Abstract
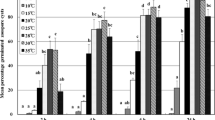
In controlled environments, the influence of rice growth stage, temperature, relative humidity and wetness duration on infection by Villosiclava virens (cause of rice false smut) was assessed by inoculating the rice cultivar ‘Yueyou938’ with a conidial suspension (2 × 106 spores) until run-off. Rice plants grown in vitro, were inoculated at a late stage of panicle development, and averaged 90 % diseased panicles which was a higher incidence compared with those inoculated at a mid-stage in panicle development (66.5 %). There were significant differences in the effects of temperature and wetness duration on disease incidence, which increased rapidly from 48 to 120 h at both 20 and 25 °C. The highest level of disease (92.9 %) was obtained at 25 °C and 95 % RH with 120 h of wetness. In another set of experiments, inoculated rice plants were incubated in a plant growth chamber at 25 °C and 95 % RH for a wetness period; of 120 h, and then subjected to different combinations of temperature and relative humidity to determine the effects of both factors on infection by V. virens. A higher temperature (28 °C) during incubation was found to induce a significantly higher disease incidence compared with a lower temperature (20 °C). Given a wetness period of at least 120 h, temperature was the primary factor affecting disease development during the 2 week period after that. Disease incidence was modeled as a function of both temperature and wetness duration using a modified version of the Weibull model. There was good agreement between observed and predicted values (R 2 = 0.951 and P = 0.0001). The model was used to construct a risk chart for estimating the potential for infection based on observed or forecast temperatures and wetness durations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brooks, S. A., Anders, M. M., & Yeater, K. M. (2009). Effect of cultural management practices on the severity of false smut and kernel smut of rice. Plant Disease, 93, 1202–1208.
Brooks, S. A., Anders, M. M., & Yeater, K. M. (2010). Effect of furrow irrigation on the severity of false smut in susceptible rice varieties. Plant Disease, 94, 570–574.
Carisse, O., Bourgeois, G., & Duthie, J. A. (2000). Influence of temperature and leaf wetness duration on infection of strawberry leaves by Mycosphaerella fragariae. Phytopathology, 10, 1120–1125.
Chen, Y., Xiao, Y., & Zhao, Y. (1995). The capacity of germination and infection of overwintered chlamydospores of Ustilaginoidea virens (Cooke) Tak. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 22, 102–106. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Dent, J. B., & Blackie, M. J. (1979). Systems simulation in agriculture. Model Evaluation (p. 95). London: Applied Science Publishers Ltd.
Ding, Y. (1961). Growth and development of rice. Chinese Rice Cultivation (pp. 81–83). Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press.
Duthie, J. A. (1997). Models of the response of foliar parasites to the combined effects of temperature and duration of wetness. Phytopathology, 87, 1088–1095.
Fang, Z. (1998). Isolation and culture of fungi. Research Method of Plant Pathology (pp. 122–125). Beijing: China Agriculture Press. In Chinese.
Fujita, Y., Sonoda, R., & Yaegashi, H. (1989). Inoculation with conidiospores of false smut fungus to rice panicles at the booting stage. Annual Phytopathology Society Japan, 55, 629–634. In Japanese, abstract in English.
Gao, B., & Zhong, J. (2011). Research advances in infection process of Ustilaginoiden virens. Hunan Agricultural Sciences, 3, 93–97. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Huang, X. (1978). Development of rice panicles. Physiology of Rice Cultivation (pp. 120–128). Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers. In Chinese.
Huang, S., & Yu, L. (2002). Present situation of studies on rice false smut (Ustilaginoidea virens) in China. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2, 45–51. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Ikegami, H. (1962). Study on false smut of rice v. seeding inoculation with the chlamydospores of the rice false fungus. The phytopathological Society of Japan, 27, 16–23. In Japanese, summary in English.
Li, Y., Kang, B., Zhang, B., Lan, Y., Zeng, H., Ma, H., Xie, K., & Li, T. (1986). A preliminary study on the rice false smut. Guangdong Agricultural Science, 4, 45–47 (In Chinese).
Li, Y., Koiso, Y., Kobayashi, H., Hashimoto, Y., & Iwasaki, S. (1995). Ustiloxins, new antimitotic cyclic peptides: interaction with porcine brain tubulin. Biochemical Pharmacology, 49, 1367–1372.
Lu, F., Chen, Z., Chen, Y., Shi, A., Wang, F., & Zhang, H. (1996). Study on biological characters and some uncertain key point relation to infection cycle of rice false smut. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Science, 12, 35–40. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Lv, B., Luo, H., Zhang, Q., Wang, S., & Huang, J. (2008). Research advances of rice false smut. Hubei Plant Protection, S1, 47–48. In Chinese.
Ma, H., Liu, P., Liu, S., Chen, L., Jiang, M., & Zhong, W. (2001). The preliminary research on raw mycotoxin produced by rice false smut. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 2, 40–41.
Nakamura, K., Izumiyama, N., Ohtsubo, K., Koiso, Y., Iwasaki, S., Sonoda, R., Fujita, Y., Yaegashi, H., & Sato, Z. (1994). “Lupinosis”-like lesions in mice caused by ustiloxin, produced by Ustilaginoidea virens: a morphological study. Natural Toxins, 2, 22–28.
Savary, S., Castilla, P. N., Elazegui, F. A., McLaren, C. G., Ynalvez, M. A., & Teng, P. S. (1995). Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen supply and disease source structure on rice sheath blight spread. Phytopathology, 85, 959–965.
Tan, W. (1991). Richards function: a general model and its application in studying plant disease epidemics in time. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 21, 235–240. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Tan, X. (2008). Evaluation of rice varieties against the false smut and genetic diversity of Ustilaginiodea virens. [D]. Changsha: Hunan Agriculture University.
Tang, Y., Jin, J., Hu, D., Yong, M., Xu, Y., & He, L. (2013). Elucidation of the infection process of Ustilaginoidea virens (teleomorph, Villosiclava virens) in rice spikelets. Plant Pathology, 62, 1–8.
Wang, G. (1988). Studies on the factors influencing the germination of the chlamydospores of Ustilaginoidea virens. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 15, 241–245. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Wang, J., & Chen, Y. (2005). A survey of epidemic situation in Hunan province of year 2004. Plant Protection Guide in China, 25, 14–15. In Chinese.
Wang, Z., Lin, K., & Fan, H. (1987). The application of Weibull model to groundnut rust forecasting. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 8, 35–39. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Wang, D., Wang, S., & Fu, J. (2004). Research progress of rice false smut. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences, 1, 21–24. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Wang, S., Li, M., Dong, H., Liu, X., Bai, Y., & Yang, H. (2008). Sporulation, inoculation methods and pathogenicity of Ustilaginoidea albicans, the cause of white rice false smut in China. Journal of Phytopathology, 156, 755–757.
Wu, L., Damicone, J. P., Duthie, J. A., & Melouk, H. A. (1999). Effects of temperature and wetness duration on infection of peanut cultivars by Cercospora arachidicola. Phytopathology, 89, 653–659.
Yang, X., & Dai, X. (2009). Observation of mitosis and meiosis in rice cells by simple squash method. Agricultural Science and Technology, 10, 96–99.
Yang, H., & Zhou, C. (1979). The whole staining technology of rice anther. Hereditas (Beijing), 1, 35–36.
Zhang, J., Zhang, B., Chen, Z., Liu, Y., & Lu, F. (2003). Study on biology of conidia of Ustilaginoidea virens. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 33, 44–47. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Zhang, J., Zhang, B., Chen, Z., Liu, Y., & Lu, F. (2004). Research on inoculation technology of rice false smut. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 34, 463–467. In Chinese, abstract in English.
Zhang, S., Chen, Q., Lv, L., Yang, X., & Yu, D. (2006). Resistance evaluation of main rice cultivars in Hubei province to Ustilaginoidea virens. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 12, 76–78.
Zhou, Y. (2004). Specific and sensitive detection of the fungal pathogen Ustilaginoidea virens by nested PCR. Mycosystema, 23, 102–108.
Zhou, Y., Pan, Y., & Li, Z. (2008). Genetic diversity of rice false smut fungus, Ustilaginoidea virens and its pronounced differentiation of populations in North China. Journal of Phytopathology, 156, 559–564.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Daohong Jiang and Guoqing Li for their instructive advice and comments during the course of this work. This work was supported by the Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (200903039-5), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1247), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. 2013JC006) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. 2013PY110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Q., Lv, B., Guo, M. et al. Effect of rice growth stage, temperature, relative humidity and wetness duration on infection of rice panicles by Villosiclava virens . Eur J Plant Pathol 141, 15–25 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0516-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0516-4