Abstract
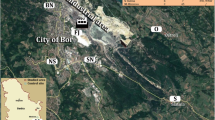
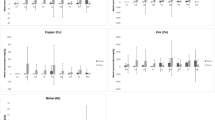
Laportea peduncularis is a medicinal plant consumed by the native communities in South Africa. Due to its oral consumption, its potential for harming the human health and the distribution of metals in the leaves of L. peduncularis as a function of soil characteristics were evaluated. Broadly, the concentrations of metals in the soil were in decreasing order of Fe > Ca > Mg > Mn > Zn > Cr > Cu > Ni > As > Co > Cd > Pb. Low-molecular-weight organic acid, calcium chloride, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid extraction methods were employed to assess for exchangeable forms of metals in the soil. Geoaccumulation indices and enrichment factors showed no contamination or enrichment for most of the heavy metals studied except for Cd, which showed moderate contamination and significant enrichment at Mona, KwaZulu-Natal. Principal component and cluster analyses revealed that As, Cd, Fe, and Ni in the soil came from the same source, whilst Cu, Pb, and Zn in the soil were from a common origin. Correlation analysis showed significantly positive correlation between heavy metals As, Cd, Fe, and Ni in the soil, as well as between Cu, Pb, and Zn, confirming the metals’ common origin. Concentrations of metals in plants and soil were influenced by site, but the availability and uptake of the metals solely depended on the plant’s inherent controls.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Dousari, A. S., Majki, K., Moustafa, S., & Al-Saleh, E. (2012). Effects of atmospheric lead on soil microbata in Kuwait. In C. A. Brebbia & T. S. Chon (Eds.), Environmental impact (p. 486). United Kingdom: Wits Press.
Cataldo, D. A., Garland, T. R., & Wildung, R. E. (1983). Cadmium uptake kinetics in intact soybean plants. Plant Physiology, 73, 844–848.
Chapman, H. D. (1965). Cation exchange capacity. In C. A. Black (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties (pp. 891–901). American Society of Agronomy: Madison, Wisconsin.
Fageria, N. K., Baligar, V. C., & Wright, R. J. (1990). Iron nutrition of plants: an overview on the chemistry and physiology of its deficiency and toxicity. Psequisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 25(4), 553–570.
Feng, M., Shan, Q., Zheng, S., & Wen, B. (2005). Comparison of rhizosphere-based method with other one-step extraction methods for assessing the bioavailability of soil metals to wheat. Chemosphere, 59, 939–949.
Fuentes, A., Lloréns, M., Sáez, J., Soler, A., Aquilar, M. I., Ortuño, J. F., & Meseguer, V. F. (2004). Simple and sequential extractions of heavy metals from different sewage sludges. Chemosphere, 54, 1039–1047.
Hernandez, L., Probst, A., Probst, J. L., & Ulrich, E. (2003). Heavy metal distribution in some French forest soils: evidence for atmospheric contamination. Science of the Total Environment, 312, 195–219.
Herselmann, J. E., Steyn, C. E., & Fey, M. V. (2005). Baseline concentration of Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni and Zn in surface soils of South Africa. South African Journal of Science, 101, 509–512.
Houba, V. J. G., Temminghoff, E. J. M., Gaikhorst, G. A., & van Vark, W. (2000). Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 31(9&10), 1299–1396.
Hu, Y., Liu, X., Bai, J., Shih, K., Zeng, E. Y., & Cheng, H. (2013). Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 6150–6159.
Huang, J. W., & Chen, J. (2003). Role of pH in phytoremediation of contaminated soils. In Z. Rengel (Ed.), Handbook of soil acidity (p. 453). New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Iqbal, J., & Shah, M. H. (2014). Occurrence, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in surface sediments from Khanpur Lake, Pakistan. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 5(28), 1–12.
Ivanciuc, T., Ivanciuc, O., & Klein, D. J. (2006). Modeling the bioconcentration factors and bioaccumulation factors of polychlorinated biphenyls with posetic quantitative super-structure/activity relationships (QSSAR). Molecular Diversity, 10(2), 133–145.
Jonnalagadda, S. B., Kindness, A., Kubayi, S., & Cele, M. N. (2008). Macro, minor and toxic elemental uptake and distribution in Hypoxis hemerocallidea, “the African potato”—an edible medicinal plants. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, 43, 271–280.
Krishna, A. K., & Govil, P. K. (2007). Soil contamination due to heavy metals from an industrial area of Surat, Gujarat, Western India. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 124, 263–275.
Kučak, A., & Blanuša, M. (1998). Comparison of two extraction procedures for the determination of trace metals in soil by atomic absorption spectrometry. Archives of Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology, 49(4), 327–334.
Mahlangeni, N., Moodley, R., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2012). Soil nutrient content on elemental uptake and distribution in sweet potatoes. International Journal of Vegetable Science, 18, 245–259.
Marschner, M. (1995). Mineral nutrition of higher plants (p. 657). London: Academic Press.
McGrath, D. (1996). Application of single and sequential extraction procedures to polluted and unpolluted soils. The Science of the Total Environment, 178, 37–44.
McLaughlin, M. J., Hamon, R. E., McLaren, R. G., Speir, T. W., & Rogers, S. L. (2000). Review: bioavailability-based rationale for controlling metal and metalloid contamination of agricultural land in Australia and New Zealand. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 38, 1037–1086.
Mendiola, L. L., Dominguez, M. C. D., & Sandoval, M. R. G. (2008). Environmental assessment of active tailings pile in the state of Mexico (Central Mexico). Research Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2(3), 197–208.
Moodley, R., Koorbanally, N., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2012). Elemental composition and fatty acid profile of the edible fruits of Amatungula (Carissa macrocarpa) and impact of soil quality on chemical characteristics. Analytica Chimica Acta, 730, 33–41.
Moodley, R., Koorbanally, N., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2013). Elemental composition and nutritional value of edible fruits of Harpephyllum caffrum and impact of soil quality on their chemical characteristics. Journal of Environmental Science and Health. Part. B, 48, 539–547.
Müller, G. (1969). Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal, 2(3), 108–118.
Nickel, S., Hertel, A., Pesch, R., Schröder, W., Steinnes, E., & Uggerud, H. T. (2015). Correlating concentrations of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition with respective accumulation in moss and natural surface soil for ecological land classes in Norway between 1990 and 2010. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22, 8488–8498.
Novozamsky, I., Lexmond, T. M., & Houba, V. J. G. (1993). A single extraction procedure of soil for evaluation of uptake f some heavy metals by plants. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 51, 47–58.
Nowak, B. (1998). Contents and relationship of elements in human hair for a non-industrialised population in Poland. Science of the Total Environment, 209(1), 59–68.
Oliver, D. P., Bramley, R. G. V., Riches, D., Porter, I., & Edwards, J. (2013). Review: soil physical and chemical properties as indicators of soil quality in Australian viticulture. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 19, 129–139.
Oze, C., Skinner, C., Schroth, A., & Coleman, R. G. (2008). Growing up green on serpentine soils: biogeochemistry of serpentine vegetation in the Central Coast Range of California. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3391–3403.
Quattrocchi, U. (2012). CRC world dictionary of medicinal and poisonous plants (p 2219). Boca Raton: Taylor and Francis Group.
Quevauriller, P., Lachica, M., Barahona, E., Rauret, G., Ure, A., Gomez, A., & Muntau, H. (1996). Interlaboratory comparison of EDTA and DTPA procedures prior to certification of extractable trace elements in calcareous soil. Science of the Total Environment, 178, 137–132.
Reddy, M., Moodley, R., & Jonnalagadda, S. B. (2014). Elemental uptake and distribution of nutrients in avocado mesocarp and the impact of soil quality. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 186, 4519–4529.
Schippers, R. R. (2000). African indigenous vegetables: an overview of the cultivated species (p 214). Chatham, UK: Natural Resource Institute.
Schoenholtz, S. H., Van Miegroet, H., & Burger, J. A. (2000). A review of chemical and physical properties as indicators of forest soil quality: challenges and opportunities. Forest and Ecology Management, 138, 335–356.
Sutherland, R. A. (2000). Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environmental Geology, 39, 611–637.
Tahar, K., & Keltoum, B. (2011). Effects of heavy metals pollution in soil and plant in industrial area, West Algeria. Journal of the Korean Chemical Society, 55(6), 1018–1023.
Takáč, P., Szabová, T., Kozáková, L., & Benková, M. (2009). Heavy metals and their bioavailability from soils in the long-term polluted Central Spiš region of SR. Plant, Soil and Environment, 55(4), 167–172.
Ure, A. M. (1996). Single extraction schemes for soil analysis and related applications. The Science of the Total Environment, 178, 3–10.
van Rensburg, W. S. J., van Averbeke, W., Slabbert, R., Faber, M., van Jaarsveld, P., van Heerden, I., Wenhold, F., & Oelofse, A. (2007). African leafy vegetables in South Africa. Water S.A, 33(3), 317–326.
Violante, A., Cozzolino, V., Perelomov, L., Caporale, A. G., & Pigna, M. (2010). Mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals and metalloids in soil environment. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 10(3), 268–292.
Walkley, A., & Black, I. A. (1934). An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science, 37, 29–38.
Wu, Z., Monro, A. K., Milne, R. I., Wanga, H., Yi, T., Liu, J., & Li, D. (2013). Molecular phylogeny of the nettle family (Urticaceae) inferred from the multiple loci of three genomes and extensive generic sampling. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 69, 814–827.
Zaccherio, M. T., & Finzi, A. C. (2007). Atmospheric deposition may affect northern hardwood forest composition by altering soil nutrient supply. Ecological Applications, 17(7), 1929–1941.
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. L. (2002). Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China—weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes estuarine. Coastal and Shelf Science, 54(6), 1051–1070.
Zhang, S., Shan, X., & Li, F. (1999). Low-molecular weight acids as extractant to predict plant bioavailability to rare earth elements. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 76(4), 283–294.
Zhou, M., Lv, Y., Shen, R., Zhou, Z., Zhou, J., Hu, S., & Zhou, X. (2014). Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of Hankou region in Wuhan, China. In F. Bian & Y. Xie (Eds.), Geo-informatics in resource management and sustainable ecosystem (p.742). Springer: 2nd international conference proceedings October 3–5, Ypsilanti.
Zhu, Q. H., Huang, D. Y., Liu, S. L., Luo, Z. C., Zhu, H. H., Zhou, B., Lei, M., Rao, Z. X., & Cao, X. L. (2012). Assessment of single extraction methods for evaluating the immobilization effect of amendments on cadmium in contaminated acidic paddy soil. Plant, Soil and Environment, 58(2), 98–103.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Research Foundation (NRF) for financial support and the School of Chemistry and Physics at UKZN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahlangeni, N.T., Moodley, R. & Jonnalagadda, S.B. Heavy metal distribution in Laportea peduncularis and growth soil from the eastern parts of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Environ Monit Assess 188, 76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5044-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-5044-y