Abstract
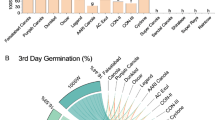
In developing countries like Pakistan, irrigation of crops with industrial and municipal wastewater is a common practice. However, the impact of wastewater irrigation on vegetables growth has rarely been studied. Therefore, the present study was conducted to determine the effect of industrial wastewater on the germination and seedling growth of some commonly grown vegetables in Pakistan. Wastewater samples were collected from two different industries (marble industry and match alam factory) at Hayatabad Industrial Estate (HIE) in Peshawar, Pakistan, and their effect on different growth parameters of four vegetables including Hibiscus esculentus, Lactuca sativa, Cucumis sativus, and Cucumis melo was investigated. The obtained results revealed that wastewater from marble industry did not affect seed germination except a minor inhibition in H. esculentus. Effluents from match alam factory stimulated seed germination in C. melo and C. sativus but had no effect on seed germination in the other two vegetables. Wastewater increased root and shoot length in H. esculentus, L. sativa and C. melo, but decreased it in C. sativus. Similarly, differential effects of wastewater were observed on fresh and dry biomass of seedlings in all vegetables. It can be concluded that wastewater may have different effects on different crops, depending upon the nature of wastewater and sensitivity of a plant species to wastewater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbar, F., Hadi, Z., & Ullah, Z. M. A. (2007). Effect of marble industry effluent on seed germination, post germinative growth and productivity of Zea mays L. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 10, 4148–4151.
Almansouri, M., Kinet, J. M., & Lutts, S. (2001). Effect of salt and osmotic stresses on germination in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.). Plant and Soil, 231, 243–254.
Ahmad, K., Ejaz, A., Azam, M., Khan, Z. I., Ashraf, M., Al-Qurainy, F., Fardous, A., Gondal, S., Bayat, A. R. & Valeem, E. E. (2011). Lead, cadmium and chromium contents of canola irrigated with sewage water. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 43(2), 1403–1410.
Aslam, M. M., Baig, M. A., Hassan, I., Qazi, I. A., Malik, M., & Saeed, H. (2004). Textile waste water characterization and reduction of its COD and BOD by oxidation. Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 3, 804–811.
Azizullah, A., Khattak, M. N. K., Richter, P., & Häder, D.-P. (2011). Water pollution in Pakistan and its impact on public health—a review. Environment International, 37, 479–497.
Azizullah, A., Richter, P., & Häder, D.-P. (2012). Sensitivity of various parameters in Euglena gracilis to short-term exposure to industrial wastewaters. Journal of Applied Phycology, 24, 187–200.
Azizullah, A., Jamil, M., Richter, P., & Häder, D.-P. (2014). Fast bioassessment of wastewater and surface water quality using freshwater flagellate Euglena gracilis—a case study from Pakistan. Journal of Applied Phycology, 26, 421–431.
Baroni, L., Cenci, L., Tettamanti, M., & Berati, M. (2007). Evaluating the environmental impact of various dietary patterns combined with different food production systems. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 61, 279–286.
Bibi, A., Sadaqat, H. A., Tahir, M. H. N., & Akram, H. M. (2012). Screening of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor var Moench) for drought tolerance at seedling stage in polyethylene glycol. The Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences, 22, 671–678.
Briscoe, J., & Qamar, U. (2006). Pakistan’s water economy: running dry. World Bank document: Oxford University Press.
Dhanam, S. (2009). Effect of dairy effluent on seed germination, seedling growth and biochemical parameters in Paddy. Botany Research International, 2, 61–63.
Ensink, J. H. J., Vander, H. W., Matsuno, Y., Munir, S., & Aslam, M. R. (2002). Use of untreated wastewater in peri-urban agriculture in Pakistan: risks and opportunities. IWMI Research Report No. 64. Colombo: International Water Management Institute (IWMI).
Ensink, J. H. J., Mahmood, T., Vander, H. W., Raschid-Sally, L., & Amerasinghe, F. P. (2004). A nation-wide assessment of waste water use in Pakistan: an obscure activity or a vitally important one? Water Policy, 6, 1–10.
Fakayode, S. O. (2005). Impact assessment of industrial effluent on water quality of the receiving Alaro River in Ibadan, Nigeria. African Journal of Environmental Assessment and Management, 10, 1–13.
Gvozdenac, S., & Inđić, D. (2012). International Conference on BioScience: biotechnology and biodiversity—step in the future. The Forth Joint UNS-PSU Conference (pp. 331–341).
Heikens, A. (2006). Arsenic contamination of irrigation water, soil and crops in Bangladesh: risk implications for sustainable agriculture and food safety in Asia. RAP Publication (FAO)
Hussain, F., Malik, S. A., Athar, M., Bashir, N., Younis, U., Hassan, M. U., & Mahmood, S. (2010). Effect of tannery effluents on seed germination and growth of two sunflower cultivars. African Journal of Biotechnology, 9, 5113–5120.
Islam, M. O., Khan, H. R., Das, A. K., Akhtar, M. S., Oki, Y., & Adochi, T. (2006). Impacts of industrial effluents on plant growth and soil properties. Soil and Environment, 25, 113–118.
Kaydan, D., & Yagmur, M. (2008). Germination, seedling growth and relative water content of shoot in different seed sizes of triticale under osmotic stress of water and NaCl. African Journal of Biotechnology, 7, 2862–2868.
Khan, S., Khan, A. M., & Khan, M. N. (2002). Investigation of pollutants load in wastewater of Hayatabad industrial estate, Peshawar, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Applied Sciences, 2, 457–461.
Khan, S., Haq, F., & Saeed, K. (2012). Pollution load in industrial effluent and ground water due to marble industries in District Buner, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. International Journal of Recent Scientific Research, 3(5), 366–368.
Kocak, S., Tokusoglu, O., & Aycan, S. (2005). Some heavy metal and trace essential element detection in canned vegetable foodstuffs by differential pulse polarography (DPP). Electronic Journal of Environmental, Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 4, 871–878.
Liu, J., Dorjderem, A., Fu, J., Lei, X., & Macer, D. (2011). Water Ethics and Water Resource Management. Ethics and Climate Change in Asia and the Pacific (ECCAP) Project Working Group 14 Report. UNESCO
Luo, X., Yu, S., Zhu, Y., & Li, X. (2012). Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Science of the Total Environment, 441–442, 17–30.
Mulk, S., Azizullah, A., Korai, A. L., & Khattak, M. N. K. (2015). Impact of marble industry effluents on water and sediment quality of Barandu River in Buner District, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187, 8.
Murtaza, G., & Zia, M. H. (2012). Wastewater production, treatment and use in Pakistan. In Second Regional Workshop of the Project ‘Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture’ (pp. 16–18).
Nagada, G. K., Diwan, A. M., & Ghole, V. S. (2006). Seed germination bioassays to assess toxicity of molasses fermentation based bulk drug industry effluent. Eur J Environ Agri Food Chem, 5, 1598–1603.
Nagajyothi, P. C., Dinakar, N., Suresh, S., Udaykiran, Y., Suresh, C., & Damodharam, T. (2009). Effect of industrial effluent on the morphological parameters and chlorophyll content of green gram (Phaseolus aureus Roxb). Journal of Environmental Biology, 30(3), 385–388.
Nasrullah, Naz, R., Bibi, H., Iqbal, M., & Durrani, M. I. (2006). Inadequately treated effluent discharged from several types of industrial units. Journal of Agricultural and Biological Science, 1(3), 18–24.
Nath, K., Singh, D., Shyam, S., & Sharma, Y. K. (2009). Phytotoxic effects of chromium and tannery effluent on growth and metabolism of Phaseolus mungo Roxb. Journal of Environmental Biology, 30, 227–234.
Nawaz, S., Ali, S. M., & Yasmin, A. (2006). Effect of industrial effluents on seed germination and early growth of Cicer arientum. Journal of Biological Sciences, 6, 49–54.
Niroula, B. (2003). Comparative effects of industrial effluents and submetropolitan sewage of Biratnagar on germination and seedling growth of rice and black gram. Our Nature, 1, 10–14.
Orhue, E. R., Osaigbovo, A. U., & Vwioko, D. E. (2005). Growth of maize (Zea mays L.) and changes in some chemical properties of an ultisol amended with brewery effluent. African Journal of Biotechnology, 4, 973–978.
Pandey, S., Tyagi, P., & Gupta, A. (2007). Physicochemical analysis and effect of distillery effluent on seed germination of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and lady’s finger (Abelomoschus esculentus). ARPN Journal of Agriculture and Biological Sciences, 2, 35–40.
Pathak, H., Joshi, H. C., Chaudhary, A., Chaudhary, R., Kalra, N., & Dwivedi, M. K. (1999). Distillery effluent as soil amendment for wheat and rice. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 113, 133–140.
Ramana, S., Biswas, A. K., Singh, A. B., & Yadava, R. B. R. (2001). Relative efficacy of different distillery effluents on growth, nitrogen fixation and yield of groundnut. Bioresource Technology, 81, 117–121.
Ramana, S., Biswas, A. K., Kundu, S., Saha, J. K., & Yadava, R. B. (2002). Effect of distillery effluent on seed germination in some vegetable crops. Bioresource Technology, 82, 273–275.
Singh, P. K., Kumar, V., & Singh, S. (2011). Management of tannery waste: it use as planting medium for chrysanthemum plants. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4, 560–567.
Tariq, M., Ali, M. & Shah, Z. (2006). Characteristics of industrial effluents and their possible impacts on quality of underground water. Soil and Environment, 25(1), 64–69.
Ullah, H., Khan, I., & Ullah, I. (2012). Impact of sewage contaminated water on soil, vegetables and underground water of peri-urban Peshawar, Pakistan. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 84, 6411–6421.
Uzair, M., Ahmed, M., & Nazim, K. (2009). Effects of industrial waste on seed bank and growth of wild plants in Dhabeji area, Karachi, Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Botany, 41(4), 1659–1665.
Wins, J. A., & Murugan, M. (2010). Effect of textile mill effluent on growth and germination of black gram Vigna mungo (L.) Hepper. International Journal of Pharma and Biosciences, 1, 1–7.
Yadav, R. K., Goyal, B., Sharma, R. K., Dubey, S. K., & Minhas, P. S. (2002). Post irrigation impact of domestic sewage effluent on composition of soils, crops and ground water—a case study. Environment International, 28, 481–486.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all the staff members at the Department of Botany, Kohat University of Science and Technology (KUST) for their support. We are thankful to KUST for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uzma, S., Azizullah, A., Bibi, R. et al. Effects of industrial wastewater on growth and biomass production in commonly grown vegetables. Environ Monit Assess 188, 328 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5338-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5338-8