Abstract
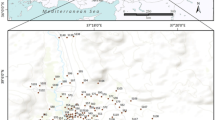
Tunçbilek, one of the major thermal power plants (TTPP) in Turkey running on coal, has capacity to generate 365 MW (per year) electricity. Fifty top soil samples were collected from a depth about 0–20 cm in the close vicinity of the TTPP from random points and at different distances. The samples were analyzed using ICP-MS for heavy metals. Heavy metal contents in soils around TTPP varied from 4.4 to 317.5 mg/kg for As, 0.03 to 0.26 mg/kg for Cd, 20.3 to 1028 mg/kg for Cr, 4.8 to 76.8 mg/kg for Cu, 0.09 to 9.3 mg/kg for Hg, 16.6 to 2385 mg/kg for Ni, 4.8 to 58.6 mg/kg for Pb, and 14.5 to 249.5 mg/kg for Zn. Geoaccumulation index (I geo) and enrichment factor (EF) have been calculated in order to evaluate heavy metal pollution in the soils. According to the I geo calculations, the surface soils around TTPP are contaminated by As, Hg, and Ni from uncontaminated to extremely contaminated. I geo values for Cr show practically uncontaminated to be heavily contaminated. The contamination of soil samples changes from practically uncontaminated to moderately contaminated degree for Pb and Zn. The soil samples were uncontaminated for Cd and Cu metals. The enrichment factors of As, Cr, Hg, and Ni in most of the sampling locations indicate significant to extremely high enrichment. The EF for Pb is also high and indicates moderate to very high enrichment of chromium in the soils. The average EF values for Cd, Cu, and Zn are showing moderate enrichment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeyi, A. A., & Torto, N. (2014). Profiling heavy metal distribution and contamination in soil of old power generation station in Lagos, Nigeria. Am J Sci Technol, 1(1), 1–10.
Agrawal, P., Mittal, A., Prakash, R., Kumar, M., Singh, T. B., & Tripathi, S. K. (2010). Assessment of contamination of soil due to heavy metals around coal fired thermal power plants at Singrauli Region of India. Bull Environ Toxicol, 85, 219–223.
ATSDR, (2005a). Toxicological profile for nickel. Atlanta: U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services.
ATSDR, (2005b). Toxicological profile for zinc. Atlanta: U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services.
ATSDR, (2007a). Toxicological profile for arsenic. Atlanta: U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services.
ATSDR, (2007b). Toxicological profile for lead. Atlanta: U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services.
ATSDR. (2012). Toxicological profile for chromium. Atlanta: U.S. Dept. of Health & Human Services.
Baba, A. (2003). Geochemical assessment of environmental effects of ash From Yatagan (Mugla-Turkey) Thermal Power Plant. Water Air Soil Pollut, 144, 3–18.
Baş, H. (1986). Domaniç-Tavşanlı-Kütahya-Gediz yöresinin Tersiyer jeolojisi. Jeoloji Mühendisliği, 27, 11–19.
Buat-Menard, P., & Chesselet, R. (1979). Variable influence of the atmospheric flux on the trace metal chemistry of oceanic suspended matter. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 42, 399–411.
Chatterjee, M., Filho, E. V. S., Sarkar, S. K., Sella, S. M., Bhattacharya, A., Satpathyc, K. K., Prasadc, M. V. R., Chakrabortya, S., & Bhattacharyaa, B. D. (2007). Distribution and possible source of trace elements in the sediment cores of a tropical macrotidal estuary and their ecotoxicological significance. Environ Int, 33, 346–356.
Chung, S., & Chon, H. T. (2014). Assessment of the level of mercury contamination from some anthropogenic sources in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. J Geochem Explor, 147, 237–244.
Çiçek, A., & Koparal, A. S. (2004). Accumulation of sulfur and heavy metals in soil and tree leaves sampled from the surroundings of Tunçbilek Thermal Power Plant. Chemosphere, 57, 1031–1036.
Cordos, E. A., Roman, C., Ponta, M., Frentiu, T., & Rautiu, R. (2007). Evaluation of soil pollution with copper, lead, zinc and cadmium in the mining area Baia Mare. Rev Chim (Bucharest), 58, 470–474.
Dang, Z., Liu, C., & Haigh, M. J. (2002). Mobility of heavy metals associated with the natural weathering of coal mine soils. Environ Pollut, 118, 419–426.
Dobra, M., & Viman, V. (2006). Determination of concentration of air and soil pollutant heavy metals by ICP-AES. Revista De Chimie, 57(12), 1283–1286.
Dragović, S., Ćujić, M., Slavković-Beškoski, L., Gajić, B., Bajat, B., Kilibarda, M., & Onjia, A. (2013). Trace element distribution in surface soils from a coal burning power production area: a case study from the largest power plant site in Serbia. Catena, 104, 288–296.
Fuge, R. (2005). Anthropogenic sources. Chap3. In O. Selinus, B. Alloway, J. A. Centeno, R. B. Finkelman, R. Fuge, U. Lindh, & P. Smedley (Eds.), Essentials of medical geology (pp. 43–60). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Gabbard, A. (1993). Coal combustion: nuclear resource or danger. Oak Ridge National Laboratory Review, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, 26(3-4), 24–32.
Galvin, J. M., & Wagner, H. (1982). Use of ash to improve strata control in bord and pillar working. Proc. Strata Mechanics, April 9-13, 1982, Newcastle-upon-Tyne.
Hedrick, J. B. (1995). The global rare-earth cycle. J Alloys Compd, 225, 609–618.
Herpin, U., Berlekamp, J., Markert, B., Wolterbeek, B., Grodzinska, K., Siewers, U., Lieth, H., & Weckert, V. (1996). The distribution of heavy metals in a transect of the three states the Netherlands, Germany and Poland, determined with the aid of moss monitoring. Sci Total Environ, 187, 185–198.
Jankiewicz, B., & Adamczyk, D. (2010). Assessing heavy metal content in soils surrounding a power plant. Polish J of Environ Stud, 19(4), 849–853.
Kabata-Pendias, A. (2011). Trace elements in soils and plants. Florida: CRC Press.
KİÇDR. (2014). Kütahya il çevre durum raporu. Kütahya: Kütahya Valiliği Çevre ve Şehircilik İl Müdürlüğü.
Lazar, G., Capatina, C., & Simonescu, C. M. (2008). Evaluation of the heavy metals content in soil around a thermal station. Revista de Chimie, 59(8), 939–943.
Lu, X., Liu, W., Zhao, C., & Chen, C. (2013). Environmental assessment of heavy metal and natural radioactivity in soil around a coal-fired power plant in China. J Radioanal Nucl Chem, 295, 1845–1854.
Machender, G., Dhakate, R., Prasanna, L., & Govil, P. K. (2011). Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils around Balanagar industrial area, Hyderabad, India. Environ Earth Sci, 63, 945–953.
Mandal, A., & Sengupta, D. (2006). An assessment of soil contamination due to heavy metals around a coal-fired thermal power plant in India. Environ Geol, 51, 409–420.
Markert, B., Herpin, U., Siewers, U., Berlekamp, J., & Lieth, H. (1996). The German heavy metal survey by means of mosses. Sci Total Environ, 182(Issues 1–3), 159–168.
Mason, B. (1966). Principals of geochemistry. New York: Wiley.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo J, 2, 108–118.
Nriagu, J. O., & Pacyna, J. M. (1988). Quantitative assessment of worldwide contamination of air, water and soils by trace metals. Nature, 1669, 14–139.
Obiajunwa, E. I., Pelemo, D. A., Owolabi, S. A., Fasai, M. K., & Johnson-Fatokun, F. O. (2002). Characterization of heavy metal pollutants of soils and sediments around a crude-oil production terminal using EDXRF. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res Sect B, 194, 61–64.
Okay, A. I. (1981). Kuzeybatı Anadolu’daki ofiyolitlerin jeolojisi ve mavişist metamorfizması (Tavşanlı-Kütahya). Türkiye Jeoloji Kurumu Bülteni, 24, 85–95.
Pacyna, J. M., & Winchester, J. W. (1990). Contamination of the global environment as observed in the Arctic. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol, 82, 149–57.
Pirrone, N., & Mason, R. (2009). Mercury fate and transport in the global atmosphere. New York: Springer.
Pokale, W. K. (2012). Effects of thermal power plant on environment. Sci Revs Chem Commun, 2(3), 212–215.
Quevauviller, P., Lavigne, R., & Cortez, L. (1989). Impact of industrial and mine drainage wastes on the heavy metal distribution in the drainage basin and estuary of the Sado River (Portugal). Environ Pollut, 59, 267–86.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (1998). Chemical elements in the environment. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Reimann, C., & de Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environ Sci Technol, 34, 5084–91.
Rose, A. W., Hawkes, H. E., & Webb, J. S. (1991). Geochemistry in mineral exploration. London: Academic Press.
Sandru, C., & David, E. (2014). The assessment of heavy metals content in soil samples taken from the vicinity of thermal power plants. Prog Cryogenics Isot Sep, 17(1), 87–96.
Saur, E., & Juste, C. (1994). Enrichment of trace elements from long-range aerosol transport in sandy podzolic soils of Southwest France. Water Air Soil Pollut, 73, 235–46.
Schiff, K. C., & Weisberg, S. B. (1999). Iron as a reference element for determining trace metal enrichment in Southern California coastal shelf sediments. Marine Environmental Research, 48(2), 161–176.
Sengupta, S., Chatterjee, T., Ghosh, P. B., & Saha, T. (2010). Heavy metal accumulation in agricultural soils around a coal fired thermal power plant (Farakka) in India. Environ Sci Engg, 52(4), 299–306.
Sinha, M., Datta, J., & Mondal, N. K. (2012). Agricultural soil contaminated by heavy metals exposed by the byproducts of Durgapur Thermal Power Station, Durgapur, W.B., Asian Journal Research in Chemistry, 5(6),742–747.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol, 39, 611–27.
Thomson, I. (1986). Exploration geochemistry: design and interpretation of soil surveys. Rev Econ Geol, 3, 1–18.
TKİ. (2014). Kömür sektör raporu. Ankara: Türkiye Kömür İşletmeleri Kurumu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkul, C. Heavy metal contamination in soils around the Tunçbilek Thermal Power Plant (Kütahya, Turkey). Environ Monit Assess 188, 284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5295-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5295-2