Abstract
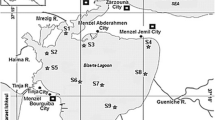
Contamination of aquatic ecosystems by potentially toxic elements (PTEs) is a concerning environmental issue, given their persistence, toxicity potential, and ability to accumulate in living organisms. Several studies have been conducted to assess the contamination of aquatic ecosystems by PTEs, using pollution and ecological risk indices that rely on the concentration of these elements in aquatic sediments. However, many of these studies use global reference values for calculating the indices, which can lead to misleading interpretations due to substantial variations in PTEs concentrations influenced by the geological characteristics of each region. Therefore, the use of regional reference values is more appropriate when available. This study aimed to investigate variations in the results of five indices, employing global, regional, and quality reference values, based on sediment samples collected from rivers in the Ipanema National Forest, a protected area in Brazil exposed to various anthropogenic pressures. The results revealed that elements such as Al, Fe, and Mn exceeded the limits allowed by legislation in water samples, while As and Cr surpassed the limits in sediment samples. Comparative analysis highlighted significant discrepancies in the results of the indices when global reference values were used compared to regional and quality reference values, especially for As and Ba. Thus, this study underscores the importance of establishing specific regional values for an accurate assessment of sediment quality and the risks associated with contamination by PTEs in different regions worldwide.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahirvar, B. P., Das, P., Srivastava, V., & Kumar, M. (2023). Perspectives of heavy metal pollution indices for soil, sediment, and water pollution evaluation: An insight. Total Environment Research Themes, 6, 100039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.totert.2023.100039
Alonso, D. L., Pérez, R., Okio, C. K. Y. A., & Castillo, E. (2020). Assessment of mining activity on arsenic contamination in surface water and sediments in southwestern area of Santurbán paramo, Colombia. Journal of Environmental Management, 264, 110478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110478
Amin, S., Muhammad, S., & Fatima, H. (2021). Evaluation and risks assessment of potentially toxic elements in water and sediment of the Dor River and its tributaries, Northern Pakistan. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 21, 101333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101333
APHA (2000). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, twenty ed., Washington, DC. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2105/SMWW.2882. Accessed at 2023.
Aydi, A., Ghannem, S., Nasri, A., Hessine, R., & Mezni, A. (2022). Evaluation of heavy metals contamination and pollution indices levels in surface sediments of the Bizerte coastal line, Tunisia. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 184, 114171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114171
Bai, J., Zhao, Q., Lu, Q., Wang, J., & Reddy, K. R. (2015). Effects of freshwater input on trace element pollution in salt marsh soils of a typical coastal estuary, China. Journal of Hydrology, 520, 186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.007
Barhoumi, B., Beldean-Galea, M. S., Al-Rawabdeh, M. S., Roba, C., Martonos, I. M., Balc, R., Kahlaoui, M., Touil, S., Tedetti, M., Driss, M. R., & Baciu, C. (2019). Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk of trace metals and organic pollutants in surface sediments from a Southeastern European river (Someşu Mic River, Romania). Science of the Total Environment, 660, 660–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.428
Brasil (2000). Federal Law No. 9,985, dated July 18, 2000. Brasília, Brazil. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil_03/leis/l9985.htm
Brasil (2005). Resolução CONAMA nº 357, de 17 de março de 2005. Ministry of the Environment, Brasília, Brazil. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.ibama.gov.br/component/legislacao/?view=legislacao&legislacao=111724
Brasil (2012). CONAMA Resolution No. 454, dated November 1, 2012. Ministry of the Environment, Brasília, Brazil. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.ibama.gov.br/component/legislacao/?view=legislacao&legislacao=128537
CCME (1995). Protocol for the derivation of Canadian Sediment quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Ottawa, Canada, 38p. Retrieved 2023, from https://publications.gc.ca/site/eng/9.871649/publication.html
CETESB (2019). Apêndice E: Environmental and Sanitary Significance of Water and Sediment Quality Variables and Analytical Sampling Methodologies. Sao Paulo State Environmental Agency, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Retrieved 2021, from https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-interiores/publicacoes-e-relatorios/
CETESB (2021). List of Guideline Values for Soil and Groundwater in the State of Sao Paulo. Sao Paulo State Environmental Agency, Sao Paulo, Brazil. Retrieved 2023, from https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-subterraneas/valores-orientadores-para-solo-e-agua-subterranea/
Chen, Y. F., Shi, Q. Y., Qu, J. Y., He, M. X., & Liu, Q. (2022). A pollution risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments: A case study of Lake Gehu, China. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 50(5), 100077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjac.2022.100077
Dytłow, S., & Górka-Kostrubiec, B. (2021). Concentration of heavy metals in street dust: An implication of using different geochemical background data in estimating the level of heavy metal pollution. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 43(1), 521–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-020-00726-9.
El Azhari, A., Rhoujjati, A., & Hachimi, M. L. A. (2016). Assessment of heavy metals and arsenic contamination in the sediments of the Moulouya River and the Hassan II Dam downstream of the abandoned mine Zeïda (High Moulouya, Morocco). Journal of African Earth Sciences, 119, 279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.04.011
ESRI (2023). How inverse distance weighted interpolation works. Environmental Systems Research Institute, Redlands, United States of America. Retrieved 2023, from https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/analysis/geostatistical-analyst/how-inverse-distance-weighted-interpolation-works.htm
Gall, J. E., Boyd, R. S., & Rajakaruna, N. (2015). Transfer of heavy metals through terrestrial food webs: A review. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 187(4). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-015-4436-3
Green, A. J., & Planchart, A. (2018). The neurological toxicity of heavy metals: A fish perspective. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part c: Comparative Pharmacology, 208, 12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.11.008
Hakanson, L. (1980). An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution-control – a sedimentological approach. Water Research, 14(8), 975–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
Hassan, M., Rahman, M. A. T. M. T., Saha, B., & Kamal, A. K. I. (2015). Status of Heavy Metals in Water and Sediment of the Meghna River, Bangladesh. American Journal of Environmental Sciences, 11, 427–439. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajessp.2015.427.439
Hou, A., DeLaune, R. D., Tan, M. H., Reams, M., & Laws, E. (2009). Toxic elements in aquatic sediments: Distinguishing natural variability from anthropogenic effects. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 203, 179–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0002-3
Huang, L., Rad, S., Xu, L., Gui, L., Song, X., Li, Y., Wu, Z., & Chen, Z. (2020). Heavy Metals Distribution, Sources, and Ecological Risk Assessment in Huixian Wetland. South China. Water, 12, 431. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020431
ICMBIO (2017). Management Plan for Ipanema National Forest. The Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation, Brasília, Brazil. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.icmbio.gov.br/flonaipanema/
Igiri, B. E.; Okoduwa, S. I. R.; Idoko, G. O.; Akabuogu, E. P.; Adeyi, A. O.; Ejiogu, I. K. (2018). Toxicity and Bioremediation of Heavy Metals Contaminated Ecosystem from Tannery Wastewater: A Review. Journal of Toxicology, 16p., 2568038. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2568038
Jadoon, S., Hilal, Z., Ali, M., & Muhammad, S. (2019). Potentially toxic elements in drinking water and associated health risk assessment in Abbottabad city, northern Pakistan. Desalination and Water Treatement, 151, 392–402. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2019.23909
Jardim, W. F. (2014). Medição e interpretação de valores de potencial redox (EH) em matrizes ambientais. Química Nova, 37(7), 1233–1235.
Kosten, S., Piñeiro, M., Goede, E., Klein, J., Lamers, L. P. M., & Ettwig, K. (2016). Fate of methane in aquatic systems dominated by free-floating plants. Water Research, 104, 200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.054
Li, Q., Dai, J., Zhang, H., Wan, Z., & Xu, J. (2023). Potentially toxic elements in lake sediments in China: Spatial distribution, ecological risks, and influencing factors. Science of the Total Environment, 868, 1611596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161596
Manoj, K., Kumar, B., & Padhy, P. K. (2012). Characterization of metals in water and sediments of Subarnarekha river along the projects’ sites in Lower Basin, India. Universal Journal of Environmental Research and Technology, 2, 402–410.
Mazhar, S. N., & Ahmad, S. (2020). Assessment of water quality pollution indices and distribution of heavy metals in drinking water in Ramganga aquifer, Bareilly District Uttar Pradesh, India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10, 100304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100304
Mihali, C., & Dippong, C. (2023). Water quality assessment of Remeți watercourse, Maramureș, Romania, located in a NATURA 2000 protected area subjected to anthropic pressure. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 257, 104216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2023.104216
Muller, G. (1969). Index of Geoaccumulation in Sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal, 2, 109–118.
Nascimento, M. R. L. (2003). Proposição de valores de referência para concentração de metais e metalóides em sedimentos limnicos e fluviais da bacia hidrográfica do Rio Tietê (p. 111p). Thesis (Doctoral in Science), Federal University of Sao Carlos, Sao Carlos.
Nascimento, M. R. L., & Mozeto, A. A. (2008). Reference Values for Metals and Metalloids Concentrations in Bottom Sediments of Tietê River Basin, Southeast of Brazil. Soil & Sediment Contamination, 17(3), 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320380802006996
Niu, L., Li, J., Luo, X., Fu, T., Chen, O., & Yang, Q. (2021). Identification of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments under long-term reclamation: Ecological toxicity, sources and implications for estuary management. Environmental Pollution, 290, 118126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118126
Post, C. J., Cope, M. P., Gerard, P. D., Masto, N. M., Vine, J. R., Stiglitz, R. Y., Hallstrom, J. O., Newman, J. C., & Mikhailova, E. A. (2018). Monitoring spatial and temporal variation of dissolved oxygen and water temperature in the Savannah River using a sensor network. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 190(5), 272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6646-y
Reimann, C., & De Caritat, P. (2000). Intrinsic flaws of element enrichment factors (EFs) in environmental geochemistry. Environmental Science & Technology, 34(24), 5084–5091.
Romero, F. M., Prol-Ledesma, R. M., Canet, C., Alvares, L. N., & Pérez-Vázquez, R. (2010). Acid drainage at the inactive Santa Lucia mine, western Cuba: Natural attenuation of arsenic, barium and lead, and geochemical behavior of rare earth elements. Applied Geochemistry, 25, 716–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.02.004
Rudnick, R. L., & Gao, S (2003). The Composition of the Continental Crust. In H. D. Holland & K. K. Turekian (Eds.), Treatise on Geochemistry (3rd ed., pp. 1–64). https://doi.org/10.1016/b0-08-043751-6/03016-4
Shakeri, A., Fard, M. S., Mehrabi, B., & Mehr, M. R. (2020). Occurrence, origin and health risk of arsenic and potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in sediments and fish tissues from the geothermal area of the Khiav River, Ardebil Province (NW Iran). Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 208, 106347. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.106347
Singh, U. K., & Kumar, B. (2017). Pathways of heavy metals contamination and associated human health risk in Ajay River basin, India. Chemosphere, 174, 183–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.103
Tokatli, C., & Islam, A. R. M. T. (2023). Spatial–temporal distributions, probable health risks, and source identification of organic pollutants in surface waters of an extremely hypoxic river basin in Türkiye. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 195, 435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11042-x
Tomlinson, D. L., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffney, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuarines and the formation of a pollution index. Helgolander Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–572.
Turekian, K., & Wedepohl, K. H. (1961). Distribution of the elements in some major units of the Earth’s crust. Geological Society of American Bulletin, 72, 641–664.
Ustaoglu, F., & Islam, M. S. (2020). Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: A preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecological Indicators, 113, 106237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106237
US EPA (2007). Method 3051A: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, Soils, and Oils. United States Environmental Protection Agency, Washinghton, D.C. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.epa.gov/esam/us-epa-method-3051a-microwave-assisted-acid-digestion-sediments-sludges-and-oils
US EPA (2016). Surface Water Sampling. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Washington, D.C. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.epa.gov/quality/surface-water-sampling
US EPA (2020). Sediment Sampling. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Washington, D.C. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.epa.gov/quality/sediment-sampling
US EPA (2022). Dissolved Oxygen. United States Environmental Protection Agency. Washinghton, D.C. Retrieved 2023, from https://www.epa.gov/caddis-vol2/dissolved-oxygen
WHO (2008). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality (3rd ed., pp. 5115). World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Zhang, W., Jin, X., Di, Z., Zhu, X., & Shan, B. (2016). Heavy metals in surface sediments of the shallow lakes in eastern China: Their relations with environmental factors and anthropogenic activities. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23, 25364–25373.
Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Li, H., Tu, Y., Liu, B., & Yang, Z. (2018). Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Science of the Total Environment, 645, 235–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.026
Zhuang, W., Ying, S. C., Frie, A. L., Wang, Q., Song, J., Liu, Y., Chen, Q., & Lai, X. (2019). Distribution, pollution status, and source apportionment of trace metals in lake sediments under the influence of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, China. Science of the Total Environment, 671, 108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.306
Acknowledgements
This study was financed in part by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brazil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 (Process No 88887.668029/2022-725 00) and pro-equipment project (Proposal No 189683) CAPES no 11/2014, and was supported by Grant 2016/10796-5, Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP).
Funding
This work was supported by the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 (process no 88887.668029/2022–725 00) and pro-equipment project (proposal no 189683) CAPES no 11/2014, and was supported by grant 2016/10796–5, Sao Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author Contributions Statement M.A.R.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation, Writing—Original Draft, Visualization. L.M.T.R.: Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Data Curation. J.P.M.G.: Methodology, Investigation. M.A.: Investigation, Resources. W.G.B.: Writing—Review & Editing. L.C.O.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation, Writing—Review & Editing, Supervision. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, M.A.R., Rosa, L.M.T., Godinho, J.P.M. et al. Comparative analysis of sediment quality indices using different reference values in an environmental protection area in Southeastern Brazil. Environ Geochem Health 46, 154 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01938-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-024-01938-z