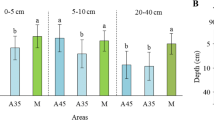
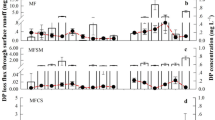
Abstract
Successive swine effluent applications can substantially increase the transfer of phosphorus (P) forms in runoff. The aim of this study was to evaluate P accumulation in the soil and transfer of P forms in surface runoff from a Hapludalf soil under no-tillage subjected to successive swine effluent applications. This research was carried out in the Agricultural Engineering Department of the Federal University of Santa Maria, Brazil, from 2004 to 2007, on a Typic Hapludalf soil. Swine effluent rates of 0, 20, 40, and 80 m3 ha−1 were broadcast over the soil surface prior to sowing of different species in a crop rotation. Soil samples were collected in stratified layers, and the levels of available P were determined. Samples of water runoff from the soil surface were collected throughout the period, and the available, soluble, particulate, and total P were measured. Successive swine effluent applications led to increases in P availability, especially in the soil surface, and P migration through the soil profile. Transfer of P forms was closely associated with runoff, which is directly related to rainfall volume. Swine effluent applications also reduced surface runoff. These results show that in areas with successive swine effluent applications, practices that promote higher water infiltration into the soil are required, e.g., crop rotation and no-tillage system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abipecs (2012) Associação brasileira da indústria produtora e exportadora de carne suína. Available in: http://www.abipecs.org.br. Accessed August 04, 2012.
Adeli, A., Bolster, C. H., Rowe, D. E., Mclaughlin, M. R., & Brink, G. E. (2008). Effect of long-term swine effluent application on selected soil properties. Soil Science, 173, 223–235.
Allen, B. L., & Mallarino, A. R. (2008). Effect of liquid swine manure rate, incorporation, and timing of rainfall on phosphorus loss with surface runoff. Journal of Environmental Quality, 37, 125–137.
Amado, T. J. C., Bayer, C., Conceição, P. C., Spagnollo, E., Campos, B. C., & Veiga, M. (2006). Potential of carbon accumulation in no till soils with intensive use and cover crops in southern Brazil. Journal of Environmental Quality, 35, 1599–1607.
Andrade, F. V., Mendonça, E. S., Alvarez, V. H., & Novais, R. F. (2003). Addition of organic and humic acids to Latosols and phosphate adsorption effects. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 27, 1003–1011.
Bertol, O. J., Rizzi, N. E., Favaretto, N., & Lana, M. C. (2010). Phosphorus loss by surface runoff in no-till system under mineral and organic fertilization. Scientia Agricola Journal, 67, 71–77.
Brookes, P. C., & Powlson, D. C. (1982). Preventing phosphorus losses during perchloric acid digestion of sodium bicarbonate soil extracts. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 32, 671–674.
Bundy, L. G., Andraski, T. W., & Powell, J. M. (2001). Management practice effects on phosphorus losses in runoff in corn production systems. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30, 1822–1828.
Cassol, P. C., Gianello, C., & Costa, V. E. U. (2001). Phosphorus fractions in manures and their efficiency as phosphate fertilizer. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 25, 635–644.
Ceretta, C. A., Basso, C. J., Vieira, F. C. B., Herbes, M. G., Moreira, I. C. L., & Berwanger, A. L. (2005). Pig slurry: I—nitrogen and phosphorus losses by surface runoff in a soil cropped under no tillage. Ciência Rural, 35, 1296–1304.
Ceretta, C. A., Lorensini, F., Brunetto, G., Girotto, E., Gatiboni, L. C., Lourenzi, C. R., Tiecher, T. L., Conti, L., Trentin, G., & Miotto, A. (2010a). Phosphorus fractions in soil after successive pig slurry applications in no-tillage system. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 45, 593–602.
Ceretta, C. A., Girotto, E., Lourenzi, C. R., Trentin, G., Vieira, R. C. B., & Brunetto, G. (2010b). Nutrient transfer in runoff under no tillage in a soil treated with successive applications of pig slurry. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 139, 689–699.
Chardon, W. J., Aalderink, G. H., & van der Salm, C. (2007). Phosphorus leaching from cow manure patches on soil columns. Journal of Environmental Quality, 36, 17–22.
Cordell, D., Drangert, J. O., & Stuart, W. (2009). The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought. Global Environmental Change, 19, 292–305.
CQFS-RS/SC - Comissão de química e fertilidade do solo (2004). Manual de adubação e calagem para os estados do Rio Grande do Sul e Santa Catarina. Porto Alegre.
Daverede, I. C., Kravchenko, A. N., Hoeft, R. G., Nafziger, E. D., Bullock, D. G., Warren, J. J., & Gonzini, L. C. (2004). Phosphorus runoff from incorporated and surface-applied liquid swine manure and phosphorus fertilizer. Journal of Environmental Quality, 33, 1535–1544.
Ferreira, D. F. (2008). SISVAR: um programa para análises e ensino de estatística. Rev Symposium, 6, 36–41.
Flores, H., Arumí, J. L., Rivera, D., & Lagos, L. O. (2012). A simple method to identify areas of environmental risk due to manure application. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 3915–3928.
Gatiboni, L. C., Brunetto, G., Kaminski, J., Rheinheimer, D. S., Ceretta, C. A., & Basso, C. J. (2008). Soil phosphorus forms after successive pig slurry application in a native pasture. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 32, 1753–1761.
Gatiboni, L.C., Smith, T.J., Schmitt, D.E., Cassol, P.C., & Oliveira, C.M.B. (2014). Proposta de limites críticos ambientais de fósforo para solos de Santa Catarina. (Boletin Técnico), Lages, Universidade do Estado de Santa Catarina.
Girotto, E., Ceretta, C. A., Lourenzi, C. R., Lorensini, F., Tiecher, T. L., Vieira, R. C. B., Trentin, G., Basso, C. J., Miotto, A., & Brunetto, G. (2013). Nutrient transfer by leaching in a no-tillage system through soil treated with repeated pig slurry applications. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 95, 115–131.
Guardini, R., Comin, J. J., Schmitt, D. E., Tiecher, T., Bender, M. A., Rheinheimer, D. S., Mezzari, C. P., Oliveira, B. S., Gatiboni, L. C., & Brunetto, G. (2012). Accumulation of phosphorus fractions in typic Hapludalf soil after long-term application of pig slurry and deep pig litter in a no-tillage system. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 93, 215–225.
Guo, Y., & Li, G. (2012). Nitrogen leaching and phosphorus accumulation in a perennial pasture after composted goat manure was top dressed and incorporated in the Three Gorges region. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 12, 674–682.
Hahn, C., Prasuhn, V., Stamm, C., & Schulin, R. (2012). Phosphorus losses in runoff from manured grassland of different soil P status at two rainfall intensities. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 153, 65–74.
Hart, M. R., & Cornish, P. S. (2012). Available soil phosphorus, phosphorus buffering and soil cover determine most variation in phosphorus concentration in runoff from pastoral sites. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 93, 227–244.
Haygarth, P. M., & Sharpley, A. N. (2000). Terminology for phosphorus transfer. Journal of Environmental Quality, 29, 10–15.
Holford, I. C. R., Hird, C., & Lawrie, R. (1997). Effects of animal effluent on the phosphorus sorption characteristics of soils. Australian Journal of Soil Research, 35, 365–373.
Jiao, P., Xu, D., Wang, S., & Zhang, T. (2011). Phosphorus loss by surface runoff from agricultural field plots with different cropping systems. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 90, 23–32.
Kang, J., Amoozegar, A., Hesterberg, D., & Osmond, D. L. (2011). Phosphorus leaching in a sandy soil as affected by organic and inorganic fertilizer sources. Geoderma, 161, 194–201.
Kleinman, P. J. A., Sharpley, A. N., Saporito, L. S., Buda, A. R., & Bryant, R. B. (2009). Application of manure to no-till soils: phosphorus losses by sub-surface and surface pathways. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 84, 215–227.
Krutz, L. J., Locke, M. A., & Steinriede, R. W., Jr. (2009). Interactions of tillage and cover crop on water, sediment, and pre-emergence herbicide loss in glyphosate-resistant cotton: implications for the control of glyphosate-resistant weed biotypes. Journal of Environmental Quality, 38, 1240–1247.
Lehmann, J., Lan, Z., Hyland, C., Sato, S., Solomon, D., & Ketterings, Q. M. (2005). Long-term dynamics of phosphorus forms and retention in manure-amended soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 6672–6680.
Lourenzi, C. R., Ceretta, C. A., Silva, L. S., Girotto, E., Lorensini, F., Tiecher, T. L., De Conti, L., Trentin, G., & Brunetto, G. (2013). Nutrients in soil layers under no-tillage after successive pig slurry applications. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 37, 157–167.
McDowell, R. W., Sharpley, A. N., Crush, J. R., & Simmons, T. (2011). Phosphorus in pasture plants: potential implications for phosphorus loss in surface runoff. Plant and Soil, 345, 23–35.
Conama - Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente (2005) Resolução Conama N° 357. Available at: http://www.crq4.org.br/downloads/resolucao357.pdf. Accessed August 12, 201.
Meng, Q., Fu, B., Tang, X., & Ren, H. (2008). Effects of land use on phosphorus loss in the hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 139, 195–204.
Murphy, J., & Riley, J. P. (1962). A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta, 27, 31–36.
Oliveira, P. A. V. (1994). Impacto ambiental causado pelos dejetos de suínos. Simpósio Latino-Americano de Nutrição de Suínos. 27-40.
Payet, N., Findeling, A., Chopart, J. L., Feder, F., Nicolini, E., Macary, H. S., & Vauclin, M. (2009). Modelling the fate of nitrogen following pig slurry application on a tropical cropped acid soil on the Island of Réunion (France). Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 134, 218–233.
Scherer, E. E., Nesi, C. N., & Massotti, Z. (2010). Long-term swine manure fertilization and its effects on soil chemical properties in Santa Catarina, southern Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo, 34, 1375–1383.
Sharpley, A. N., Chapra, S. C., Wedepohl, R., Sims, J. T., Daniel, T. C., & Reddy, K. R. (1994). Managing agricultural phosphorus for protection of surface waters: issues and options. Journal of Environmental Quality, 23, 437–451.
Smith, K. A., Jackson, D. R., & Withers, P. J. A. (2001). Nutrient losses by surface run-off following the application of organic manure to arable land. 2. Phosphorus. Environmental Pollution, 112, 53–60.
Smith, D. R., Owens, P. R., Leytem, A. B., & Warne-Muende, E. A. (2007). Applications as impacted by time to first runoff event. Environmental Pollution, 147, 131–137.
Soil Survey Staff. (1999). Soil taxonomy 2nd. Washington: United States Department of Agriculture.
Sweeney, D. W., Pierzynski, G. M., & Barnes, P. L. (2012). Nutrient losses in field-scale surface runoff from claypan soil receiving turkey litter and fertilizer. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 150, 19–26.
Tedesco, M.J., Gianello, C., Bissani, C.A., Bohnen, H., Volkweiss, S.J. (1995). Análises de solo, planta e outros materiais. 2nd. ed. (Boletim técnico, 5), Porto Alegre, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul.
Udawatta, R. P., Motavalli, P. P., Garrett, H. E., & Krstansky, J. J. (2006). Nitrogen losses in runoff from three adjacent agricultural watersheds with claypan soils. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 117, 39–48.
Vadas, P. A., Jokela, W. E., Franklin, D. H., & Endale, D. M. (2011). The effect of rain and runoff when assessing timing of manure application and dissolved phosphorus loss in runoff. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 47, 877–886.
Wang, W., Liang, T., Wang, L., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Zhang, C. (2013). The effects of fertilizer applications on runoff loss of phosphorus. Environmental Earth Sciences, 68, 1313–1319.
Wu, L., Long, T., Liu, X., & Mmereki, D. (2012). Simulation of soil loss processes based on rainfall runoff and the time factor of governance in the Jialing River Watershed, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 184, 3731–3748.
Ye, D., Li, T., Chen, G., Zheng, Z., Yu, H., & Zhang, X. (2014). Influence of swine manure on growth, P uptake and activities of acid phosphatase and phytase of Polygonum hydropiper. Chemosphere, 105, 139–145.
Yu, S., He, Z. L., Stoffella, P. J., Calvert, D. V., Yang, X. E., Banks, D. J., & Baligar, V. C. (2006). Surface runoff phosphorus (P) loss in relation to phosphatase activity and soil P fractions in Florida sandy soils under citrus production. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38, 619–628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Carlos Alberto Ceretta is a Dr., Federal University of Santa Maria.
Tadeu Luis Tiecher is a Ms., Federal University of Santa Maria.
Felipe Lorensini is a Dr., Federal University of Santa Maria.
Adriana Cancian is a Student, Federal University of Santa Maria.
Lincon Stefanello is a Student, Federal University of Santa Maria.
Eduardo Girotto is a Dr., Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Rio Grande do Sul.
Renan Costa Beber Vieira is a Dr., Department of Soil Science of the Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul.
Paulo Ademar Avelar Ferreira is a Dr., Federal University of Santa Maria.
Gustavo Brunetto is a Dr., Federal University of Santa Maria.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lourenzi, C.R., Ceretta, C.A., Tiecher, T.L. et al. Forms of phosphorus transfer in runoff under no-tillage in a soil treated with successive swine effluents applications. Environ Monit Assess 187, 209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4437-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4437-2