Abstract
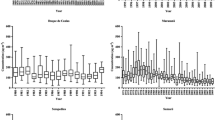
Particle deposition in three selected “urban/suburban” sites in Sfax city, southern Tunisia, was studied through biweekly monitoring particulate deposits from April 12 to November 26, 2014. Two sites (S1 and S2) were located at the proximity of well-exposed cross-roads; however, the third (S3) was located at a street canyon. A very high fluctuation in those particle fluxes, ranging from 0.1 and 17.9 g/m2, was clearly observed. Spatiotemporal distribution of the deposited particulate fluxes proved the concomitant effects of multiple (local and synoptic) sources. The industrial contribution rate in terms of particulate deposits was demonstrated to be negligible, and as for that of traffic, it was confirmed to be more significant. The highest particulate deposition seemed to be associated with the sirocco wind phenomenon. Humidity appeared as a main parameter reinforcing the particle deposition (by gathering process); however, the rain was considered as an important factor in terms of atmosphere washing. The intersite distribution was also threatened by local wind movements, shown as a non-negligible factor in terms of deposition, especially in the street canyon.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dousari, A. M., Al-Awadhi, J., & Ahmed, M. (2013). Dust fallout characteristics within global dust storm major trajectories. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 6(10), 3877–3884.
Azri, C., & Medhioub, K. (2000). Caractérisation physico-chimique de l’aérosol urbain dans la ville de Sfax (Tunisie). Pollution Atmosphérique, n, 170, 279–291.
Azri, C., Maalej, A., Tlili, A., & Medhioub, K. (2002). Caractérisation du niveau de pollution atmosphérique dans la ville de Sfax (Tunisie): Influence des sources et des facteurs météorologiques. Techniques, Sciences, Méthodes (TSM), 1(97), 78–92.
Azri, C., Maalej, A., Medhioub, K., & Rosset, R. (2007). Evolution of atmospheric pollutants in the city of Sfax (Tunisia) (October 1996-June 1997). Atmosfera, 20(3), 223–246.
Bahloul, M., Chabbi, I., Dammak, R., Amdouni, R., Medhioub, K., & Azri, C. (2015a). Geochemical behaviour of PM10 aerosol constituents under the influence of succeeding anticyclonic/cyclonic situations: case of Sfax City, southern Tunisia. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 757. doi:10.1007/s10661-015-4980-x.
Bahloul, M., Chabbi, I., Sdiri, A., Amdouni, R., Medhioub, K., & Azri, C. (2015b). Spatiotemporal variation of particulate fallout instances in Sfax City, Southern Tunisia: influence of sources and meteorology. Advances in Meteorology, 471396, 11. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/471396.
Binggan, W., Fengqing, J., Li, X., & Mu, S. (2009). Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dust from Urumqi, NW China. Microchemical Journal, 93, 147–152.
Chen, L., Peng, S., Liu, J., & Hou, Q. (2012). Dry deposition velocity of total suspended particles and meteorological influence in four locations in Guangzhou, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(4), 632–639.
Cindoruk, S. S., & Tasdemir, Y. (2007). Deposition of atmospheric particulate PCBs in suburban site of Turkey. Atmospheric Research, 85, 300–309.
DGAT (Direction Générale de l’Aménagement du Territoire). (1995). Atlas du gouvernorat de Sfax. Rapport de la Deuxième Phase, Direction Générale de l’Aménagement du Territoire.
Ellouz, F., Masmoudi, M., Medhioub, K., & Azri, C. (2014). Temporal evolution and particle size distribution of aerosol constituents collected in Northern Tunisia (Boukornine) under sirocco wind circulations. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(10), 4399–4406.
Fang, G. C. (1992). A study of mass size distributions and particle deposition velocities in ambient air (Ph.D. Thesis). Chicago: Illinois useful in predicting particle mass dry deposition.
Gabet, M. C. (1999). Dépôt de poussières au voisinage des tunnels routiers. Lyon (France): Centre d’étude des tunnels.
Henia, L., & Mougou, R. (1997). Contribution à l’étude des phénomènes atmosphériques à risque en Tunisie: le cas du sirocco. Publication de l’Association Internationale de Climatologie, 10, 84–90.
Huang, J., Liu, Y., & Holsen, T. M. (2011). Comparison between knife-edge and Frisbee shaped surrogate surfaces for making dry deposition measurements: wind tunnel experiments and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling. Atmospheric Environment, 45(25), 4213–4219.
JICA (Japan International Cooperation Agency). (1993). The study on waste water treatment and recycling of selected industries in the region of Sfax in the republic of Tunisia. Japan
Langner, M., Draheim, T., & Endlicher, W. (2011). Particulate matter in the urban atmosphere: concentration, distribution, reduction-results of studies in the Berlin metropolitan area.
Lequy, E., Calvaruso, C., Conil, S., & Turpault, M. P. (2014). Atmospheric particulate deposition influence by tree canopy in beech forests in the north of France. Science of the Total Environment, 487, 206–215.
Lin, J. J., Noll, K. E., & Holsen, T. M. (1994). Dry deposition velocities as a function of particle size in the ambient atmosphere. Aerosol Science and Technology, 20, 239–252.
Liu, L., & Zhang, J. L. (2009). Ambient air pollution and children’s lung function in China. Environment International, 35(1), 178–186.
Lopez-Garcia, P., Gelado-Caballero, M. D., Santana-Castellano, D., Suarez de Tangil, M., Collado-Sanchez, C., & Hernandez-Brito, J. J. (2013). A three-year time-series of dust deposition flux measurements in Gran Canaria, Spain: a comparison of wet and dry surface deposition samplers. Atmospheric Environment, 79, 689–694.
Marx, S. K., & McGowan, H. A. (2005). Dust transportation and deposition in a superhumid environment, West Coast, South Island, New Zealand. Catena, 59(2), 147–171.
MEHAT (Ministère de l’Equipement, de l’Habitat et de l’Aménagement du Territoire). (2007). Stratégie de Développement du Grand Sfax 2016. Rapport Phase II (SDGS2), Sfax (Tunisie).
Mercado, L. M., Bellouin, N., Sitch, S., Boucher, O., Huntingford, C., & Wild, M. (2009). Impact of changes in diffuse radiation on the global land carbon sink. Assessment of trace element concentrations and their estimated dry deposition fluxes in an urban atmosphere. Nature, 458(7241), 1014–1017.
Noll, K. E., Fang, K. Y. P., & Watkins, L. A. (1987). Characterization of the deposition of particles from the atmosphere to a flat plate (Chicago). Atmospheric Envirennement, 22(7), 1461–1468.
Orange, D., & Gac, J. Y. (1990). Bilan géochimique des apports atmosphériques en domaines sahélien et soudano-guinéen d’Afrique de l’Ouest (bassins supérieurs du Sénégal et de la Gambie). Géodynamique (Paris), 5(1), 51–65.
Tai, H. S., Lin, J. J., & Noll, K. E. (1999). Characterization of atmospheric dry deposited particles at urban and non-urban locations. Journal of Aerosol Sciences, 30, 1057–1068. NOAA ARL. Data (http://www.arl.noaa.gov/ready.html).
Terzi, E., & Samara, C. (2005). Dry deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban and rural sites of Western Greece. Atmospheric Environment, 39(34), 6261–6270.
USEPA (US Environmental Protection Agency). (1995). Screen 3 model user’s guide. Tech. Rep. EPA/600/4-90/027F.
Yang, H. H., Hsieh, L. T., Lin, M. C., Mi, H. H., & Chen, P. C. (2004). Dry deposition of sulfate-containing particulate at the highway intersection coastal and suburban areas. Chemosphere, 54, 369–378.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dammak, R., Bahloul, M., Chabbi, I. et al. Spatial and temporal variations of dust particle deposition at three “urban/suburban” areas in Sfax city (Tunisia). Environ Monit Assess 188, 336 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5341-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5341-0