Abstract
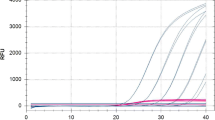
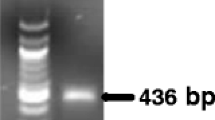
Phytophthora lateralis is an oomycete responsible for Port-Orford Cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana) dieback and mortality since the 1920s in western North America. It is recommended for quarantine regulation by EPPO (A2 list) and has been recently detected in Europe. In order to implement efficient control of the disease, a sensitive real-time PCR assay was developed to detect the presence of P. lateralis in plant tissues. In this study, we used the species-specific polymorphisms within the RAS-related protein gene Ypt1 to design a primer pair and a hydrolysis probe targeting the pathogen. The tool proved to be specific and inclusive, based on in silico and in vitro assessments, and could detect as few as 47 copies of target DNA. In addition, the test demonstrated its robustness and remained highly sensitive and specific under deliberately modified experimental conditions such as the hybridization temperature, or the reaction and DNA template volumes. The DNA extraction step from diseased tissues was also optimized, and the reliability of the results was ensured by a set of controls and a test targeting plant DNA that enabled the assessment of the quality of the extracts.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2000) Council directive 2000/29/EC of 8 May 2000 on protective measures against the introduction into the community of organisms harmful to plants or plant products and against their spread within the Community. O.J.L 169, 10.7.2000, 1.
Brasier, C. M., Vettraino, A. M., Chang, T. T., & Vannini, A. (2010). Phytophthora lateralis discovered in an old growth Chamaecyparis forest in Taiwan. Plant Pathology, 59, 595–603.
Brasier, C. M., Francheschini, S., Vettraino, A. M., Hansen, E. M., Green, S., Robin, C., Webber, J. F., & Vannini, A. (2012). Four phenotypically and phylogenetically distinct lineages in Phytophthora lateralis. Fungal Biology, 116(12), 1232–1249.
Bustin, S. A. (2000). Absolute quantification of mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays. Journal of Molecular Endocrinolology, 25, 169–193.
Cooke, D. E. L., & Duncan, J. M. (1997). Phylogenetic analysis of Phytophthora species based on ITS1 and ITS2 sequences of the ribosomal RNA gene repeat. Mycological Research, 101, 667–677.
DeNitto, G. A., & Kliejunas, J. T. (1991). First report of Phytophthora lateralis on Pacific yew. Plant Disease, 75(9), 968.
EPPO (2010). PM 7/98 (1). specific requirements for laboratories preparing accreditation for a plant pest diagnostic activity. EPPO Bulletin, 40, 5–22.
Erwin, D. C., & Ribeiro, O. K. (1996). Phytophthora Diseases Wordwide. St Paul MN USA: American Phytopathological Society press.
Green, S., Brasier, C. M., Schlenzig, A., McCracken, A., MacAskill, G. A., Wilson, M., & Webber, J. F. (2012). The destructive invasive pathogen Phytophthora lateralis found on Chamaecyparis lawsoniana across the UK. Forest Pathology. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0329.2012.00788.x.
Hansen, E. M., Streito, J. C., & Delatour, C. (1999). First confirmation of Phytophthora lateralis in Europe. Plant Disease, 83, 587.
Hansen, E. M., Goheen, D. J., Jules, E. S., & Ullian, B. (2000). Managing Port-Orford-Cedar and the introduced pathogen Phytophthora lateralis. Plant Disease, 84, 4–14.
Ioos, R., & Fourrier, C. (2011). Validation and accreditation of a duplex real-time PCR test for reliable in planta detection of Chalara fraxinea. EPPO Bulletin, 41, 21–26.
Ioos, R., Laugustin, L., Rose, S., Schenck, N., Husson, C., & Frey, P. (2006). Usefulness of single copy genes containing introns in Phytophthora for the development of detection tools for the regulated species P. ramorum and P. fragariae. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 116, 171–176.
Ioos, R., Fourrier, C., Iancu, G., & Gordon, T. R. (2009). Sensitive detection of Fusarium circinatum in pine seed by combining an enrichment procedure with a real-time polymerase chain reaction using dual-labeled probe chemistry. Phytopathology, 99, 582–590.
Ioos, R., Fourrier, C., Wilson, V., Webb, K., Schereffer, J. L., & Tourvieille de Labrouhe, D. (2012). An optimised duplex real-time PCR tool for sensitive detection of the quarantine oomycete Plasmopara halstedii in sunflower seeds. Phytopathology, 102, 908–917.
Robin, C., Desprez-Lousteau, M. L., Capron, G., & Delatour, C. (1998). First record of Phytophthora cinnamomi on cork and holm oaks in France and evidence of pathogenicity. Annales des Sciences Forestières, 55(8), 869–883.
Robin, C., Piou, D., Feau, N., Douzon, G., Schenck, N., & Hansen, E. M. (2011). Root and aerial infections of Chamaecymaris lawsoniana by Phytophthora lateralis: a new threat for European countries. Forest Pathology, 41, 417–424.
Roth L.F., Harvey R.D., & Kliejunas J.T. (1987). Port-orford-cedar root disease. US Department of agriculture, forest service, pacific northwest region, R6-FMP-PR-294-87, 11 pp.
Sansford, C. E. (2009). Development of U.K. ⁄EU⁄EPPO pest risk analyses for Phytophthora kernoviae, P. ramorum and P. lateralis. In: Phytophthora in forests and natural ecosystems. In Proceedings of the fourth meeting of the International Union of Forest Research Organizations (IUFRO) Working Party S07.02.09: phytophthoras in forests and natural ecosystems, general technical report PSW-GTR-221. S.J. Albany, CA: U.S. department of agriculture, forest service, pacific southwest research station (pp. 139–153).
Schena, L., & Cooke, D. E. L. (2006). Assessing the potential regions of the nuclear and mitochondrial genome to develop a ‘molecular tool box’ for the detection and characterization of Phytophthora species. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 67, 70–85.
Schena, L., Duncan, J. M., & Cooke, D. E. L. (2008). Development and application of a PCR-based ‘molecular tool box’ for the identification of Phytophthora species damaging forests and natural ecosystems. Plant Pathology, 57, 64–75.
Schlenzig, A., Campbell, R., & Mulholland, V. (2011). Thuja occidentalis: a new host for Phytophthora lateralis. New Disease Reports, 24, 8.
Tucker, C. M., & Milbrath, J. A. (1942). Root rot of Chamaecyparis caused by a species of Phytophthora. Mycologia, 34, 94–101.
White, T. J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., & Taylor, J. (1990). Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR protocols: a guide to method and applications (pp. 315–322). NewYork: Academic Press.
Winton, L. M., & Hansen, E. M. (2001). Molecular diagnosis of Phytophthora lateralis in trees, water and foliage baits using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Forest Pathology, 31, 275–283.
Zobel D.B., Roth L., & Hawk G. (1985). Ecology, pathology and management of Port-Orford-cedar (Chamaecyparis lawsoniana). General Technical Report of the Pacific Northwest Forest Range Experiment Station USDA Forest Service No PNW-184, 161pp.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported financially by the French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health & Safety (ANSES).
We thank Gilbert Douzon, Dominique Sage (Pôle Santé des Forêts, Orléans, France), Maurice Nicolas, Xavier Grenie and Laurence Roche (Office National des Forêts, France) for their collaboration in the collection of the Port-Orford Cedar samples in Bretagne ; Cécile Robin (Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, Bordeaux, France), Everett E. Hansen (Oregon University, USA), Karin Rosendahl (Nieuwe Voedsel en Waren Autoriteit, Wageningen, the Netherlands) and Alexandra Schlenzig (Science and Advice for Scottish Agriculture, Edinburgh, Scotland) for supplying numerous P. lateralis isolates used in this study; Claude Husson (INRA Champenoux, France) for providing healthy C. lawsoniana material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schenck, N., Fourrier-Jeandel, C. & Ioos, R. A robust and specific real-time PCR tool for the detection of Phytophthora lateralis in plant tissues. Eur J Plant Pathol 146, 231–244 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0909-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-016-0909-7