Abstract
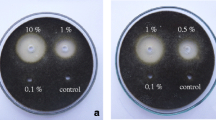
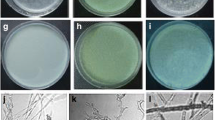
The control efficacy of Platycladus orientalis extract against Rhizoctonia sonali Kühn, the causal agent of rice sheath blight, was evaluated by pot experiments under greenhouse conditions, and the antifungal compounds were isolated and identified through antifungal bioassay-guided fractionation using R. sonali as a tested fungus. The results indicate that the extracts from P. orientalis exhibited a significant reduction in the severity of rice sheath blight. The petroleum ether fraction partitioned from the ethanolic crude extract, showing the highest antifungal activity, was further separated, and two diterpenoid compounds with antifungal property, totarol and sclareol, were isolated and identified from the active subfractions. Totarol and sclareol possessed antifungal activity against most of the tested fungal pathogens of cereal crops such as R. solani, R. cerealis and Fusarium graminearum, indicating a similar broad antifungal spectrum. These findings suggest that the P. orientalis extract and its derived active compounds may be promising candidate agents for controlling plant fungal diseases like rice sheath blight.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Mughrabi, K. I. (2003). Antimicrobial activity of extracts from leaves, stems and flowers of Euphorbia macroclada against plant pathogenic fungi. Phytopathologia Mediterranea, 42, 245–250.
Amadioha, A. C. (2000). Controlling rice blast in vitro and in vivo with extracts of Azadirachta indica. Crop Protection, 19, 287–290.
Aye, S. S., & Matsumoto, M. (2011). Effect of some plant extracts on Rhizoctonia spp. and Sclerotium hydrophilum. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5(16), 3751–3757.
Bai, H. J. (2004). Studies on synthesis and bioactivity of sclareol derivatives (in Chinese). Yangling, China: Northwest Sci-Tech University of Agriculture and Forestry, thesis for Master degree.
Bailey, J. A., Vincent, G. G., & Burden, R. S. (1974). Diterpenes from Nicotiana glutinosa and their effect on fungal Growth. Journal of General Microbiology, 85, 57–64.
Bailey, J. A., Carter, G. A., Burden, R. S., & Wain, R. L. (1975). Control of rust disease by diterpenes from Nicotiana glutinosa. Nature, 255, 328–329.
Becerra, J., Flores, C., Mena, J., Aqueveque, P., Alarcón, J., Bittner, M., Hernández, V., Hoeneisen, M., Ruiz, E., & Silva, M. (2002). Antifungal and antibacterial activity of diterpenes isolated from wood extractables of Chilean Podocarpaceae. Boletin De La Sociedad Chilena De Quimica, 47, 151–157.
Brent, K. J., & Hollomon, D. W. (1998). Fungicide resistance: the assessment of risk. In FRAC Monograph 2 (pp. 1–48). Brussels, Belgium: Global Crop Protection Federation (Now CropLife International).
Campbell, E. J., Schenk, P. M., Kazan, K., Penninckx, I. A. M. A., Anderson, J. P., Maclean, D. J., Cammue, B. P. A., Ebert, P. R., & Manners, J. M. (2003). Pathogen-responsive expression of a putative ATP-binding cassette transporter gene conferring resistance to the diterpenoid sclareol is regulated by multiple defense signaling pathways in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiology, 133, 1–13.
Chutia, M., Deka Bhuyan, P., Pathak, M. G., Sarma, T. C., & Boruah, P. (2009). Antifungal activity and chemical composition of Citrus reticulata Blanco essential oil against phytopathogens from North East India. LWT--Food Science and Technology, 42, 777–780.
Cole, M. D., Bridge, P. D., Dellar, J. E., Fellows, L. E., Cornish, M. C., & Anderson, J. C. (1991). Antifungal activity of neoclerodane diterpenoids from Scutellaria. Phytochemistry, 30(4), 1125–1127.
Deka Bhuyan, P., Chutia, M., Pathak, M. G., & Baruah, P. (2010). Effect of essential oils from Lippia geminata and Cymbopogon jwarancusa on in vitro growth and sporulation of two rice pathogens. Journal of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 87, 1333–1340.
Fawcett, C. H., & Spencer, D. M. (1970). Plant chemotherapy with natural product. Annual Review of Phytopathology, 8, 403–419.
IRRI. (1996). Standard evaluation system for rice (4th ed., p. 25). Manila: International Rice Research Institute.
Jackson, D. M., & Danehower, D. A. (1996). Integrated dace study: Nicotiana leaf-surface components and their effects on insect pests and diseases. In G. Kerstines (Ed.), Plant Cuticles: An Integrated Functional Approach (pp. 231–254). Oxford: BIOS Scientific Publishers.
Kagale, S., Marimuthu, T., Thayumanavan, B., Nandakumar, R., & Samiyappan, R. (2004). Antimicrobial activity and induction of systemic resistance in rice by leaf extract of Datura metel against Rhizoctonia solani and Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 65, 91–100.
Kandhari, J., & Devakumar, C. (2003). Effect of neem oil and its fraction against sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani Kühn) of rice. Journal of Mycopathology Research, 41, 185–187.
Kennedy, B. S., Nielsen, M. T., Severson, R. T., Sisson, V. A., Stephenson, M. K., & Jackson, D. M. (1992). Leaf surface chemicals from Nicotiana affecting germination of Peronospora tabacina (Adam) sporangia. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 18, 1467–1478.
Kurucheve, V., Gerard Ezhilan, J., & Jayaraj, J. (1997). Screening of higher plants for fungitoxicity against Rhizoctonia solani in vitro. Indian Phytopathology, 50, 235–241.
Laks, P. E., & Pruner, M. (1989). Flavonoid biocides: Structure/activity relations of flavonoid phytoalexin analogues. Phytochemistry, 28(1), 87–91.
Latha, P., Anand, T., Ragupathi, N., Prakasam, V., & Samiyappan, R. (2009). Antimicrobial activity of plant extracts and induction of systemic resistance in tomato plants by mixtures of PGPR strains and Zimmu leaf extract against Alternaria solani. Biological Control, 50, 85–93.
Lee, F. N., & Rush, M. C. (1983). Rice sheath blight: a major rice disease. Plant Disease, 67(7), 829–832.
Li, L. N., Ji, M. S., & Su, Z. Y. (2006). Research advances in use of the agricultural fungicide Sophora flavescens (in Chinese). Agrochemicals, 45(9), 581–583.
Matook, S. M., & Toshihiko, S. (2006). Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the methanol extracts from pummelo (Citrus grandis Osbeck) fruit albedo tissues. European Food Research Technology, 224, 39–47.
Pal, T. K., Bhattacharya, S., & Chakraborty, K. (2011). Induction of systemic resistance in rice by leaf extract of Cymbopogan citrus and Ocimum sanctum against sheath blight disease. Archives of Applied Science Research, 3(1), 392–400.
Quiroga, E. N., Sampietro, A. R., & Vattuone, M. A. (2001). Screening antifungal activities of selected medicinal plants. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 74, 89–96.
Rabindran, R., & Vidhyasekaran, P. (1996). Development of a formulation of Pseudomonas iluorescens PfALR2 for management of rice sheath blight. Crop Protection, 15, 715–721.
Seo, S., Gomi, K., Kaku, H., Abe, H., Seto, H., Nakatsu, S., Neya, M., Kobayashi, M., Nakaho, K., Ichinose, Y., Mitsuhara, I., & Ohashi, Y. (2012). Identification of natural diterpenes that inhibit bacterial wilt disease in tobacco, tomato and Arabidopsis. Plant and Cell Physiology, 53(8), 1432–1444.
Solís, C., Becerra, J., Flores, C., Robledo, J., & Silva, M. (2004). Antibacterial and antifungal terpenes from Pilgerodendron uviferum (D. Don) Florin. Journal of the Chilean Chemical Society, 49, 157–161.
Srinivasachary, Willocquet, L., & Savary, S. (2011). Resistance to rice sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani Kühn) [(teleomorph: Thanatephorus cucumeris (A.B.. Frank) Donk.] disease: current status and perspectives. Euphytica, 178(1), 1–22.
Wang, J. Y., Peng, X. X., Yin, B., Xie, Z. H., Gao, J., & Wang, H. H. (2011). Inhibitory effects of extracts from Platycladus orientalis cv. sieboldii on rice sheath blight fungus (in Chinese). Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 26(1), 115–117.
Xie, Z. H., Gao, J., Wang, J. Y., Peng, X. X., Tang, X. K., & Wang, H. H. (2012). Isolation and identification of an antagonistic bacterium against Rhizoctonia solani, the causing agent of rice sheath blight (in Chinese). Microbiology China, 39(4), 477–485.
Yamaji, K., Mori, S., Akiyama, M., Kato, A., & Nakashima, T. (2007). The antifungal compound totarol of Thujopsis dolabrata var. hondai seeds selects for fungi on seedling root surfaces. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 33, 2254–2265.
Yang, D. J., Wang, B., Wang, J. X., Chen, Y., & Zhou, M. G. (2009). Activity and efficacy of Bacillus subtilis strain NJ-18 against rice sheath blight and Sclerotinia stem rot of rape. Biological Control, 51, 61–65.
Ying, B. P., & Kubo, I. (1991). Complete 1H and 13C NMR assignments of totarol and its derivatives. Phytochemistry, 30(6), 1951–1955.
Zhang, C. Q., Liu, Y. H., Ma, X. Y., Feng, Z., & Ma, Z. H. (2009). Characterization of sensitivity of Rhizoctonia solani, causing rice sheath blight, to mepronil and boscalid. Crop Protection, 28, 28381–28386.
Zhou, L. G. (2005). Antimicrobial compounds in plants (in Chinese). Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yu Xian-Yong from Hunan University of Science and Technology for NMR analysis. This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31171803, 31301617) and Hunan Provincial Education Department (12C0129).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Wang, J., Peng, X. et al. Control efficacy against rice sheath blight of Platycladus orientalis extract and its antifungal active compounds. Eur J Plant Pathol 140, 515–525 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0485-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0485-7