Abstract
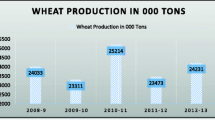
This paper estimates Malaysian farmers’ willingness to pay (WTP) for a planned adaptation programme for addressing climate issues in the Malaysian agricultural sector. We used the contingent valuation method (CVM) for a monetary valuation of farmers’ preferences for a planned adaptation programme by ascertaining the value attached to address climatic issues in the Malaysian agricultural sector. Structured questionnaires were distributed among the sampled farmers. The study found that 74 % of respondents were willing to pay for a planned adaptation programme and that several socioeconomic and motivation factors have greater influence on their WTP. This paper clearly specifies the steps needed for all institutional bodies to better address issues in climate change. The outcomes of this paper will support policy makers to better design an efficient adaptation framework for adapting to the adverse impacts of climate change.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, M. Y. (2007). Climate change and food security. MARDI
Adams, R. M., McCarl, B. A., Dudek, D. J., & Glyer, J. D. (1988). Implications of global climate change for western agriculture. Western Journal of Agricultural Economics, 348-356
Afroz, R., & Masud, M. M. (2011). Using a contingent valuation approach for improved solid waste management facility: evidence from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Waste Management, 31(4), 800–808.
Alam, M. M., Toriman, M. E. B., Siwar, C., Molla, R. I., & Talib, B. (2011). Impact of agricultural supports for climate change adaptation: a farm level assessment. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 7(2), 178.
Andersson, H., Hole, A. R., & Svensson, M. (2014). Valuation of small and multiple health risks: a critical analysis of SP data applied to food and water safety.
Bain, P. G., Hornsey, M. J., Bongiorno, R., & Jeffries, C. (2012). Promoting pro-environmental action in climate change deniers. Nature Climate Change, 2(8), 600–603.
Bollen, J., Hers, S., & Van der Zwaan, B. (2010). An integrated assessment of climate change, air pollution, and energy security policy. Energy Policy, 38(8), 4021–4030.
Boyle, K. J. (2003). Contingent valuation in practice. In P. A. Champ, K. J. Boyle, & T. C. Brown (Eds.), A primer on nonmarket valuation. London: Kluwer.
Building Nigeria’s response to climate change (BNRCC), (2008): 2008 annual workshop on Nigerian environmental study team (NEST) the recent global and local action on climate change, held on hotel Millennium, Abuja, Nigeria 8–9 October 2008
Canadell, J. G., & Raupach, M. R. (2008). Managing forests for climate change mitigation. Science, 320(5882), 1456–1457.
Carson, R. (2012). Contingent valuation: a comprehensive bibliography and history. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Carson, R. T., Louviere, J. J., & Wei, E. (2010). Alternative Australian climate change plans: the public’s views. Energy Policy, 38(2), 902–911.
Carvalho, A., Flannigan, M. D., Logan, K. A., Gowman, L. M., Miranda, A. I., & Borrego, C. (2010). The impact of spatial resolution on area burned and fire occurrence projections in Portugal under climate change. Climatic Change, 98(1–2), 177–197.
Curtis, L. (2012). Unit costs of health and social care 2012, Personal Social Services Research Unit.
Damigos, D., Tourkolias, C., & Diakoulaki, D. (2009). Households’ willingness to pay for safeguarding security of natural gas supply in electricity generation. Energy Policy, 37(5), 2008–2017.
de Bekker‐Grob, E. W., Ryan, M., & Gerard, K. (2012). Discrete choice experiments in health economics: a review of the literature. Health Economics, 21(2), 145–172.
Del Borghi, A., Strazza, C., Gallo, M., Messineo, S., & Naso, M. (2013). Water supply and sustainability: life cycle assessment of water collection, treatment and distribution service. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 18(5), 1158–1168.
Department of Statistics Malaysia (2009). Compendium of Environment Statistics, Malaysia. Putrajaya, DOSM. Retrieved from www.statistics.gov.my/
Downing, T. E., Ringius, L., Hulme, M., & Waughray, D. (1997). Adapting to climate change in Africa. Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies for Global Change, 2(1), 19–44.
Everard, M., Pontin, B., Appleby, T., Staddon, C., Hayes, E. T., Barnes, J. H., & Longhurst, J. W. S. (2013). Air as a common good. Environmental Science & Policy, 33, 354–368.
Fischer, G., Shah, M., Tubiello, F. N., & Van Velhuizen, H. (2005). Socio-economic and climate change impacts on agriculture: an integrated assessment, 1990–2080. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, B: Biological Sciences, 360(1463), 2067–2083.
Gelo, D., & Koch, S. F. (2012). Does one size fit all? Heterogeneity in the valuation of community forestry programs. Ecological Economics, 74, 85–94.
Georgescu, M., Lobell, D. B., & Field, C. B. (2011). Direct climate effects of perennial bioenergy crops in the United States. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(11), 4307–4312.
Georgiou S., & Turner R.K. (2012) Valuing ecosystem services: the case of multi-functional wetlands. Routledge.
Hess, S., Orr, S., & Sheldon, R. (2012). Consistency and fungibility of monetary valuations in transport: an empirical analysis of framing and mental accounting effects. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 46(10), 1507–1516.
Howard, G., Charles, K., Pond, K., Brookshaw, A., Hossain, R., & Bartram, J. (2010). Securing 2020 vision for 2030: climate change and ensuring resilience in water and sanitation services. Journal of Water and Climate Change, 1(1), 2–16.
Iglesias, A., Garrote, L., Flores, F., & Moneo, M. (2007). Challenges to manage the risk of water scarcity and climate change in the Mediterranean. Water Resources Management, 21(5), 775–788.
Iglesias, A., Garrote, L., Diz, A., Schlickenrieder, J., & Martin-Carrasco, F. (2011). Re-thinking water policy priorities in the Mediterranean region in view of climate change. Environmental Science & Policy, 14(7), 744–757.
INC (2000). Malaysia national communication. Ministry of Science, Technology and the Environment. United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. http://unfeee.int/response/does/nate/malnel.pdf.
IPCC (2007) Climate Change 2007: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K and Reisinger, A. (eds.). IPCC, Geneva, Switzerland.
Jamaludin, S., Suhaila, S., Wan Zin, W. Z., & Jemain, A. A. (2008). Tracing trends in the sequences of dry and wet days over peninsular Malaysia. Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 1(3), 97–110.
Kaffashi, S., Shamsudin, M. N., Radam, A., Rahim, K. A., & Yacob, M. R. (2013). We are willing to pay to support wetland conservation: local users’ perspective. International Journal of Sustainable Development & World Ecology, 20(4), 325–335.
Kellens, W., Terpstra, T., & De Maeyer, P. (2013). Perception and communication of flood risks: a systematic review of empirical research. Risk Analysis, 33(1), 24–49.
Kristiansen, S. (2013). Maritime transportation: safety management and risk analysis. Routledge.
Lantz, V., Trenholm, R., Wilson, J., & Richards, W. (2012). Assessing market and non-market costs of freshwater flooding due to climate change in the community of Fredericton, Eastern Canada. Climatic Change, 110(1–2), 347–372.
Lobell, D. B., Burke, M. B., Tebaldi, C., Mastrandrea, M. D., Falcon, W. P., & Naylor, R. L. (2008). Prioritizing climate change adaptation needs for food security in 2030. Science, 319(5863), 607–610.
Lobell, D. B., Schlenker, W., & Costa-Roberts, J. (2011). Climate trends and global crop production since 1980. Science, 333(6042), 616–620.
Mason, E. G., Manley, B. R., & Sands, R. (2013). Forestry and climate change. Forestry in a global context, (Ed. 2), 149–157.
Ojeda, M. I., Mayer, A. S., & Solomon, B. D. (2008). Economic valuation of environmental services sustained by water flows in the Yaqui River Delta. Ecological Economics, 65(1), 155–166.
Olesen, J. E., & Bindi, M. (2002). Consequences of climate change for European agricultural productivity, land use and policy. European Journal of Agronomy, 16, 239–262.
Orgill, J., Shaheed, A., Brown, J., & Jeuland, M. (2013). Water quality perceptions and willingness to pay for clean water in peri-urban Cambodian communities. Journal of Water and Health, 11(3), 489–506.
Park, M., Hagishima, A., Tanimoto, J., & Chun, C. (2013). Willingness to pay for improvements in environmental performance of residential buildings. Building and Environment, 60, 225–233.
Rowe, R. D., Schulze, W. D., & Breffle, W. S. (1996). A test for payment card biases. Journal of Environmental Economics and Management, 31(2), 178–185.
Royal Society (2005) Impact of climate change on crops worse than previously thought: http://roralsociety.org/news.asp? Accessed Jun 2008
Siwar, C., Alam, M. M., Murad, M. W., & Al-Amin, A. Q. (2009). A review of the linkages between climate change, agricultural sustainability and poverty in Malaysia. International Review of Business Research Papers, 5(6), 309–321.
Smit, B., & Pilifosova, O. (2003). Adaptation to climate change in the context of sustainable development and equity. Sustainable Development, 8(9), 9.
Sovacool, B. K. (2011). Evaluating energy security in the Asia pacific: towards a more comprehensive approach. Energy Policy, 39(11), 7472–7479.
SPORE (2008). Climate Change, Spore Special Issue-August, 2008
Stern, N. (2007). The stern review of the economics of climate change. Cambridge University Press.
Stern, N. H., G. Britain and H. Treasury (2006). Stern review: the economics of climate change, HM treasury London.
Tao, F., Hayashi, Y., Zhang, Z., Sakamoto, T., & Yokozawa, M. (2008). Global warming, rice production and water use in China: developing a probabilistic assessment. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 148, 94–110.
Tonglet, M., Phillips, P. S., & Read, A. D. (2004). Using the theory of planned behaviour to investigate the determinants of recycling behaviour: a case study from Brixworth, UK. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 41(3), 191–214.
Turner, K. (2013). Sustainable wetlands: an economic perspective. Wetlands Market and Intervention Failures Four Case Studies, 10, 1.
Vo, Q. T., Kuenzer, C., Vo, Q. M., Moder, F., & Oppelt, N. (2012). Review of valuation methods for mangrove ecosystem services. Ecological Indicators, 23, 431–446.
Vörösmarty, C. J., McIntyre, P. B., Gessner, M. O., Dudgeon, D., Prusevich, A., Green, P., & Davies, P. M. (2010). Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature, 467(7315), 555–561.
Wang, Y. M., & Elhag, T. (2007). A comparison of neural network, evidential reasoning and multiple regression analysis in modelling bridge risks. Expert Systems with Applications, 32(2), 336–348.
Wicker, P., Hallmann, K., Breuer, C., & Feiler, S. (2012). The value of Olympic success and the intangible effects of sport events—a contingent valuation approach in Germany. European Sport Management Quarterly, 12(4), 337–355.
Yoo, S. H., & Kwak, S. Y. (2009). Willingness to pay for green electricity in Korea: a contingent valuation study. Energy Policy, 37(12), 5408–5416.
Yoon, C. G. (2009). Wise use of paddy rice fields to partially compensate for the loss of natural wetlands. Paddy and Water Environment, 7(4), 357–366.
Acknowledgments
The author(s) would like to thank University of Malaya (UM) and Ministry of Education Malaysia who has generously funded this study under the research grant FL001G-13BIO (Marketing Survey Strategy Compounds).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masud, M.M., Junsheng, H., Akhtar, R. et al. Estimating farmers’ willingness to pay for climate change adaptation: the case of the Malaysian agricultural sector. Environ Monit Assess 187, 38 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4254-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4254-z