Abstract
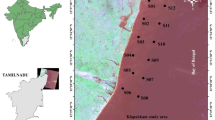
Spatial and temporal variations of sediment quality in Matanzas Bay (Cuba) were studied by determining a total of 12 variables (Zn, Cu, Pb, As, Ni, Co, Al, Fe, Mn, V, CO3 2−, and total hydrocarbons (THC). Surface sediments were collected, annually, at eight stations during 2005–2008. Multivariate statistical techniques, such as principal component (PCA), cluster (CA), and lineal discriminant (LDA) analyses were applied for identification of the most significant variables influencing the environmental quality of sediments. Heavy metals (Zn, Cu, Pb, V, and As) and THC were the most significant species contributing to sediment quality variations during the sampling period. Concentrations of V and As were determined in sediments of this ecosystem for the first time. The variation of sediment environmental quality with the sampling period and the differentiation of samples in three groups along the bay were obtained. The usefulness of the multivariate statistical techniques employed for the environmental interpretation of a limited dataset was confirmed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Academy of Sciences of Cuba. (1989). New Atlas of Cuba. Madrid: Academy of Sciences of Cuba.
Ajlec, R., Štupar, J., & Čop, M. (1988). Interferences in the determination of chromium in plant materials and soil samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyst, 113, 585–590.
Andrade Passos, E., Alves, J. C., Santos, I. S., Alves, J. P. H., García, C. A. B., & Spinola Costa, A. C. (2010). Assessment of trace metals contamination in estuarine sediments using a sequential extraction technique and principal component analysis. Microchemical Journal, 96(1), 50–57.
Astel, A., Tsakovski, S., Barbieri, P., & Simeonov, V. (2007). Comparison of self-organizing maps classification approach with cluster and principal components analysis for large environmental datasets. Water Research, 41(19), 4566–4578.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (2008) Screening quick reference tables (SquiRTs). http://response.restoration.noaa.gov/sites/default/files/SQuiRTs.pdf. Accessed June 2014.
Barwick, V.J., Ellinson, S.R.L. (2000). VAM Project 3.2.1. Development and harmonisation of measurement uncertainty principles. Part D: Protocol for uncertainty evaluation from validation data. Report No: LGC/VAM/1998/088. LGC (Teddington) Ltd., UK.
Bengraine, K., & Marhaba, T. F. (2003). Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. Journal of Hazardous Materials, B100, 179–195.
Bogomólov, A. I. (1981). Química del petróleo y del gas. Ed. Mir, Moscú.
Buccolieri, A., Buccolieri, G., Cardellicchio, N., Dell’Atti, A., Di Leo, A., & Mac, A. (2006). Heavy metals in marine sediments of Taranto Gulf (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Marine Chemistry, 99(1), 227–235.
Carrasco, M., López-Ramírez, J. A., Benavente, J., López-Aguayo, F., & Sales, D. (2003). Assessment of urban and industrial contamination levels in the bay of Cádiz, SW Spain. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46(3), 335–345.
CCREM. (1996). Canadian water quality guidelines. Task Force in Water Quality Guidelines. Ottawa: Canadian Council of Resource and Environment Ministers. 118 pp.
Companioni, E. Y., Núñez, A. C., Cora, M. O., González, L., Marbot, R., Montes De Oca, R., et al. (2009). Petroleum Hydrocarbon Assessment in the sediments of the north-eastern Havana Littoral. Cuba. Revista Internacional de Contaminación Ambiental, 25(1), 5–14.
El Nemr, A., Khaled, A., & Sikaily, E. (2006). Distribution and statistical analysis of leachable and total heavy metals in the sediments of the Suez gulf. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 118(1–3), 89–112.
Essien, J. P., Antai, S. P., & Olajire, A. A. (2009). Distribution, seasonal variations and ecotoxicological significance of heavy metals in sediments of cross river estuary Mangrove swamp. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 197(1), 91–105.
Filgueiras, A. V., Lavilla, I., & Bendicho, C. (2004). Evaluation of distribution, mobility and binding behavior of heavy metals in superficial sediments of Louro River (Galicia, Spain) using chemometric analysis: a case study. Science of the Total Environment, 330(1), 115–129.
Förstner, U., & Wittmann, G. T. W. (1983). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment, Second revised edition. Berlin: Springer.
González, H. (1991). Heavy metals surveys in sediments of five important Cuban bays. Biochemistry, 14, 113–128.
González, M. C., Méndez, L. C., López, V., & Vázquez, A. (2006). Evaluación de la contaminación en sedimentos del área portuaria y zona costera de Salina Cruz, Oaxaca, México. Interciencia, 31(9), 647–656.
Grande, J. A., Borrego, J., Morales, J. A., & de la Torre, M. L. (2003). A description of how metal pollution occurs in the Tinto-Odiel River (Huelva-Spain) through the application of cluster analysis. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46(4), 475–480.
Horowitz, A. J., & Elrick, K. A. (1987). The relation of stream sediment surface area, grain size and composition to trace element chemistry. Applied Geochemistry, 2, 437–451.
Liao, S. W., Gau, H. S., Lai, W. L., Chen, J. J., & Lee, C. G. (2008). Identification of pollution of Tapeng Lagoon from neighbouring rivers using multivariate statistical method. Journal of Environmental Management, 88(2), 286–292.
Liu, W. X., Li, X. D., Shen, Z. G., Wang, D. C., Wai, O. W. H., & Li, Y. S. (2003). Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary. Environmental Pollution, 121(3), 377–388.
Long, E. R., & MacDonald, D. D. (1998). Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 2, 1019–1039.
Mingoti, S. A., & Lima, J. O. (2006). Comparing SOM neural network with fuzzy c-means, K-means and traditional hierarchical clustering algorithms. European Journal of Operational Research, 174, 1742–1759.
Parizanganeh, A., Lakhan, V. C., & Jalalian, H. (2007). A geochemical and statistical approach for assessing heavy metal pollution in sediments from the southern Caspian coast. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 4(3), 351–358.
Pejman, A. H., Nabi Bidhendi, G. R., Karbassi, A. R., Mehrdadi, N., & Esmaeili Bidhendi, M. (2009). Evaluation of spatial and seasonal variations in surface water quality using multivariate statistical techniques. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 6(3), 467–476.
Reid, M. K., & Spencer, K. L. (2009). Use of principal components analysis (PCA) on estuarine sediment datasets: The effect of data pre-treatment. Environmental Pollution, 157, 2275–2281.
Ruíz, F., Pérez, M., Beltrán, J., Mancebo, H., Regadera, R., Martín, A., et al. (2008). Estado actual de la calidad ambiental de la bahía de Matanzas y su evolución en el tiempo. Revista Investigaciones Marinas, 29(1), 13–22.
Stanimirova, I., Walczak, B., & Massart, D. L. (2005). Multiple factor analysis in environmental chemistry. Analytica Chimica Acta, 545(1), 1–12.
Tsakovski, S., Kudlak, V., Simeonov, L., Wolska, L., García, G., & Namiesnik, J. (2012). Relationship between heavy metal distribution in sediment samples and their ecotoxicity by the use of the Hasse Diagram Technique. Analytica Chimica Acta, 719, 16–23.
Vandeginste, B. G., & Massart, D. L. (Eds.). (1998). Handbook of Chemometrics and Qualimetrics: Part B (pp. 243–307). New York: Elsevier.
Wiesmann, M., & Nehring, K. (1951). Agrikulturchemisches Praktikum. Berlin: Paul Parey.
Wong, C. S. C., Wu, S. C., Duzgoren-Aydin, N. S., Aydin, A., & Wong, M. H. (2007). Trace metal contamination of sediments in an e-waste processing village in China. Environmental Pollution, 145(2), 434–442.
Zhou, F., Huang, G. H., Guo, H. C., Zhang, W., & Hao, Z. J. (2007). Spatial-temporal patterns and sources apportionment of coastal water pollution in eastern Hong Kong. Water Research, 41(15), 3429–3439.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Iberoamerican University Association of Postgraduate (AUIP) of the Junta de Andalucia, Spain for the financing granted to implement a part of this investigation. The present work was developed as part of the Project ACUMMAMA, 2011–2013 Convocation supported by the Institute of Materials Research and Engineering (IMRE) of the University of Havana and also as part of the 2813, 6009 and 7019 Projects financed by the Oil Research Center of the Ministry of Energy and Mines of Cuba.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Pattern of water circulation Matanzas Bay (GIF 789 kb)
ESM 2
Concentration of analytes expressed in milligrams per kilogram, except Al, Fe, and CO3 2− in percent. Samples were identified by two numbers. The first one described the year of the sampling campaign (1, 2005; 2, 2006; 3, 2007; and 4, 2008) and the second one corresponded to the sampling station (DOC 93 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez, O.Q., Tagle, M.E.V., Pascual, J.L.G. et al. Evaluation of spatial and temporal variations in marine sediments quality using multivariate statistical techniques. Environ Monit Assess 186, 6867–6878 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3895-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3895-2