, Q., Lu, W., Wang, H., & Christensen, T. H. (2019). Material flow analysis of alternative biorefinery systems for managing Chinese food waste. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 149, 197–209.
Haug, R. T. (1993). The practical handbook of compost engineering (p. 213). Florida: Lewis Publishers.
Huang, G. F., Wong, J. W. C., Wu, Q. T., & Nagar, B. B. (2004). Effect of C/N on composting of pig manure with sawdust. Bioresource Technology, 24, 805–813.
Kaçar, H. (2018). The effect of different temperature applications on the process performance of composting of apple processing (pre-screening) solid waste. MSc thesis, Suleyman Demirel University.
Keener, H. M., Marugg, C., Hansen, R. C., & Hoitink, H. A. J. (1993). Optimizing the efficiency of the composting process. In H. A. J. Hoitink & P. H. M. Keener (Eds.), Science and engineering of composting: design, environmental, microbiological and utilization aspects (pp. 59–94). Columbus: Renaissance Publications.
Keener, H. M., Hansen, R. C., & Elwell, D. L. (1997). Airflow through compost: design and cost implications. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 13(3), 377–384.
Kumbul, B. S. (2015). A study on composting of opium poppy processing wastes. MSc thesis, Suleyman Demirel University.
Li, Z., Huang, G., Yu, H., Zhou, Y., & Huang, W. (2015). Critical factors and their effects on product maturity in food waste composting. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 217.
Marugg, C., Grebus, M., Hansen, R. C., Keener, H. M., & Hoitink, H. A. J. (1993). A kinetic model of the yard waste composting process. Compost Science and Utilization, 1(1), 38–51.
Muktadirul Bari Chowdhury, A. K. M., Akratos, C. S., Vayenas, D. V., & Pavlou, S. (2013). Olive mill waste composting: a review. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 85, 108–119.
Nafez, A. H., Nikaeen, M., Kadkhodaie, S., Hatamzadeh, M., & Moghim, S. (2015). Sewage sludge composting: quality assessment for agricultural application. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 709.
Onursal, E., & Ekinci, K. (2017). A kinetic study on how C/N ratio affects energy consumption of composting of rose oil-processing wastes with caged layer manure and straw. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 36(1), 129–137.
Prommuak, C., Jarunglumlert, T., Putmai, N., Sawatdee, S., Sanguanwong, A., & Pavasant, P. (2018). Comparative study on different turning device alignments for household food waste composters. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 37(6), 1954–1958.
Rashidi, S., Shahmoradi, B., Maleki, A., Sharafi, K., & Darvishi, E. (2017). Density assessment and mapping of microorganisms around a biocomposting plant in Sanandaj, Iran. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 189(5), 233.
Şevik, F., Tosun, İ., & Ekinci, K. (2016). Composting of olive processing wastes and tomato stalks together with sewage sludge or dairy manure. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13(5), 1207–1218.
Srivastava, V., Vaish, B., Singh, R. P., & Singh, P. (2020). An insight to municipal solid waste management of Varanasi city, India, and appraisal of vermicomposting as its efficient management approach. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(3), 1–23.
USCC. (2002). The US Composting Council Research and Education Foundation, and the United States Department of Agriculture. Test methods for the examination of composting and compost (TMECC). Houston: Edaphos International.
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TÜBİTAK) (grant numbers KAMAG-111G055/111G149).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekinci, K., Tosun, İ., Kumbul, B.S. et al. Aeration requirement and energy consumption of reactor-composting of rose pomace influenced by C/N ratio. Environ Monit Assess 192, 563 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08528-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08528-3