Abstract
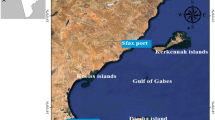
The Fusaro Lagoon is a shallow lagoon, located in SW Italy, largely influenced in the last decades by several anthropic impacts. The study examined the pollution status of the lagoon, during year 2011–2012 at nine sampling stations with the aim to find out proper measurements of water lagoon restoration. Concentrations of heavy metals (HMs) (aluminium [Al], barium [Ba], cadmium [Cd], copper [Cu], iron [Fe], manganese [Mn], vanadium [V] and zinc [Zn]) were examined in water, sediments and specimens of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis sp. A. Low levels of dissolved oxygen concentration were detected at many stations, with mean values of 5.2–6.4 mg L−1. The redox potential of surface waters was also low, −2.7 to 50.7 mV. Sediments possessed high organic matter content, 17.7–29.4 %. In sediments, the mean Zn level, 251.4 mg kg−1, was about sixfold higher than that recorded in year 2000 (38.5 mg kg−1) and considerably higher than that recorded in 2007 (191 mg kg−1). The mean levels of Cd were outstandingly high, with a mean value of 70.5 mg kg−1, about 30- and 50-fold higher than those determined in 2000 and 2007, respectively. Cadmium (Cd), Cu and nickel (Ni) appeared in excess with respect to most current guidelines, reaching significant pollution levels. C. intestinalis sp. A was detected only at few stations, with metals accumulated preferentially in the body in respect to the tunic, from 1.2 times for Zn (178 mg kg−1) to 4.0 times for V (304 mg kg−1). Data suggests the necessity of an immediate action of eco-compatible interventions for environmental restoration.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andolfo, F., Arciprete, R., Buonfiglio, G., Casola, E. (1993). Studi propedeutici alla definizione degli accordi di programma nell’area Flegrea (Lago Fusaro). Terzo Programma Nazionale per la Pesca e l’Acquacoltura 1991–1993 (art. 20 L. 41/82 Min. Trasp. Mar. Merc.), AICP, AGCI, p. 108.
Bellas, J., Beiras, R., & Vazquez, E. (2004). Sublethal effects of trace metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg) on embryogenesis and larval settlement of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 46, 61–66.
Bhuvendralingam, M., Azmy, S.A.M. (1995). Bio-accumulation of trace metals in the Negombo Lagoon, Sri Lanka. Proc. of II Int. Conf. on the Mediterranean Coastal Env., Medcoast 95, Tarragona (Spain). Ankara (Turkey): Ozhan, p. 937–44.
Budillon, G., & Moretti, M. (1994). Assimilazione delle misure dirette ed indirette di corrente. Annali Istituto Universitario Navale Napoli, 61, 9–17.
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (2002) Canadian sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic lives. Summary tables. Update. In: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg, Canada
Caputi, L., Andreakis, N., Mastrototaro, F., Cirino, P., Vassillo, M., & Sordino, P. (2007). Cryptic speciation in a model invertebrate chordate. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104, 9364–9369.
Caputi, L., Crocetta, F., Toscano, F., Sordino, P., & Cirino, P. (2013). Long-term demographic and reproductive trends in Ciona intestinalis sp. A. Marine Ecology. doi:10.1111/maec.12125.
Carrada, G. C. (1973). Profilo ecologico di una laguna salmastra flegrea: il lago Fusaro. Archives of Oceanography and Limnology, 18, 145–164.
Carrada, G. C, Fresi, E. (1988). Le lagune salmastre costiere Alcune riflessioni sui problemi e sui metodi. In: Carrada, G. C, Cicogna, F., Fresi, E. (Eds.), Le lagune costiere, ricerca e gestione. Massalubrense (Italy), CLEM, p. 35–56.
Centro Ittico Tarantino-Campano. (1967). Valutazione dello stato di contaminazione delle acque e dei sedimenti di fondo del Lago del Fusaro. Risultati della campagna di campionamento ed analisi (p. 21). Rome: IGEAM.
Cicchella, D., De Vivo, B., Lima, A., Albanese, S., Mc Gill, R. A. R., & Parrish, R. R. (2008). Heavy metal pollution and Pb isotopes in urban soils of Napoli, Italy. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 8, 103–112.
De Maio, A., Moretti, M., Sansone, E., Spezie, G. (1988). Rilevamento dei parametri fisici nelle acque del Golfo di Napoli. Istituto Idrologia Marina Rapporto Tecnico, 9–68.
De Maio, A., Moretti, M., Sansone, E., Spezie, G. (1994). Lineamenti fisici delle acque delle coste campane dal Volturno a Capri. Istituto Idrologia Marina Rapporto Finale, 7–19.
De Pippo, T., Donadio, C., Grottola, D., & Pennetta, M. (2004). Geomorphological evolution and environmental reclamation of Fusaro Lagoon (Campania Province, southern Italy). Environment International, 30, 199–208.
Dias, A., & Peneda, C. (1986). Some proposal for a coastal management (the lagoon of Albufeira case). Thalassas, 4, 37–42.
Ergun, O. N., Buyukgungor, H., Orhan, Y. (1995). Effects of urbanisation and agricultural activities in the lagoons of Kizilirmak Delta, Turkey. Proc of II Int Conf on the Mediterranean Coastal Env Medcoast 95. Ankara (Turkey): Ozhan, p. 945–52.
Ferro, R., & Russo, G. F. (1981). Le biocenosi bentoniche del lago Fusaro. Osservazioni faunistiche. Bollettino Società Naturalistica Napoli, 89, 33–45.
Gallo, A., Silvestre, F., Cuomo, A., Papoff, F., & Tosti, E. (2011). The impact of metals on the reproductive mechanisms of the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Marine Ecology, 32, 222–231.
Guerra-García, J. M., & García-Gómez, J. C. (2005). Oxygen levels versus chemical pollutants: do they have similar influence on macrofaunal assemblages? A case study in a harbour with two opposing entrances. Environmental Pollution, 135, 281–291.
Howe P. D., Malcolm, H. M., Dobson, S. (2004). Manganese and its compounds: environmental aspects. (Concise international chemical assessment document. Centre for Ecology & Hydrology, Monks Wood, United Kingdom World Health Organization, Geneva.
Improta, C., Andini, S., & Ferrara, L. (2004). Chemical and ecotoxicological characterization of Averno Lake. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 472–481.
Italian Ministry of Environment (1991). DM471-Regolamento recante criteri, procedure e modalità per la messa in sicurezza, la bonifica e il ripristino ambientale dei siti inquinati. Supplemento Ordinario Gazzetta Ufficiale N. 360.
Kobayashi, N. (1993). Marine pollution bioassay by sea urchin eggs, Diadema setusum. Its manual and applied fundamental results, short report. Phuket Marine Biology Center Research Bulletin, 40, 83–88.
Leccese, A., & Speziale, V. (1967). I laghi Fusaro e Miseno e l’inquinamento delle loro acque (p. 84). Cassano Jonio (Italy): Jonica.
Milenkovic, N., Damjanovic, M., & Ristic, M. (2005). Study of heavy metal pollution in sediments from the Iron Gate (Danube River), Serbia and Montenegro. Poland Journal of Environmental Study, 14, 781–787.
Muniz, P., Danulat, E., Yannicelli, B., Garcia-Alonso, J., Medina, G., & Bicego, M. C. (2004). Assessment of contamination by heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons in sediments of Montevideo Harbour (Uruguay). Environment International, 29, 1019–1028.
Naranjo, S. A., Carballo, J. L., & Garcia-Gomez, J. C. (1996). Effects of environmental stress on ascidian populations in Algeciras Bay (southern Spain). Possible marine bioindicators? Marine Ecology Progress Series, 144, 119–131.
National Research Council (1974). Committee on Biologic Effects of Atmospheric Pollutants. Vanadium. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, D. C.
Odum, E. P. (1988). Fundamentals of ecology (p. 544). Pennsylvania: Saunders.
Official Bulletin of the Italian Republic (2006). Law n 152. 88, 14, April. Environmental rules. Ordinary supplement, 96.
Pacifico, R., Adamo, P., Cremisini, C., Spaziani, F., & Ferrara, L. (2007). A geochemical analytical approach for the evaluation of heavy metal distribution in lagoon sediments. Journal Soils Sediment, 7, 313–325.
Papadopoulou, C., & Kanias, G. (1977). Tunicate species as marine pollution indicators. Marine Pollution Bullettin, 8, 229–331.
Papadopoulou, C., Hadzistelios, I., & Grimanis, A. P. (1972). Trace element uptake by Cynthia claudicans (Savigny). Greek Limnology Oceanography, 11, 651–663.
Sacchi, C. F., Renzoni, A. (1962). L’ecologie de Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lam.) dans l’etang littoral du Fusaro et les rythmes annuels et nycthemeraux des facteurs environnants. Pubblicazione Stazione Zoologica “A Dohrn” Napoli, 32, 255–293.
Sordino, P., Gambi, M. C., & Carrada, G. C. (1989). Spatio-temporal distribution of polichaetes in an Italian coastal lagoon (Lago Fusaro, Naples). Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 30, 375–391.
Stoecker, D. (1978). Resistance of a tunicate to fouling. The Biological Bulletin Marine Biological Laboratory, 155, 615–626.
Stoecker, D. (1979). The ecological roles of acid and vanadium in ascidians. Ph.D. thesis. State University of New York. Stony Brook.
Swinehart, J. H., Biggs, W. R., Halko, D. J., & Schroeder, N. C. (1974). The vanadium and selected metal contents of some ascidians. The Biological Bulletin Marine Biological Laboratory, 146, 302–312.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) (1984). Regionally based assessment of persistent toxic substances Mediterranean Regional. UNEP/FAO/IAEA. Reference methods for marine pollution 12 (Rev. 1)
VROM (2000) Intervention and target values-soil quality standards. Available at: http://www.minvrom.nl/minvrom/docs/bodem/annexS&I2000.pdf. Accessed 15 Jan 2013
Warwick, R. M., & Clarke, K. R. (1993). Comparing the severity of disturbance: a meta-analysis of marine macrobenthic community data. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 92, 221–231.
Webb, D. A. (1939). Observations on the blood of certain ascidians, with special reference to the biochemistry of vanadium. Journal of Experimental Biology, 16, 499–523.
Webb, D. A. (1956). The blood of tunicates and the biochemistry of vanadium. Naples Stazione Zoologica, 28, 273–288.
Whittaker, R. H., & Feeny, P. P. (1971). Allelochemics: chemical interactions between species. Science, New York, 171, 757–770.
Woelke, C. E. (1972). Measurement of water quality with the Pacific oyster embryo bioassay. Wash Department Fish Technical Report 9.
Wright, J. F., Furse, M. T., Armitage, P. D. (1994). Use of macroinvertebrate communities to detect environmental stress in running waters. In: Sutcliffe DW (Ed) Water quality and stress indicators in marine and freshwater systems: linking levels of organization. Freshwater Biology Association Speciation Publication UK, p 15–34
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the mayor and the personnel of the technical office of the local municipality of Bacoli for providing assistance in sample collection. The reasons of the study are the pressing needs of environmental restoration on the sites selected.
Conflict of interest
We state that we do not have any financial relationship with sponsoring organization, and we declare that we do not have conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arienzo, M., Toscano, F., Di Fraia, M. et al. An assessment of contamination of the Fusaro Lagoon (Campania Province, southern Italy) by trace metals. Environ Monit Assess 186, 5731–5747 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3816-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-3816-4