Abstract
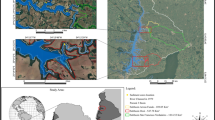
Several cores from the continental shelf of the Arabian Sea along the Indian Coast were investigated for change in sedimentation rates duly constrained for chronology based on 210Pb and 137Cs dating techniques. The emphasis was to look for spatial and temporal variation in the sedimentation rate along the continental shelf of eastern Arabian Sea between Goa to Kochi for water depth ≤ 150 m. This study showed varying sedimentation rates in coastal and distant sediment cores. Both 210Pb and 137Cs dating techniques showed comparable sedimentation rate in most sediment cores. The sedimentation in the continental shelf region of the coastal Arabian Sea is primarily controlled by discharge of sediments from rivers during Indian summer monsoon. Increased sedimentation rate from the north (off Goa) to the south (off Kochi) was triggered by high riverine flux and longshore sediment transport.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, R., Dutta, K., Bhushan, R., & Somayajulu, B. L. K. (2002). Evidence for solar forcing on the Indian monsoon during the last millennium. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 198(3–4), 521–527.
Agnihotri, R., Sarin, M. M., Somayajulu, B. L. K., Jull, A. J. T., & Burr, G. S. (2003). Late-Quaternary biogenic productivity and organic carbon deposition in the eastern Arabian Sea. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 197(1), 43–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00385-7.
Agnihotri, R., Kurian, S., Fernandes, M., Reshma, K., D’Souza, W., & Naqvi, S. W. A. (2008). Variability of subsurface denitrification and surface productivity in the coastal eastern Arabian Sea over the past seven centuries. The Holocene, 18(5), 755–764. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683608091795.
Aoyama, M., Hirose, K., Suzuki, Y., Inoue, H., & Sugimura, Y. (1986). High level radioactive nuclides in Japan in May. Nature (London), 321(6073), 819–820.
Appleby, P. G. (1997). Dating recent sediments by 210Pb: problems and solutions. In Proc. 2nd NKS/EKO-1 Seminar, Helsinki (Vol. 2).
Appleby, P. G., & Oldfield, F. (1992). Applications of lead-210 to sedimentation studies. In Uranium-series disequilibrium: applications to earth, marine, and environmental sciences (2nd ed., pp. 731–778).
Banerji, U. S., Pandey, S., Bhushan, R., & Juyal, N. (2015). Mid-Holocene climate and land–sea interaction along the southern coast of Saurashtra, western India. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111, 428–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.06.021.
Banerji, U. S., Bhushan, R., & Maurya, D. M. (2016). sedimentary records of paleoredox conditions at relict mudflat of Vasoj, Southern Saurashtra Coast, Gujarat, India. Earth Science India, 9, 114–125.
Banerji, U. S., Bhushan, R., & Jull, A. J. T. (2017). Mid−late Holocene monsoonal records from the partially active mudflat of Diu Island, southern Saurashtra, Gujarat, western India. Quaternary International, 443, 200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.09.060.
Bhushan, R., Dutta, K., & Somayajulu, B. L. K. (2001). Concentrations and burial fluxes of organic and inorganic carbon on the eastern margins of the Arabian Sea. Marine Geology, 178(1), 95–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00179-7.
Bruland, K. W., Bertine, K., Koide, M., & Goldberg, E. D. (1974). History of metal pollution in southern California coastal zone. Environmental Science & Technology, 8(5), 425–432.
Butler, D. (2011). Radioactivity spreads in Japan: fallout is localized, but could persist for years in some regions. Nature, 471(7340), 555–556.
Chakrapani, G. J. (2005). Factors controlling variations in river sediment loads. Current Science, 88(4), 569–575 http://www.jstor.org/stable/24110256.
Chandramohan, P., Jena, B. K., & Kumar, V. S. (2001). Littoral drift sources and sinks along the Indian coast. Current Science, 81(3), 292–297 http://www.jstor.org/stable/24106330.
Chino, M., Nakayama, H., Nagai, H., Terada, H., Katata, G., & Yamazawa, H. (2011). Preliminary estimation of release amounts of 131 I and 137 Cs accidentally discharged from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant into the atmosphere. Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology (Tokyo), 48(7), 1129–1134.
Cutshall, N. H., Larsen, I. L., & Olsen, C. R. (1983). Direct analysis of 210Pb in sediment samples: self-absorption corrections. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, 206(1–2), 309–312.
Dalai, T. K., Rengarajan, R., & Patel, P. P. (2004). Sediment geochemistry of the Yamuna River system in the Himalaya: implications to weathering and transport. Geochemical Journal, 38(5), 441–453.
Dilli, K. (1986). Geochronology and geochemistry of a sediment core from Bombay Coast. Mahasagar, 19(2), 87–95 http://ijs.nio.org/index.php/msagar/article/view/1860.
Dwarakish, G. S., Vinay, S. A., Dinakar, S. M., Pai, J. B., Mahaganesh, K., & Natesan, U. (2008). Integrated coastal zone management plan for Udupi coast using remote sensing, geographical information system and global position system. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2(1), 23515.
Dwarakish, G. S., Abdu Rahiman, K. U., & Natesan, U. (2009). Changes in river hydrology and coastal sedimentation by dams in Periyar River basin Keraa, India. In Proceedings of the 4th IASME/WSEAS International Conference on Water Resources, Hydraulics and Hydrology (WHH-09).
Frankel, E. G. (1995). Ocean environmental management: a primer on the role of the oceans and how to maintain their contributions to life on earth. Upper Saddle River: PTR Prentice Hall.
Galvin, C. J. (1973). A gross longshore transport rate formula. In Coastal Engineering (Vol. 1972, pp. 953–970). https://doi.org/10.1061/9780872620490.053.
Garcia Agudo, E. (1998). Global distribution of137Cs inputs for soil erosion and sedimentation studies. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Garzanti, E., Vezzoli, G., Andò, S., Paparella, P., & Clift, P. D. (2005). Petrology of Indus River sands: a key to interpret erosion history of the Western Himalayan Syntaxis. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 229(3), 287–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.11.008.
Goswami, V., Singh, S. K., Bhushan, R., & Rai, V. K. (2012). Temporal variations in 87Sr/86Sr and ?Nd in sediments of the southeastern Arabian Sea: impact of monsoon and surface water circulation. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(1), 1–13.
Hamilton, T. F., Ballestra, S., Baxter, M. S., Gastaud, J., Osvath, I., Parsi, P., Povinec, P. P., & Scott, E. M. (1994). Radiometric investigations of Kara Sea sediments and preliminary radiological assessment related to dumping of radioactive wastes in the Arctic seas. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 25(1), 113–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0265-931X(94)90011-6.
Han, Y. M., Cao, J. J., Kenna, T. C., Yan, B., Jin, Z. D., Wu, F., & An, Z. S. (2011). Distribution and ecotoxicological significance of trace element contamination in a~ 150 yr record of sediments in Lake Chaohu, Eastern China. Journal of Environmental Monitoring, 13(3), 743–752.
Hay, W. W. (1998). Detrital sediment fluxes from continents to oceans. Chemical Geology, 145(3–4), 287–323.
Hirose, K., Sugimura, Y., & Aoyama, M. (1992). Plutonium and 137Cs in the western North Pacific: Estimation of residence time of plutonium in surface waters. International Journal of Radiation Applications and Instrumentation. Part A. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 43(1), 349–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2889(92)90105-N.
Holeman, J. N. (1968). The sediment yield of major rivers of the world. Water Resources Research, 4(4), 737–747.
Jha, S. K., Gothankar, S. S., Sartandel, S., Pote, M. B., Hemalatha, P., Rajan, M. P., Vidyasagar, D., Indumati, S. P., Shrivastava, R., & Puranik, V. D. (2012). Spatial distribution of fallout 137Cs in the coastal marine environment of India. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 113, 71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2012.04.018.
Joshi, L. U., Rangarajan, C., & Gopalakrishnan, S. (1969). Measurement of lead-210 in surface air and precipitation. Tellus, 21(1), 107–112.
Krishnaswami, S., & Lal, D. (1978). Radionuclide limnochronology. In A. Lerman (Ed.), Lakes: Chemistry, geology, physics (pp. 153–177). New York: Springer New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-1152-3_6.
Kumar, V. S., Pathak, K. C., Pednekar, P., Raju, N. S. N., & Gowthaman, R. (2006). Coastal processes along the Indian coastline. Current Science, 91(4), 530–536.
Kunte, P. D. (1994). Sediment transport along the Goa-North Karnataka coast, western India. Marine Geology, 118(3), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(94)90084-1.
Kunte, P. D., Wagle, B. G., & Sugimori, Y. (2001). Littoral transport studies along west coast of India-a reivew. Indian journal of marine sciences, 30, 57–64.
Longmore, M. E. (1982). The caesium-137 dating technique and associated applications in Australia-a review. In Archaeometry: an Australasian perspective (pp. 310–321).
Mabit, L., Benmansour, M., & Walling, D. E. (2008). Comparative advantages and limitations of the fallout radionuclides 137Cs, 210Pbex and 7Be for assessing soil erosion and sedimentation. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 99(12), 1799–1807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2008.08.009.
Manjunatha, B. R., & Shankar, R. (1992). A note on the factors controlling the sedimentation rate along the western continental shelf of India. Marine Geology, 104(1), 219–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(92)90097-2.
Martin, G. D., Nisha, P. A., Balachandran, K. K., Madhu, N. V, Nair, M., Shaiju, P., et al. (2011). Eutrophication induced changes in benthic community structure of a flow-restricted tropical estuary (Cochin backwaters), India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 176(1–4), 427–438.
McKee, B. A., Nittrouer, C. A., & DeMaster, D. J. (1983). Concepts of sediment deposition and accumulation applied to the continental shelf near the mouth of the Yangtze River. Geology, 11(11), 631–633.
Milliman, J., & Farnsworth, K. L. (2013). River discharge to the coastal ocean: a global synthesis. Cambridge University Press.
Milliman, J. D., Quraishee, G. S., & Beg, M. A. A. (1984). Sediment discharge from the Indus River to the ocean: past, present and future. In Marine geology and oceanography of Arabian Sea and Coastal Pakistan (pp. 65–70).
Morino, Y., Ohara, T., & Nishizawa, M. (2011, 2011). Atmospheric behavior, deposition, and budget of radioactive materials from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant in. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(7).
Naidu, A. S., Mowatt, T. C., Somayajulu, B. L. K., & Rao, K. S. (1985). Characteristics of clay minerals in the bed loads of major rivers of India. Transport of carbon and minerals in major world rivers, part, 3, 559–568.
Naik, D., & Kunte, P. (2016). Impact of port structures on the shoreline of Karnataka, west coast, India. International Journal of Advanced Remote Sensing and GIS, 5(5), 1726–1746.
Nair, R. R., & Pylee, A. (1968). Size distribution and carbonate content of the sediments of the western shelf of India. Bulletin of National Institute of Sciences of India, 38, 411–420.
Nambiar, A. R., & Rajagopalan, G. (1995). Radiocarbon dates of sediment cores from inner continental shelf off Taingapatnam, southwest coast of India. Current Science, 68(11), 1133–1137 http://www.jstor.org/stable/24097045.
Nambiar, A. R., Rao, B. R. J., & Rajagopalan, G. (1991). Radiocarbon dates of sediment cores from innercontinental shelf off Karwar, west coast of India. Current Science (Bangalore), 61(5), 353–354.
Naqvi, S. W. A., Narvekar, P. V., & Desa, E. (2006). Coastal biogeochemical processes in the North Indian Ocean (14, SW). Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Nigam, R., Khare, N., & Borole, D. V. (1991). Morphogroups of benthic foraminifera: proxy for Palaeomonsoonal precipitation. In International Symposium on Oceanography of Indian Ocean. National Institute of Oceanography, Goa (p. 57).
Nigam, R., Khare, N., & Nair, R. R. (1995). Foraminiferal evidences for 77-year cycles of droughts in India and its possible modulation by the Gleissberg solar cycle. Journal of Coastal Research, 11(4), 1099–1107 http://www.jstor.org/stable/4298414.
Papucci, C. (1997). Sampling marine sediments for radionuclide monitoring.
Perkins, R. W., & Thomas, C. W. (1980). Worldwide fallout. In Transuranic elements in the environment.
Pheiffer Madsen, P., & Sørensen, J. (1979). Validation of the lead-210 dating method. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 54(1–2), 39–48.
Preiss, N., Mélières, M.-A., & Pourchet, M. (1996). A compilation of data on lead 210 concentration in surface air and fluxes at the air-surface and water-sediment interfaces. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 101(D22), 28847–28862.
Ramaswamy, V., & Nair, R. R. (1994). Fluxes of material in the Arabian sea and bay of Bengal sediment trap studies. Journal of Earth System Science, 103(2), 189–210.
Rao, K. L. (1979). India’s water wealth. New Delhi: Orient Blackswan.
Rao, V. P., & Rao, B. R. (1995). Provenance and distribution of clay minerals in the sediments of the western continental shelf and slope of India. Continental Shelf Research, 15(14), 1757–1771. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4343(94)00092-2.
Rao, P., & Wagle, B. G. (1997). Geomorphology and surficial geology of the western continental shelf and slope of India: a review. Current Science, 73(4), 330–350.
Rao, V. P., Kessarkar, P. M., Thamban, M., & Patil, S. K. (2010). Paleoclimatic and diagenetic history of the late quaternary sediments in a core from the Southeastern Arabian Sea: geochemical and magnetic signals. Journal of Oceanography, 66(1), 133–146.
Robbins, J. A., & Edgington, D. N. (1975). Determination of recent sedimentation rates in Lake Michigan using Pb-210 and Cs-137. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 39(3), 285–304.
Rubio, R., & Ure, A. M. (1993). Approaches to sampling and sample pretreatments for metal speciation in soils and sediments. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51(1–4), 205–217.
Sharma, P., Borole, D. V., & Zingde, M. D. (1994). 210Pb based trace element fluxes in the nearshore and estuarine sediments off Bombay, India. Marine Chemistry, 47(3), 227–241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(94)90022-1.
Singh, S. K. (1999). Isotopic and geochemical studies of the lesser Himalayan sedimentaries. Vadodara.
Singh, K. T., Nayak, G. N., Fernandes, L. L., Borole, D. V., & Basavaiah, N. (2014). Changing environmental conditions in recent past — reading through the study of geochemical characteristics, magnetic parameters and sedimentation rate of mudflats, central west coast of India. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 397, 61–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.008.
Sinha, A., Berkelhammer, M., Stott, L., Mudelsee, M., Cheng, H., & Biswas, J. (2011). The leading mode of Indian summer monsoon precipitation variability during the last millennium. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(15). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047713.
Sirocko, F., & Sarnthein, M. (1989). Wind-borne deposits in the northwestern Indian Ocean: record of Holocene sediments versus modern satellite data. Paleoclimatology and Paleometeorology: modern and past patterns of global atmospheric transport, 282, 401–433.
Smith, J. N., & Schafer, C. T. (1987). A 20th-century record of climatologically modulated sediment accumulation rates in a Canadian fjord. Quaternary Research, 27(3), 232–247.
Somayajulu, B. L. K., Yadav, D. N., & Sarin, M. M. (1994). Recent sedimentary records from the Arabian Sea. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences-Earth and Planetary Sciences, 103(2), 315–327.
Somayajulu, B. L. K., Bhushan, R., Sarkar, A., Burr, G. S., & Jull, A. J. T. (1999). Sediment deposition rates on the continental margins of the eastern Arabian Sea using 210Pb, 137Cs and 14C. Science of the Total Environment, 237, 429–439. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(99)00155-2.
Sontakke, N. A., Pant, G. B., & Singh, N. (1993). Construction of all-India summer monsoon rainfall series for the period 1844-1991. Journal of Climate, 6(9), 1807–1811.
Sontakke, N. A., Singh, N., & Singh, H. N. (2008). Instrumental period rainfall series of the Indian region (AD 1813-2005): revised reconstruction, update and analysis. The Holocene, 18(7), 1055–1066.
Thamban, M., & Rao, V. P. (2000). Distribution and composition of verdine and glaucony facies from the sediments of the western continental margin of India. Society for Sedimentary Geology, 233–244.
Thamban, M., Kawahata, H., & Rao, V. P. (2007). Indian summer monsoon variability during the holocene as recorded in sediments of the Arabian Sea: Timing and implications. Journal of Oceanography, 63(6), 1009–1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10872-007-0084-8.
Turekian, K. K., Nozaki, Y., & Benninger, L. K. (1977). Geochemistry of atmospheric radon and radon products. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 5(1), 227–255.
Yadava, M. G., Ramesh, R., & Pant, G. B. (2004). Past monsoon rainfall variations in peninsular India recorded in a 331-year-old speleothem. The Holocene, 14(4), 517–524.
Yamagata, N., Matsuda, S., & Kodaira, K. (1963). Run-off of caesium-137 and strontium-90 from rivers. Nature, 200(4907), 668–669.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful for the support of the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Govt. of India, under the GEOTRACES Project. We thank cruise participants, Sneha, Shubhananad, K.D. Damodarao, for their help and support during sediment core collection. We also thank Captain and Crew members of Sagar Manjusha and NIOT for providing logistic support during the cruise. We thank Director, PRL, for the support and encouragement. Authors thank anonymous reviewers and editor for their constructive comments which improved the manuscript significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, C., Banerji, U.S., Chandana, K.R. et al. 210Pb dating of recent sediments from the continental shelf of western India: factors influencing sedimentation rates. Environ Monit Assess 192, 468 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08415-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08415-x