Abstract
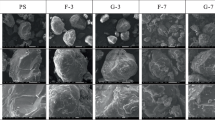
Microplastics (MPs), as emerging contaminants, usually experience aging processes in natural environments and further affect their interactions with coexisted contaminants, resulting in unpredictable ecological risks. Herein, the effect of MPs aging on their adsorption for coexisting antibiotics and their joint biotoxicity have been investigated. Results showed that the adsorption capacity of aged polystyrene (PS, 100 d and 50 d) for ciprofloxacin (CIP) was 1.10–4.09 times higher than virgin PS due to the larger BET surface area and increased oxygen-containing functional groups of aged PS. Following the increased adsorption capacity of aged PS, the joint toxicity of aged PS and CIP to Shewanella Oneidensis MR-1 (MR-1) was 1.03–1.34 times higher than virgin PS and CIP. Combined with the adsorption process, CIP posed higher toxicity to MR-1 compared to aged PS due to the rapid adsorption of aged PS for CIP in the first 12 h. After that, the adsorption process tended to be gentle and hence the joint toxicity to MR-1 was gradually dominated by aged PS. A similar transformation between the adsorption rate and the joint toxicity of PS and CIP was observed under different conditions. This study supplied a novel perception of the synergistic effects of PS aging and CIP on ecological health.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper and its Supplementary Information files. Should any raw data files be needed in another format they are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Arp, H. P. H., Kuehnel, D., Rummel, C., MacLeod, M., Potthoff, A., Reichelt, S., Rojo Nieto, E., Schmitt Jansen, M., et al. (2021). Weathering plastics as a planetary boundary threat: Exposure, fate, and hazards. Environmental Science & Technology., 55, 7246–7255. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01512
Avneri Katz, S., Young, R. B., McKenna, A. M., Chen, H., Corilo, Y. E., Polubesova, T., Borch, T., & Chefetz, B. (2017). Adsorptive fractionation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) by mineral soil: Macroscale approach and molecular insight. Organic Geochemistry., 103, 113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.11.004
Baysal, A., & Saygin, H. (2022). Co-occurence of antibiotics and micro(nano)plastics: A systematic review between 2016–2021. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part a-Toxic/hazardous Substances & Environmental Engineering., 57, 519–539. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2022.2082222
Bender, S. F., Wagg, C., & van der Heijden, M. G. A. (2016). An underground revolution: Biodiversity and soil ecological engineering for agricultural sustainability. Trends in Ecology & Evolution., 31, 440–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.016
Brandon, J., Goldstein, M., & Ohman, M. D. (2016). Long-term aging and degradation of microplastic particles: Comparing in situ oceanic and experimental weathering patterns. Marine Pollution Bulletin., 110, 299–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.048
Brigante, M., Zanini, G., & Avena, M. (2010). Effect of humic acids on the adsorption of paraquat by goethite. Journal of Hazardous Materials., 184, 241–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.08.028
Cai, P. J., Xiao, X., He, Y. R., Li, W. W., Yu, L., Lam, M. H. W., & Yu, H. Q. (2012). Involvement of type cytochrome CymA in the electron transfer of anaerobic nitrobenzene reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Biochemical Engineering Journal., 68, 227–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2012.07.022
Chen, S., Yue, Q., Gao, B., & Xu, X. (2010). Equilibrium and kinetic adsorption study of the adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) using modified wheat residue. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science., 349, 256–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2010.05.057
Chen, W., Sandoval, H., Kubiak, J. Z., Li, X. C., Ghobrial, R. M., & Kloc, M. (2018). The phenotype of peritoneal mouse macrophages depends on the mitochondria and ATP/ADP homeostasis. Cellular Immunology., 324, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2017.11.003
de Souza Machado, A. A., Kloas, W., Zarfl, C., Hempel, S., & Rillig, M. C. (2018). Microplastics as an emerging threat to terrestrial ecosystems. Global Change Biology, 24, 1405–1416. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14020
Dong, Y., Gao, M., Song, Z., & Qiu, W. (2020). As(III) adsorption onto different-sized polystyrene microplastic particles and its mechanism. Chemosphere, 239, 124792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124792
Fajardo, C., Martin, C., Costa, G., Sanchez-Fortun, S., Rodriguez, C., de Lucas Burneo, J. J., Nande, M., Mengs, G., et al. (2022). Assessing the role of polyethylene microplastics as a vector for organic pollutants in soil: Ecotoxicological and molecular approaches. Chemosphere, 288, 132460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132460
Gao, D., Li, X. Y., & Liu, H. T. (2020). Source, occurrence, migration and potential environmental risk of microplastics in sewage sludge and during sludge amendment to soil. Science of the Total Environment., 742, 140355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140355
Gao, Z., Yu, H., Li, M., Li, X., Lei, J., He, D., Wu, G., Fu, Y., et al. (2022). A battery of baseline toxicity bioassays directed evaluation of plastic leachates-Towards the establishment of bioanalytical monitoring tools for plastics. Science of the Total Environment., 828, 154387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154387
Gillman, G. P., & Uehara, G. (1980). Charge characteristics of soils with variable and permanent charge minerals: II. experimental. Soil Science Society of America Journal., 44, 252–255. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400020009x
Guo, X. Y., Cai, Y. P., Ma, C. X., Han, L. F., & Yang, Z. F. (2021). Combined toxicity of micro/nano scale polystyrene plastics and ciprofloxacin to Corbicula fluminea in freshwater sediments. Science of the Total Environment., 789, 147887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147887
Hu, E., Shang, S., Fu, Z., Zhao, X., Nan, X., Du, Y., & Chen, X. (2020). Cotransport of naphthalene with polystyrene nanoplastics (PSNP) in saturated porous media: Effects of PSNP/naphthalene ratio and ionic strength. Chemosphere, 245, 125602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125602
Khan, K. Y., Li, G., Du, D., Ali, B., Zhang, S., Zhong, M., Stoffella, P. J., Iqbal, B., et al., (2023). Impact of polystyrene microplastics with combined contamination of norfloxacin and sulfadiazine on Chrysanthemum coronarium L. Environmental Pollution. 316, 120522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120522
Li, Z., Hu, X., Qin, L., & Yin, D. (2020). Evaluating the effect of different modified microplastics on the availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Water Research., 170, 115290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115290
Liu, G., Zhu, Z., Yang, Y., Sun, Y., Yu, F., & Ma, J. (2019). Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environmental Pollution., 246, 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100
Luo, H., Liu, C., He, D., Xu, J., Sun, J., Li, J., & Pan, X. (2022). Environmental behaviors of microplastics in aquatic systems: A systematic review on degradation, adsorption, toxicity and biofilm under aging conditions. Journal of Hazardous Materials., 423, 126915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126915
Luo, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Guo, X., & Zhu, L. (2020). Distribution characteristics and mechanism of microplastics mediated by soil physicochemical properties. Science of the Total Environment., 726, 138389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138389
Ma, J., Sheng, G. D., & O’Connor, P. (2020). Microplastics combined with tetracycline in soils facilitate the formation of antibiotic resistance in the Enchytraeus crypticus microbiome. Environmental Pollution., 264, 114689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114689
Qiu, Y., Zheng, M., Wang, L., Zhao, Q., Lou, Y., Shi, L., & Qu, L. (2019). Sorption of polyhalogenated carbazoles (PHCs) to microplastics. Marine Pollution Bulletin., 146, 718–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.07.034
Shen, M., Liu, S., Hu, T., Zheng, K., Wang, Y., & Long, H. (2023). Recent advances in the research on effects of micro/nanoplastics on carbon conversion and carbon cycle: A review. Journal of Environmental Management., 334, 117529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.117529
Wang, Q., Xiaoxue, W., Zhang, Y., Wang, N., Wang, Y., Meng, G., & Chen, Y. (2020). The toxicity of virgin and UV-aged PVC microplastics on the growth of freshwater algae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Science of the Total Environment., 749, 141603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141603
Wang, W., & Wang, J. (2018). Comparative evaluation of sorption kinetics and isotherms of pyrene onto microplastics. Chemosphere, 193, 567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.078
Wang, Y., Wang, X., Li, Y., Li, J., Liu, Y., Xia, S., & Zhao, J. (2021a). Effects of exposure of polyethylene microplastics to air, water and soil on their adsorption behaviors for copper and tetracycline. Chemical Engineering Journal., 404, 126412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126412
Wang, Z., Fu, D., Gao, L., Qi, H., Su, Y., & Peng, L. (2021b). Aged microplastics decrease the bioavailability of coexisting heavy metals to microalga Chlorella vulgaris. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety., 217, 112199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112199
Wu, J., Ye, Q., Li, P., Sun, L., Huang, M., Liu, J., Ahmed, Z., & Wu, P. (2023). The heteroaggregation behavior of nanoplastics on goethite: Effects of surface functionalization and solution chemistry. Science of the Total Environment., 870, 161787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161787
Xiong, Y., Zhao, J., Li, L., Wang, Y., Dai, X., Yu, F., & Ma, J. (2020). Interfacial interaction between micro/nanoplastics and typical PPCPs and nanoplastics removal via electrosorption from an aqueous solution. Water Research., 184, 116100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116100
Xu, B., Liu, F., Brookes, P. C., & Xu, J. (2018). Microplastics play a minor role in tetracycline sorption in the presence of dissolved organic matter. Environmental Pollution., 240, 87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.113
Ya, H., Jiang, B., Xing, Y., Zhang, T., Lv, M., & Wang, X. (2021). Recent advances on ecological effects of microplastics on soil environment. Science of the Total Environment., 798, 149338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.149338
Yang H., Li X., Guo M., Cao X., Zheng X., Bao D., (2023). UVinduced microplastics MPs aging leads to comprehensive toxicity. Marine Pollution Bulletin. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114745
Yilimulati, M., Wang, L., Ma, X., Yang, C., & Habibul, N. (2021). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin to functionalized nano-sized polystyrene plastic: Kinetics, thermochemistry and toxicity. Science of the Total Environment., 750, 142370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142370
Yu, Q., Zhang, R., Deng, S., Huang, J., & Yu, G. (2009). Sorption of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoate on activated carbons and resin: Kinetic and isotherm study. Water Research., 43, 1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2008.12.001
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Zhou, B., Zhou, Y., Dai, Z., Zhou, Q., Christie, P., & Luo, Y. (2018). Enhanced adsorption of oxytetracycline to weathered microplastic polystyrene: Kinetics, isotherms and influencing factors. Environmental Pollution., 243, 1550–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.122
Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Yu, X., Huang, D., Guo, X., & Zhu, L. (2022). Aging significantly increases the interaction between polystyrene nanoplastic and minerals. Water Research., 219, 118544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118544
Zhao, C., Xu, T., He, M., Shah, K. J., You, Z., Zhang, T., & Zubair, M. (2021). Exploring the toxicity of the aged styrene-butadiene rubber microplastics to petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria under compound pollution system. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety., 227, 112903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112903
Zhou, W., Han, Y., Tang, Y., Shi, W., Du, X., Sun, S., & Liu, G. (2020). Microplastics aggravate the bioaccumulation of two waterborne veterinary antibiotics in an edible bivalve species: potential mechanisms and implications for human health. Environmental Science & Technology., 54, 8115–8122. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01575
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge support of this work by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2022QB167); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21976185); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42377396).
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge support of this work by the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2022QB167); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21976185); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42377396).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design: Tongtong Li: Writing—Original Draft. Jing Lan: Investigation. Yaoyao Wang: Interpretation. Lulu Sun: Validation. Yaru Li and Zongshan Zhao: Writing—Review and Editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Lan, J., Wang, Y. et al. Enhanced biotoxicity by co-exposure of aged polystyrene and ciprofloxacin: the adsorption and its influence factors. Environ Geochem Health 46, 185 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01961-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01961-0